Inguinal hernia
Synonyms in a broader sense

Medical: inguinal hernia, inguinal hernia, inguinal hernia
- soft groin
- Athlete bar
- Groin pain
English: inguinal hernia.
Definition of inguinal hernia
The inguinal hernia, like all abdominal wall hernias, is a protrusion of contents from the abdominal cavity through the inner sheet of connective tissue that borders the abdominal cavity.
For anatomical reasons, the groin is a place in which fractures are particularly common, as this is where the connective tissue is naturally weak. The anatomy of the groin is complicated and requires more detailed illustration.
Anatomy and classification of inguinal hernias
The Abdominal wall consists (from the inside out) of:
- Peritoneum
- inner connective tissue sheet
- muscle
- outer connective tissue sheet
- Subcutaneous fatty tissue
- skin
In the development of the male Embryoyo In the course of the process, there is a lowering of those primarily located in the abdominal cavity Testicles in the Scrotum. This forms the inguinal canal, in which the spermatic cord and the supply vessels for the testes are located. This creates a natural gap in the abdominal wall through which the contents of the abdominal cavity can emerge from the actual abdominal cavity.
Such a hernia will directly called. Of the indirect Inguinal hernia is caused by a gap that forms closer to the midline of the abdominal wall.
Exits contents from the abdominal cavity into the Musculature, or in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, it can lead to a Entrapment come.
Hence the Inguinal hernias are classified into pinched and not pinched according to this criterion.
Inguinal hernias can also innate or acquired since.
A special form of inguinal hernia is the so-called. Scrotum rupture This is mainly observed in older men. Through a very large gap in the abdominal wall, parts of the intestine are shifted into the scrotum, which can stretch very far in the course. This can make the scrotum break extremely large.
In women there is another form of inguinal hernia - that Thigh fracture. This is a gap that appears below the Inguinal ligament arises and thereby the hernial sac allows itself into the Thigh to expand.
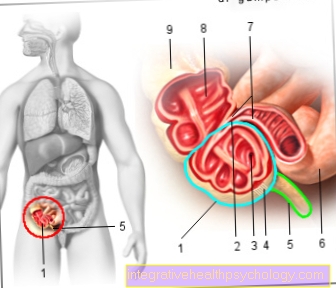
Illustration of the types of an inguinal hernia

- Peritoneal cavity -
Cavitas peritonealis - Abdominal viscera
- Peritoneum -
peritoneum - Glued peritoneum protuberance
- Vas deferens -
Deferens duct - Epididymis -
Epididymis - Testicles -
Testis - Serous testicular envelope -
Tunica vaginalis testis - Scrotum - scrotum
- Inguinal ligament -
Inguinal ligament - Hernial sac
Inguinal hernia - Inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia types:
a - Epigastric hernia
(in the upper abdomen on the midline) -
Epigastric hernia
b - umbilical hernia -
Umbilical and paraumbilical hernia
c - hernia
(at the location of a previous
surgical intervention) -
Hernia cicatrica
d - Direct inguinal hernia
(in the bar near the
Opening of the inguinal canal)
e - Indirect inguinal hernia
(in the bar at the opening
of the inguinal canal)
f - femoral fracture
(in the thigh canal) -
Femoral hernia
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
How can you get an inguinal hernia?
Congenital inguinal hernia:
There is one in the embryos natural connection between the abdominal cavity and the groin, of the Vaginal process.
If this connection does not close around the birth, a congenital hernia. The parents observe a protrusion in the area of the (or both) groin (s), which is more pronounced when crying, due to the increased pressure in the abdomen, and in most cases is painless. Under certain circumstances, however, this protrusion can be painful (pressure). In these cases one must at least incipient entrapment can be assumed.
Acquired inguinal hernia:
In adulthood, a weaker connective tissue favor the development of the inguinal hernia. This is often the case with the elderly.
In young men, an inguinal hernia develops from excessive physical exertion, e.g. B. at heavy lifting or Bodybuilding.

Symptoms and differential diagnoses of an inguinal hernia
The symptoms of the hernia range from painless swelling until Intestinal obstruction in the case of a pinched break. Sometimes pain occurs in a specific area without a break or swelling being palpable. In these cases, another cause (see below) should be ruled out before planning the surgical inguinal hernia treatment.
If there is swelling and / or pain in the groin always an inguinal hernia first thought as this is the most common cause of this. However, these symptoms could have other reasons as well.
Swelling can be expression enlarged lymph nodes of the groin which in most cases are the result of inflammation. Enlarged lymph nodes definitely require further clarification!
After punctures of the inguinal vein (e.g. during Cardiac catheter) can also Bruising (Hematoma), which are also noticeable as swellings. Such bruises often have to be treated surgically.
Pain in the groin can be caused by irritation at the point of attachment Thigh muscles at the pool be evoked. This is often the case after greater exertion of the leg muscles, e.g. after a soccer game.
Another cause of groin pain pose Problems of the hip joint signs of wear and tear ("Hip osteoarthritis") but also the Femoral neck fracture (Femoral neck fracture) are partly at Groin pain diagnosed as the sole symptom.
Read more on the topic:
- Symptoms of an inguinal hernia
or - Pain in an inguinal hernia
or - Groin pain
How can you diagnose an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernias are usually too easily recognizable for the layman.
There with one Inguinal hernia of the Fractional content, mostly a small section of intestine or the fatty tissue in the abdomen on top of the intestine (Greater omentum), through which the so-called hernial site forms a hernial sac, can be a Elevation or swelling of the affected skin area observed and groped become.
Usually this is as the name suggests Groin area can also be found at Scrotum or the Labia are in this area due to their anatomy. The symptoms also depend on the intra-abdominal (inside the abdomen) pressure increased when sneezing, coughing, lifting heavy cardboard boxes or lifting shopping bags.
In this case, the increased intra-abdominal pressure leads to further Pressing out the intestines into the hernial sac. In addition, an improvement in swelling when lying down and at rest suggests an inguinal hernia, and intensification of symptoms when lying down or at night suggests other diseases such as certain Muscle diseases down. Furthermore, a distinction must also be made whether the hernia content can be repositioned, i.e. whether the Fraction content can be moved and can be pushed back into the abdomen by hand. Then there are usually no or only slight pain such as a simple Pulling in the groin to feel.
A Hardening of the skin Above the contents of the hernia, pain and a non-displaceable hernia are typical signs of inflammation or infection, which can also be accompanied by entrapment (incarceration) of the intestinal section. This leads to a Disconnection of the oxygen and nutrient supplying blood supply of the fabric. This is accompanied by death (necrosis) of the affected tissue, which can lead to further complications. Therefore, even if the inguinal hernia is not painful, a Consulted a doctor be. l
Can you feel an inguinal hernia?
The hernia will clinically diagnosed. The doctor tries to feel the gap and, if necessary, to move the hernial sac into the abdominal cavity.
This is particularly important in order to prevent the break from becoming trapped.
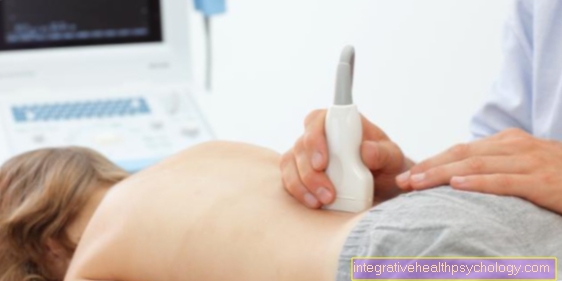
In the case of very small fractions, the gap cannot always be felt. An additional Ultrasound examination can partially provide the necessary certainty about the diagnosis in these cases. Sonography (Ultrasonic) is also used to distinguish trapped inguinal hernias from enlarged lymph nodes, although this can often be difficult.

How is the inguinal hernia operated?
Not every hernia has to be treated surgically. However, as soon as it becomes Clamping off one or more sections of the intestine Coming inside the hernial sac is one OP the only therapy option.
In such a case, the affected patient usually feels severe pain in the groin area.
An inguinal hernia that is associated with pain should immediately, surgically treated within a very short time become. Only through the timely implementation of a Inguinal hernia surgery parts of the clamped-off bowel can be prevented from dying off.
In the surgical correction of inguinal hernias there are different techniques and approaches. With the conventional method, an access in the groin area is usually chosen. The necessary skin incisions are kept relatively small and heal well. Visible scars are more of a rarity.
Furthermore, the choice of one is also with the conventional inguinal hernia surgery minimally invasive, laparoscopic approach possible.
The following surgical methods are used:
1) Shouldice method:
One of the most frequently chosen procedures is the so-called Shouldice OP method.
During this operation, a transverse skin incision is made above the inguinal ligament. Starting from this skin incision, the dissection can be carried out up to the hernial sac. If the hernial sac is completely exposed, it is opened and its contents are shifted back into the abdomen.
To avoid the recurrence of an inguinal hernia in the same place (Relapse), parts of the large abdominal fascia (fascia transversalis) are then pulled over the hernial orifice. The tensioned fascia is then sutured twice and the inner inguinal ring is narrowed in this way.
Another advantage of this procedure is the fact that during the operation the Posterior wall of the inguinal canal tightened and is reinforced.Recurrences are very rarely observed after using this surgical method.
2) Lichtenstein method:
Another inguinal hernia operation that is used relatively frequently these days is the so-called Lichtenstein procedure. During this operation, an approximately 6 cm long skin incision is made directly above the hernia. The hernial sac and its contents can be immediately relocated back into the abdominal cavity via this surgical approach.
In contrast to surgery after Shouldice In this procedure, however, the hernial opening is via the inlay of a Plastic mesh locked. The recurrence rate is also very low in this operation.
However, the disadvantage of surgical inguinal hernia correction according to Lichtenstein is the fact that foreign material is introduced into the body with the plastic mesh.
3) Rutkow's method:
The so-called surgical procedure according to Rutkow is also one of the most common surgical correction methods in the presence of an inguinal hernia. In this operation, the skin incision is made much smaller than with the methods just described.
In the inguinal hernia operation according to Rutkow, the attending surgeon also makes the incision directly above the hernial sac. In addition, with this procedure, the weak point in the area of the abdominal wall is reinforced by foreign material. During this operation, the surgeon dials in depending on the size of the hernial opening Plastic umbrella or a small net.
4) Minimally invasive surgery of the inguinal hernia:
In addition, a painful inguinal hernia can also be treated from the inside with a laparoscopy (so-called "keyhole surgery", for example: Meyer`s method). In these minimally invasive procedures, a small skin incision is made inside or just below the navel.
Afterwards, carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity and the surgical field is examined with an optical device (light source and small camera).
In addition, two more small skin incisions must be made in the right and left groin region. Each of these cuts is usually no larger than approximately 10 mm and for this reason is hardly visible after the wound has healed.
The required surgical devices can be introduced during the operation through the accesses in the right and left groin area. During the actual operation, the peritoneum in the area of the inguinal hernia is opened from the inside, the hernial sac is pushed back into the abdominal cavity and the peritoneum is closed again. With this procedure, too, the weak point is secured with a small plastic net, effectively preventing recurrences.
How long does an inguinal hernia operation take?
Depending on the procedure chosen and the severity of the hernia, the pure operating time includes (without introducing and discharging the anesthesia) between 20 minutes and a half hour. In most cases, the inguinal hernia operation is under general anesthetic carried out, but there is also the possibility of surgery local anesthesia perform.
Does an inguinal hernia have to be operated on?
Inguinal hernias are generally not always operated on. Closing the hernia is not possible without an operation. However, there are cases when surgery doesn't really make sense. The inguinal hernia is treated conservatively in very old people or patients who cannot be operated on because of their health condition. A so-called truss band is used for this purpose. The truss is like a kind of corsage. It is a leather belt with a metal plate that is placed on the hernial sac. This metal plate is supposed to push the contents of the hernial sac back into the abdominal cavity and stabilize the unstable abdominal wall.
The hernia cannot be healed as a result. However, there is a risk of entrapment of the entrails. In men, testicular atrophy (tissue shrinkage) can occur. In general, the constant pressure can cause so-called skin ulcerations (skin defects), which ultimately can cause the hernia to break through the skin. So you can see that a truss can sometimes cause great damage. Therefore it is no longer used for general therapy. As already mentioned, it is only used in patients who can no longer be operated on to alleviate their symptoms.
Read more on the topic: Inguinal hernia surgery
forecast
The Operation of the inguinal hernia in the surgical clinics, but also among the resident surgeons, is a Routine intervention.
The Aim of treatment the inguinal hernia is the permanent closure of the fracture gap. The success rate of inguinal hernia operations is high. In only about 5% of the cases there is a relapse (Recurrence) of the hernia.
The operation is nowadays carried out on an outpatient basis. However, the patients should be picked up by an attendant, as they are still under the effect of the anesthetic a few hours after the operation.
Inguinal hernia in women

A Inguinal hernia (Inguinal hernia) occurs much less often in women than in men. Only about 10% of all hernias are found in women, 90% occur in men.
The woman runs through it Inguinal canal (Canalis inguinalis) the so-called Mother band (Ligementum teres uteri) while with man the Spermatic cord pulls along here. The mother band pulls from the uterus (uterus) up to the labia.
The causes of an inguinal hernia in women are similar to those in men. So can the hernias innate be - that is, make themselves noticeable in childhood - and then mostly arise due to a deficient development or desolation of certain connective tissue structures.
Are more common Inguinal hernias however acquired. The acquired forms can for example by a Connective tissue weakness after an operation or simply as part of the body's natural aging processes.
Other risk factors include:
- Overweight,
- frequent lifting of heavy loads and
- Pregnancies
With all these factors, the tissue must be subjected to a higher pressure in the Abdomen withstand. If it is no longer up to this, one can hernia arise. The symptoms of the inguinal hernia in women are similar to those in men. So can in the area of the affected A drawing pain occur which increases with pressure (for example coughing) and can radiate into the labia. Often times remain uncomplicated Inguinal hernias but also symptomless.
Also the therapy does not differ in the woman from that in the man. It should always be operated on - as long as no intestinal contents are trapped by the hernia, but there is no urgent indication and the operation date can be planned in peace.
Inguinal hernia in men
The hernia occurs in most cases in men on. If 10 inguinal hernia operations are required, about 8 (80 percent) are surgical procedures for men.
The reason for this is the fact that the inguinal canal is greatly widened by the structures that pass through in men compared to women. Furthermore, the man's spermatic cord usually runs through the middle of a tendon plate, which actually strengthens the groin region.
In this way, this tendon plate in the area of the groin is strongly stretched and it comes to the development of Weak points in the area of the abdominal wall. The intestine can therefore not be held in the abdomen under certain circumstances. The counterpressure triggered by the tendon plate is simply missing.
In addition, in most cases, the inguinal hernia is caused by men heavy strain on the muscular structures favored. Especially that Lifting heavy weights represents a significant risk factor for intestines to leak through the abdominal wall.
In addition, can also strong pressing in the toilet cause an inguinal hernia to be provoked in men. In addition, if a man has an inguinal hernia, it must be ensured that the abdominal wall does not merely bulge in the area of the groin.
Clamping the intestine located in the hernial sac within the hernial port is not the only risk of an inguinal hernia in men. If men are affected by an inguinal hernia, the hernia can lead to the hernial sac including the intestinal sections in it Scrotum (scrotum) can sag.
This is a frequently observed phenomenon, especially if the inguinal hernia persists. In these cases one no longer speaks of an ordinary hernia, but of one Scrotum rupture or one Scrotal hernia.
Due to the limited space inside the scrotum, the testicles can become clamped over time. A rapid initiation of therapy is therefore essential.
Inguinal hernia in the baby

General
Inguinal hernias are quite common in newborns. In the fetal period, incomplete closure of the inguinal canal can lead to a congenital hernia. This type of inguinal hernia is called indirectly or innate. This congenital malformation is about five times more common in boys than in girls. In addition, the indirect hernia occurs more often on the right than on the left. Guts, such as loops of intestine, can pass through this.
causes
The cause of an inguinal hernia is an incomplete closure of the inguinal canal. The inguinal canal is an anatomical structure in the groin region, which is formed by parts of the anterior abdominal wall. The organs of the abdomen now exert a certain pressure on the groin region through gravity. If the inguinal canal is not adequately closed, organs can break through it. In girls, this so-called hernial sac, which contains the intestinal parts, can protrude up to the labia. In boys, the hernial sac runs into the scrotum (scrotum). This inguinal hernia is usually easy to feel. Physical exertion and increased pressure in the abdomen, for example by pressing when defecating, make the hernial sac stand out even more clearly.
Symptoms
The clearest symptom of an inguinal hernia is the swelling, which is also easy to feel. This swelling is soft and does not necessarily cause pain. However, it becomes painful if loops of the intestine or other organs are pinched. This can cause nausea and vomiting. There is also the risk of an intestinal obstruction if the bowel is pinched. This situation is an emergency.
diagnosis
The doctor can usually determine whether it is an inguinal hernia by feeling the swelling. In boys, the position of the testicles is still felt and checked. Furthermore, he can make an exact diagnosis using sonography (ultrasound examination).
therapy
As a rule, an inguinal hernia in babies is initially not operated on. In the first three months of life, the inguinal canal can close by itself. If this is not the case, however, the operation should be carried out up to the sixth month. A laparoscopy is performed, which results in only very small scars. This operation is uncomplicated and can often even be performed on an outpatient basis.
One difference to the minimally invasive procedures in adults (see main article) is that in children there is no need to insert foreign material. This is done because the foreign material cannot grow with the child and so does not adapt to the infant's rapid growth. Only the hernial port is closed with a seam. If the intestines are trapped, an operation must be performed immediately, otherwise there is a risk that they will die off (necrosis). In boys in particular, this can lead to permanent damage to the testicles. General possible complications are an intestinal obstruction or peritonitis.
You might also be interested in: Inguinal hernia in the baby
Summary
The inguinal hernias are that most common ruptures of the abdominal wall, where the Men much more often are affected than that Women.
This is Relocation of the contents of the abdominal cavity outside the abdominal cavity. goal of treatment is the permanent closure the fracture gap. This is achieved surgically, and conservative treatment can also be considered, especially for high-risk patients.
The operations of the inguinal hernias are Routine interventions. There are different methods of closing the fracture gaps. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages that patients should discuss with the attending surgeon before the operation. The risks of the operation are also discussed during this informative meeting.
The complications of surgical treatment are rare. In about 5% of the cases it happens again, sometimes even after decades Inguinal hernia (med. relapse).