insulin
definition

Insulin is a hormone produced by the body in the pancreas. Insulin causes sugar to be absorbed from the blood into the liver and muscles. This lowers the blood sugar level.
Insulin, which is also known as insulinum, insulin hormone or islet hormone, can be assigned to the class of proteohormones. All members of this hormone class are characterized by a high level of fat solubility. In contrast, in aqueous solutions they remain almost unaffected. For all vertebrates and mammals, insulin is one of the vital hormones that must be substituted if there is a deficiency.
Insulin is one of the most important drugs in diabetes. Insulin is usually used in type 1 diabetes and in advanced stages of type 2 diabetes that no longer respond to oral medication.
Insulin formation (synthesis)
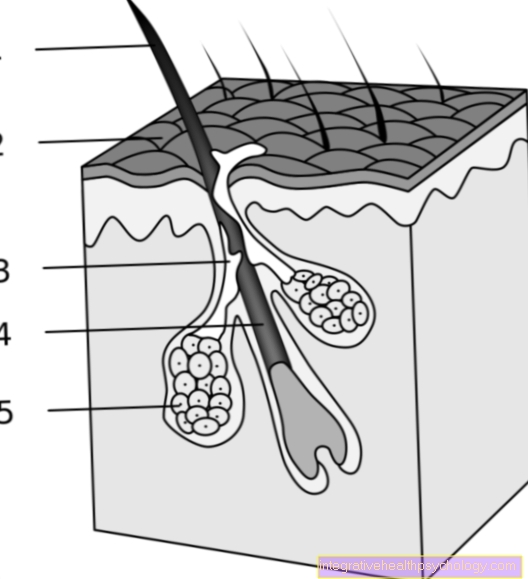
The tissue hormone insulin is in so-called ß-cells of the Langerhans Islands in the pancreas educated.
The genetic information related to insulin synthesis is in the short arm of the 11. Chromosome coded. During the insulin synthesis, the hormone precursor is the first step Preproinsulin educated. With a length of 110 amino acids this preliminary stage is essential greater than the actual, active hormone.
During one Processing phase (Adjustment phase) the insulin precursor is shortened and modified in two steps. First it comes to folding of Protein through training so-called Disulfide bridges. This is followed by the Hormone processing in which the actual shortening of preproinsulin takes place.
From the hormone precursor that is still too long, the so-called Signal sequences separated (the 2nd preliminary stage is created: Proinsulin). These usually include around 24 Amino acids. The signal sequence serves as signals for the uptake in special hormone precursors Cell compartments. It is therefore a kind of identifying feature of the hormone. Then another part of the tissue hormone, the C-peptide, be separated.
After Hormone modification what remains is ripe, active insulin. This ultimately consists of two Peptide chains (A and B chain) those about two Disulfide bridges are related to each other. A third disulfide bridge forms a contact between two amino acids of the A chain. Then the finished insulin molecules are put into Vesicles packed and by the accumulation of Zinc ions stabilized.
Insulin release
The distribution of the Insulins occurs through various initiated by the organism Stimuli. Probably the most important stimulus for the release of the tissue hormone is an increase in the Blood sugar level.
From one Glucose-Value of approximately 5 mmol / l begin the beta cells of the pancreas insulin to secrete. In addition, induce various amino acids, free Fatty acids and some others Hormones a release of insulin.
Especially the hormones Gastrin, Secretin, GIP and GLP-1 have a strong stimulating effect on the cells of the pancreas. The actual release of the hormone into the Bloodstream follows a certain cycle even with high blood sugar levels. About all of them three to six minutes insulin is delivered. Immediately after eating, the insulin secretion follows biphasic (2 phases) pattern.
About three to five minutes after ingestion of food there is a first secretion Hormone portion instead of. The first secretory phase takes about 10 mins on. This is followed by a pause during which the blood sugar value is newly detected. If the glucose level in the blood is still too high, one follows second secretion phasethat lasts until the sugar concentration has reached a normal value.
During the first phase will be predominantly saved Insulin is released while in the second interval newly formed sets of the hormone.
The actual release mechanism is through the penetration of a sugar molecule into the beta cells triggered. After the glucose is transported via a special transporter (so-called GLUT-2 transporter) has entered the cell, it is split into its individual parts. This metabolic process creates what is probably the most important energy source, the ATP.
By binding to a specific ATP receptor, the outflow of potassium-Ions throttled. The result is a change in the charge of the respective cell membranes (technical term: Depolarization). This in turn leads to an opening that is more voltage dependent Calciumchannels, the calcium content inside the cell rises brilliantly. This increased calcium concentration is the actual signal for the release of the insulin-filled vesicles.
Function and effect

The body's own hormone insulin is an important part of the Blood sugar regulating system. The regulation of the dissolved glucose (sugar) in the blood takes place via two messenger substances, depending on the currently available Blood sugar concentration be distributed.
Besides insulin also contributes Glucagon, another hormone produced in the pancreas, contributes to this regulation. While insulin is able to lower the blood glucose level via various mechanisms, the glucagon can do this increase. Glukagon therefore represents the opponent (Antagonists) of insulin.
Read more about the topic here: Abandonment of insulin
In addition to these two main regulators, the hormones have among others adrenaline and Cortisol an impact on blood sugar.
The blood sugar lowering effect of the proteohormone is based primarily on an increase in the Glucose passage from the Blood plasma and the tissue fluid into the interior of various tissues (for example in Muscle cells or the liver). Inside the tissue can sugar in the form of so-called Glycogen saved or via one as Glycolysis known metabolic pathway immediately into energy transformed become.
In addition to regulating blood sugar, the hormone insulin has an influence on the Fat and amino acid metabolism and is involved in maintaining the Potassium balance involved. Problems in the area of insulin release or its formation at specific receptors can therefore have considerable effects on the entire organism. Diseases such as Diabetes mellitus, Hyperinsulinism, Insulinomas, the Insulin resistance and the so-called metabolic syndrome are all based on a dysregulation of the insulin balance.
Diabetics have an insulin deficiency, so that glucose (sugar) can only be introduced into the cells with difficulty. This transport is only possible when the blood sugar level is increased. Due to the lack of glucose in the fat cells, ketone bodies are built up, which can cause metabolic disorders (ketoacidotic coma).
The Inuslin distribution from the pancreas takes place on the one hand in physical rest to maintain the basic metabolism and also when eating.
Insulin-associated diseases
Insulin resistance / pre-diabetes
At the one under the name Insulin resistance (Synonym: pre-diabetes) known metabolic disease is a precursor of the Type 2 diabetes.
It has now been proven that the causes of this disease are strong genetic component exhibit. Children of whom a Parent suffers from type 2 diabetes, studies have shown 40% an insulin resistance. At the same two affected parents, the probability is already increasing 80%.
Not every patient affected by insulin resistance has to develop the full picture of type 2 diabetes. In many cases there is just one decreased responsiveness the insulin-specific receptors on their binding partners. Clinically, insulin resistance can be determined by determining the so-called Fasting blood sugar level be diagnosed. A blood glucose level greater than 100 to 125 mg / dl should be interpreted as an early warning sign. In such cases the determination of the so-called HbA1c To strive for value.
While the blood sugar level in pre-diabetes can only be slightly increased in many cases, large amounts can be found in almost all those affected Insulin in the blood prove. The fatal thing about pure insulin resistance is the fact that it is mostly perfect symptomless expires and for this reason usually only to Damage to the pancreas is diagnosed.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes relies on one absolute Insulin deficiency (synonym: primarily insulin dependent diabetes). Due to a genetic defect and the formation of special against the beta cells the pancreas more directed antibody the insulin-producing cells die down.
As a result, the organ is no longer able to produce sufficient amounts of the tissue hormone and release it into the bloodstream. The glucose absorbed through food can no longer or only insufficiently be absorbed into cells of the adipose tissue, the muscles or the liver.
The blood sugar level in the affected patients is usually very high (Hyperglycemia). This condition harbors several dangers. On the one hand, the various cells cannot be supplied with sufficient amounts of sugar. This means that they cannot be supplied with enough energy and can only perform their tasks inappropriately. If type 1 diabetes is not treated in the long term, it will lead to one Acidification of the blood and a serious impairment of many metabolic processes within the organism. In the worst case, type 1 diabetes can even lead to death.
Popularly this form of insulin deficiency is called Juvenile diabetes designated. It was long assumed that young people in particular developed type 1 diabetes. This fact cannot be completely dismissed today, because the age peak for the first occurrence of this form of diabetes is in the range of 11 to 14 years. However, there are also cases in which affected patients do not show the first symptoms until they are middle-aged. Type 1 diabetes is usually treated via a external insulin supply. This can be done by taking the hormone orally or by injection. Especially with children, the so-called are now used Insulin pumps back.
Type 2 diabetes
In contrast to type 1 diabetes, in which there is an insulin deficiency from the start, this form of diabetes is based on one in the early stages Malfunction of the specific insulin receptors. Especially the insulin receptors of the liver-, Muscle- and Fat cells gradually lose the ability to respond to tissue hormone.
This stage is called in medicine Insulin resistance designated. Type 2 diabetes is also called in many specialist books relative insulin deficiency. In the initial stage, the pancreas tries to compensate for the existing insulin resistance by increasing the production and secretion of the hormone. In the long run, the pancreas is compensated by this mechanism Overwhelmed.
As the receptor resistance progresses, the amounts of insulin that can be mobilized are no longer sufficient to reduce the blood sugar level adequately. The initial insulin resistance is therefore followed by an insulin deficiency.
Most of the sick people show it especially at this point unspecific symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, Feeling hungry and Weight gain. In addition, you can depressive moods be a first indication of the presence of type 2 diabetes. Due to the very unspecific signs, this form of diabetes is recognized too late in most cases.
Indications
When is insulin used for therapy?
People with one Type 1 diabetes are dependent on externally supplied insulin, as the body's own insulin formation and release is insufficient. Type 2 diabetics are treated with insulin if dietary measures and oral medication (tablets) are no longer effective and the blood sugar control is unsatisfactory.
At a Gestational diabetes Oral anti-diabetic drugs must not be given, which is why insulin, which is injected through injection needles, is used.
Insulin preparations
There are different types of insulin, which differ mainly in their duration of action and therefore a separate administration schedule is necessary for each type of insulin.
This is one of the so-called short-acting insulins
- Regular insulin and
- the short-acting insulin analogs.
Human insulin (normal insulin) takes effect after 30-45 minutes and is injected under the skin (subcutaneously). It is part of intermittent conventional therapy or insulin pump therapy and is also used in the initial treatment of newly diagnosed diabetes. It is important that the patient maintains a spray-eating interval of 15-20 minutes so that the normal insulin works optimally.
Short acting insulin analogs, i. Chemically modified insulin are also applied under the skin, however, due to the modified chemical properties, it is not necessary to maintain a spray-eating interval: the onset of action occurs quickly, after 15 minutes.
Another type of insulin used in diabetes therapy
- the delay insulins. These preparations consist of insulin and an additive (protamine, zinc, surfing), which means that the hormone lasts longer. The delay insulins are injected subcutaneously and can be converted into intermediate insulins, the effect of which lasts for 9 to 18 hours, and in
-
Long-term insulins with a duration of action of over 24 hours. The coupling of the insulin with another substance slows down the breakdown of the insulin into its basic building blocks, so that the duration of action of the given amount of hormone is extended.
In the field of medium duration of action is the frequently used NPH insulin. At the longest effective are the analogs insulin detemir, glargine and degludec.
Most of these drugs are ineffective when taken orally. This phenomenon is based on the fact that the protein chains of the synthetic insulins in the gastrointestinal tract are broken down by the body's own enzymes before the hormone can take effect.
In the course of insulin therapy, a distinction is made between two intake mechanisms. As a rule, patients are forced to apply a so-called basal insulin dose one to three times a day. In this context, the long-acting Insulins. The basic daily requirement is covered by this basic dose.
The current blood sugar level should be determined before meals. In the case of high values or meals rich in sugar, a bolus can be injected in addition to the basal amount of insulin. Those insulins that are particularly suitable are then particularly suitable as bolus act quickly and briefly.
Also read our topic: Actrapid® pre-filled pens with short-acting normal insulin
Insulin pump
Insulin-dependent diabetics are in many cases forced to do so Independent insulin injections daily to put. This can be stressful for some sufferers. In addition, the regular breakthrough of the skin, which serves as a natural protective barrier, harbors the Risk of infection, Inflammation and unsightly bruises (Bruises).
Especially for young people who attend Diabetes mellitus this is a difficult situation. Nowadays, patients with diabetes have the option of using a so-called insulin pump. An insulin pump is a medical device that can be used for insulin therapy. The regular injection of the required amount of insulin is made possible by the replaces small, programmable pump.
To set up an insulin pump, the patient concerned is given a catheter under the skin placed. In most cases, this happens around the abdomen. The actual insulin pump should permanently on the body (for example on the belt). Theoretically, however, it is also possible to separate the device from the catheter system for a short period of time.
The use of such an insulin pump is particularly suitable for people who are under Type 1 diabetes Suffer. The principle of use of the insulin pump is roughly the same as that of an ordinary insulin injection therapy (ICT for short).
The organism regularly receives a so-called Basal rate, which should cover the basic requirement, fed. In certain situations (for example with increased glucose intake as with foods that are particularly rich in carbohydrates) via touch of a button an individual bolus of insulin can be delivered.
In most cases it is used to meet basic needs a small amount of short-acting insulin several times a day applied. In contrast to this, one takes up with the usual injection therapy long-acting insulins (e.g. NPH insulin). Despite the comparatively convenient use of an insulin pump, it should not be forgotten that this one cannot replace healthy pancreas.
A Measurement of the current blood sugar level using the insulin pump is not yet possible and must continue to be carried out by the patient independently.
The use of an insulin pump is a good alternative, especially for diabetics with the so-called dawn phenomenon. This means those patients whose Blood sugar level especially during the night (usually around four o'clock) increases sharply. The reason for this glucose rise is one Increased activity of the liver cellsthat release enormous amounts of sugar into the bloodstream at this time.
With the help of the insulin pump, affected patients are no longer forced to get up during the night and administer an insulin bolus. The insulin pump can programmed exactly that waythat while sleeping one appropriate dose of insulin delivered becomes. In this way, a typical adverse drug effect of insulin, morning hyperglycaemia, can be avoided. This advantage is very relevant in so far any metabolic imbalance (regardless of whether it is a shift to hyper- or hypoglycaemia) cause severe organ damage can.
Food combining with insulin
Insulin food combining is one Form of nutrition after the Insulin balance directs. The insulin food combining makes itself the goal of the insulin level in the blood by a Selection of suitable foods to lower. In addition to the food choice also play longer breaks between meals plays an important role in this form of diet.
The physiological basis of insulin food combining is the fact that both Fat loss (Lipolysis), as well as glycogen breakdown through a high Blood insulin levels inhibited become. By lowering this level, the Increased breakdown of body fat and the slimming effect can be improved.
The principle of insulin food combining is based on the physiological secretion and action patterns of the proteohormone insulin.
In the morning should put great emphasis on that targeted intake of carbohydrates be placed. A rich breakfast with bread, rolls and spreads containing sugar should provide the organism with enough energy that it can be consumed throughout the day. Furthermore, hunger should be satisfied in the morning with muesli and plenty of fruit. According to insulin, there must be an approximate food combining diet between breakfast and lunch 5 hour break be respected.
To Lunchtime forms one balanced mixed diet, which has a high proportion of carbohydrates, the ideal basis to keep the body going. Due to the already high insulin levels at this time of day the ingested sugar can be metabolized without any problems. Also There must be a break between lunch and dinner five hours. According to insulin, food combining is generally effective fat loss only possible during the evening hours and at night.
In the evening, the body should be adjusted to the breakdown of fat reserves. This means that completely on the Consumption of carbohydrates can be avoided got to. Eating carbohydrate-containing foods in the evenings would boost the B cells pancreas cause excessive amounts of insulin to be produced and released into the bloodstream.
As a result, it would come during the night not to break down the fatty tissue. Insulin food combining is particularly suitable in the evening Protein suppliers like fish and meat in order to optimize the success. In addition, salad and vegetables can be consumed without provoking high insulin levels.
From a medical point of view, compliance with insulin food combining is not uncritical. The German Nutrition Society (DGE for short) even explicitly advises against this type of diet. The insulin food combining and the accompanying Separation of carbohydrates and proteins According to the DGE, there is no point in eating food.
Society is of the opinion that (contrary to previously assumed) it is entirely possible for the organism to digest carbohydrates and proteins at the same time. In addition, the DGE emphasizes that carbohydrates are a important food component and a body cannot be kept healthy without them.
Complications
Possible With overdosing of the insulin or with a too small amount of ingested food it comes to low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia).
At the injection sites, fat cells can accumulate under the skin and cause hardening.
It is possible that the cells become insensitive to insulin because the utilization of glucose in the cell is disturbed and / or because the interaction of insulin and its receptor on the surface of the cell is impaired. Common causes for this are obesity and infections.