Semimembranosus muscle
- to the thigh muscles overview
- to the musculature overview
introduction

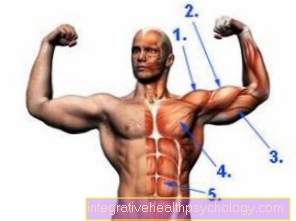
The semimembranosus muscle (flat tendon muscle) consists of a 5 cm wide and 3 cm thick muscle belly. It arises from the ischial tuberosity with a broad, flat tendon that gives it its name. However, the muscle only develops below the middle of the thigh and is clearly visible and palpable as a bulge under the skin.
Here you will find more information:
- hip
- Cruciate ligament tear
- Meniscal surgery
Synonyms
German: Flat tendon muscle
Approach, origin, innervation
Approach:
- Inner tibial gnar (Tibial condyle)
- Reverse Wall of the knee joint capsule (Lig. Popliteum obliquum)
- Fascia of the popliteal muscle (fascia m. poplitea)
Origin: ischial tuberosity (Sciatic tuberosity)
Innervation: N. tibialis, L 4 - 5, S 1 - 2
How is the muscle trained / contracted?
The semimemranosus muscle (flat tendon muscle) contracts by stretching the hip joint and flexing the knee joint.
This results in the following exercises:
- Squats
- Leg press
- Hamstrings
For more information, see Weight Training
How is the muscle stretched?

The stretching exercises for the rear thigh area are found to be very uncomfortable by many. The athlete stands with his legs closed and straight and tries to touch the tips of his toes with his fingers. The back should be kept straight.
For more information on this topic, see stretching
Note: Athletes who cannot perform this exercise usually do not have a shortened muscle, but only immobility.
In addition to the flat tendon muscle, this exercise also stretches the biceps femoris and semitendinosus.
function
Like the semitendinosus muscle, the semimembranosus muscle (flat tendon muscle) causes flexion of the lower leg in the knee joint. It also functions as an internal rotator of the knee joint and extensor of the hip joint.
Information on all directions of movement of the joints can be found under Types of movement