Neck tension
introduction
Neck tension shows up as persistent pain that is caused by increased basic tension (muscle tone) in the neck muscles. These often become stronger with movements, although they do not completely subside even when you are resting.
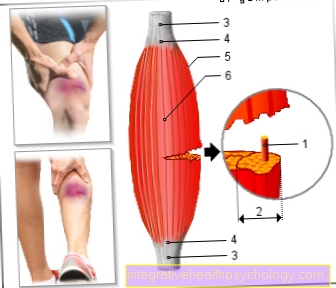
Often the Trapezius muscle affected, one of the most prominent muscles in the neck area, which extends from the underside of the back of the head, the cervical and thoracic vertebrae to the shoulder blade. As a result, neck tension can also spread to the back.
But other muscle groups can also be affected by the hardening. This depends on how far the pain radiates.
Blocked vertebrae or slipped intervertebral discs can also cause restricted mobility and pain, and subsequently lead to muscle hardening. Since many nerve pathways run in the neck area, pinching these nerves can lead to numbness and impaired mobility of the arms and hands.

anatomy
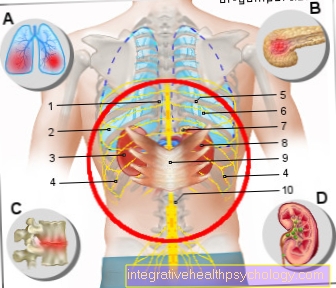
The muscles of the spine lie on the left and right as well as over the vertebral bodies of the spine and have their task in the posture, stabilization and movement of these.
The neck muscles are also significantly involved in the movement that can be performed in the neck area. The neck muscles include the Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle, of the M. rectus capitis posterior major, of the M. obliquus capitis superior as well as the M. obliquus capitis inferior.
Tensioning this muscle group very often leads to everyday complaints.
causes
There are many causes from different areas that can trigger neck tension. In general, the muscles in the neck area are no longer adequately supplied with oxygen due to overstretching, which leads to a disturbed metabolism and the resulting hardening.
The most frequently observed causes can be found in poor posture and unfavorable everyday movements. Office work on the computer, which is accompanied by long periods of sitting and a crooked posture, is particularly risky. But also the one-sided carrying of heavy loads as well as monotonous, repetitive movements (mouse arm syndrome / Repetitive Strain Injury Syndrome) can be the cause.
Sports activities generally have a preventive effect, as trained muscles are less sensitive to stress. However, incorrect execution of the activity can also trigger tension.
Another cause can be a torticollis (Torticollis) be. This describes a misalignment and a one-sided raised position of the shoulders, which is congenitally caused by a shortening of the head-turning muscle (Sternocleidomastoid muscle), but can also occur neurologically. In addition to this "shortening", a strain in the neck muscles can also result from jerky or sudden movements, which leads to tension.
In addition to incorrect movements or movements that are too fast, there are also a number of psychosomatic causes, especially in the case of recurring pain, such as stress in everyday life and poor or insufficient sleep. Tension is also common as a side effect of burnout syndromes or depression.
attitude
Muscle hardening occurs in this area, especially during activities that are frequently seated and bent forward. Office workers who do computer work in a sitting position are particularly affected here. If the eyes and head are focused on a certain viewing area (e.g. monitor) for a longer period of time, the necessary alternation between tension and relaxation phases is missing. This constant change usually guarantees that the neck muscles are supple, well supplied with blood and that they work flexibly.
The first hardening of the neck muscles occurs after an unchanged posture of approx. 15 minutes. Most of the time, those affected are so focused that they do not notice the muscles slowly hardening. Physiologically, a steady line of sight results in maximally tense muscles in the neck area.
The reason is that gravity is on the entire body and pulls it down. The longer a position is held, the more the muscles have to work to maintain that position. The constant hold leads to a hardening, which then leads to a minimization of the blood supply. This reduces the performance of the muscle even further due to a lack of oxygen. The muscle then has to work even harder to achieve the performance that is still required.
The result is the development of so-called myogeloses, in principle reversible muscle hardening, which appears in the form of swellings and nodules on the muscle that are painful to pressure.
Read more about the topic here: Exercises for strengthening and improving posture at the desk
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
trauma
The smallest acute trauma and injuries in the neck muscles can also lead to tension. Sometimes it happens that the sudden unphysiological turning of the head or crouching away leads to a sudden, sharp pain in the neck area. What is often incorrectly referred to as a pinched nerve are acutely hardened muscles in the neck area or the smallest traumatic tears in the structures of the muscles, which, similar to sore muscles, can lead to the symptoms mentioned.
After such an event, those affected often remain in a relieved or inclined posture, which is also unphysiological and promotes further tension in the neck muscles. The cause of the myogelosis (muscle hardening) that occurs here is often a mixture of trauma, acute tension and chronic tension.
Relief postures can also lead to other abnormal sensations in the neck area, read our article on: Burning in the neck
Cold stimulus
Another theory in the development of myogelosis lies in the chronic supply of cold and wind to the neck muscles.
The condition commonly referred to as “tension” is probably caused by a chronic counteracting of the neck muscles against external stimuli. The complaints are often associated with cold wind.
One theory of this development is that there is permanent slight pressure on the neck muscles from the side wind and that the muscles have to counteract this in order to maintain the desired head position. This can be done without any problems over a short period of time. However, if there is a permanent counter-steering situation, the muscles begin to harden. The above-mentioned blood and oxygen depletion and the development of myogelosis also occur here.
In addition to the counter-steering theory, lowering the temperature is also ascribed a decisive contribution to tension in the muscles in the neck area. With a longer air flow in the area of the neck and neck, the temperature in the area of the neck muscles drops. In order to be able to perform appropriate holding and movement work, on the one hand a corresponding "operating temperature" must prevail in the muscle and on the other hand sufficient nutrients must be supplied to the muscle. Both are reduced when the temperature drops. The main cause of muscle tension in this context is seen in the resulting reduced supply of nutrients. The fewer nutrients, blood, and oxygen that get into the muscle, the more difficult it is for the neck muscles to do the required work. A hardening occurs.
Psychosomatic causes
Psychosomatic causes of tense neck muscles seem to be very common today. New and unfamiliar life situations increase tension in the entire body and increase concentration. This also has an effect on the neck muscles, which are tensed to the maximum in unfamiliar situations so that they can be kept even better under control.
As with any untrained muscle that suddenly has to perform unusual maximum performance and holding power, the biochemical energy molecules (ATP) necessary for muscle movement will soon be exhausted.
The muscle now begins to carry out the required work, but at this point it burns almost exclusively sugar, as the oxygen reserves are increasingly exhausted. Similar to sore muscles, this leads to pain and massive muscle hardening.
The psychological situation determines how long the state of maximum muscle tension in the neck muscles lasts. In new, unfamiliar life situations, the corresponding muscle parts are tense in every person. In a mentally balanced person, this tension begins to improve the longer he stays in this situation. In other cases this situation persists for a longer period of time.
The causes of this muscle hardening are therefore psychosomatic. The psychologically stressful situation turns into a chronic physical state of tension, which can trigger long-lasting complaints.
What influence does the pillow have on neck tension?
The sleeping position is not only an important criterion for existing neck tension, but also crucial for prevention.
The supine position is usually the most back-friendly, as the neck muscles, head and spine are kept in a relatively neutral position. Even in the side position, with knees drawn up, people with back or neck problems can usually sleep well because the muscles on the back are slightly stretched.
The pillow is very important for the posture of the neck and head. This must not be too high, otherwise the neck will be overstretched. If, on the other hand, it sinks too deeply or if the person concerned does not use a pillow at all, the head is too low and the cervical spine is bent. With large pillows, part of the upper body is often already on the pillow, which leads to tension.
A neck pillow is adapted to the complaints of neck tension. It is slightly elevated and does not sink in, so the head is kept level with the cervical spine, while the shoulder lies in front of, rather than on the pillow. The spine is supported and held in a similar position throughout the night so that it can recover from the stresses of the day. If you know whether you are more of a back, side or stomach sleeper, the height of the pillow can vary accordingly. Testing the pillow is essential.
The material of the pillow can also be decisive and shows a variety of alternatives. These range from cold foam to latex and mineral foam. There are also water and gel pillows that adapt differently to the individual body.
Switching from a normal to a neck support pillow can be perceived as uncomfortable at first, as the body has to get used to the "wrong", unnatural lying position. After getting used to it for some time, however, you will notice clearly positive changes.
Symptoms
First of all, patients with tense neck muscles feel a mostly local pressure on the corresponding muscle parts. If the muscles do not relax afterwards, muscle hardening occurs quite quickly, which can then also affect the surrounding nerve tracts. This leads to moderate to severe pain. The pain is described as biting or cutting.
Painful tension in the neck is accompanied by a variety of accompanying symptoms:
- Neck pain / stiff neck
- Tension headache: Often described as mild to moderate in intensity, pulling or pressing on both sides of the head.
- Shoulder and back pain: This pain is often caused by a hardening of the trapezius muscle (Trapezius muscle).
- Numbness, circulatory disorders, restricted movement of the arm / hand: Nerve and conduction pathways located in the neck, which are pinched off due to severely tense muscles, can lead to the symptoms mentioned.
- Dizziness, nausea, vomiting: This can also be caused by pinched nerves.
- Earache: Neck muscles and the muscles around the ear are closely connected, which means that the pain can radiate to that point. It is perceived as lying in the ear.
- Tinnitus: Tinnitus can occur, especially with psychological stress as the cause of neck tension. Due to its high level of suffering, tinnitus can also be the cause of hardening of the neck muscles. Conversely, an increased muscle tone of the muscles described can also cause the tinnitus.
Read more on this topic at: Neck pain with headache
Pain
Hardened and tight muscles in the neck and neck area are the main cause of neck pain. These can lead to poor posture, which in turn leads to further tension.
In the worst case, this results in a vicious circle that can only be broken through active relaxation and pain treatment. Normally, however, neck pain only has a serious cause in rare cases and disappears on its own after a few days.
If the pain is chronic, the cause should always be clarified. However, this can be diverse and range from abscesses (purulent swellings in the throat area) to rheumatic diseases and scoliosis (crooked back) to meningitis (Meningitis). In addition to neck stiffness and pain, this manifests itself in fever, nausea, headache and impaired consciousness.
Neck tension and headaches - what is the connection?
Tension headaches often appear as an accompanying symptom of neck tension, but the exact cause has not yet been clearly clarified.
So-called secondary headaches emerge as a symptom of existing diseases, for example as a side effect of taking medication, vascular diseases or damage to nerves in the head, face or cervical vertebrae. These are therefore directly related to neck tension.
The pain can come from a hardened trapezius muscle as well as from deep short neck muscles and from a certain nerve, the Major occiptal nerve radiate.
The trapezius muscle pulls over the cervical spine to its insertion at the back of the head and the Major occipital nerve passes through this muscle in order to sensitively innervate the back of the head. If there is tension in the neck area, the nerves located there can be irritated, which reduces pain tolerance and the pain threshold.
The headache can show up to different degrees and in different forms. Usually it is an extremely pulling and pulsating pain, which severely restricts the person concerned in his well-being and his ability to move. The headache usually gets worse when quick, jerky and unusual movements are made.
Tension headaches, however, are more characterized by a non-pulsating, "vice-like" pain that occurs on both sides of the head, does not tend to cause nausea and does not restrict routine head and cervical movements.
Neck tension and chest pain - what is the connection?
Tension in the neck area can radiate to the chest and lead to tension in the chest muscles, the muscles between the ribs or other auxiliary breathing muscles that are placed on the back. The chest pain is breath-dependent, so depending on how deeply you inhale or exhale, the pain is also perceived differently. They are often described as an armor-like and oppressive feeling around the chest, which leads to shallow breathing. Shallow breathing in turn reduces the oxygen supply to the body and thus leads to fatigue and weakness. Tension and pain can often be relieved with a self-massage or visits to physiotherapy. Preventive measures such as exercise should be taken and "rounded back" sitting for long periods and other risk factors should be avoided.
Psychological causes can often lead to chest pain through tension and must also be ruled out.
You might also be interested in: Shoulder Neck Pain - What You Should Know About It
Nausea / dizziness
Nausea (Nausea) is a symptom that can have many causes. Long-lasting states of tension, pain and psychological causes such as strong excitement and fear can cause nausea. The emergence happens through an irritation of the vomiting center, which in the Medulla oblongata (elongated spinal cord). It forms the transition between the spinal cord and the brain. The vomiting center is irritated by various messenger substances (neurotransmitters) and information from the body is transmitted, which triggers nausea and usually a subsequent nausea. If neck tension becomes severe or chronic, the person affected is often exposed to long-lasting pain and a state of tension in the body, which can result in nausea.
Why am i dizzy?
Dizziness is a common symptom that comes with all kinds of causes and can appear in a number of ways. Today we know that there are a number of receptors in various muscle parts, connective tissue and fascia, from the soles of the feet to the neck to the eyes and muscles in the forehead area, which ensure balance and, if irritated, can lead to dizziness.
Tension in the neck area is a permanent contraction that can no longer be easily resolved. This permanently ensures that the receptors located there are blocked, which in turn ensures that balance signals are incorrectly transmitted to the brain.
In acute dizziness, it helps to lie down, drink in fluids, and raise your legs to stimulate blood flow.
high blood pressure
The fact that neck tension can be related to high blood pressure is not necessarily obvious. However, it has often been observed that when neck tension has been resolved by a chiropractor, blood pressure has subsequently stabilized.
High blood pressure and neck tension are symptoms that can have many causes. These causes are similar in many cases:
- Stress and constant strain
- little movement
- bad sleep
Experts also talk about the fact that the neck muscles are connected to certain areas of the brain. These brain areas are responsible for regulating blood pressure, heartbeat and breathing. If the muscles lying there are tense, incorrect information can be passed on, which can affect the blood pressure.
The reason that the neck muscles are connected to this brain area can be described by the fact that the blood pressure must always be kept the same. It is therefore independent of posture. The neck muscles are stressed differently when lying down than when standing and are therefore a good source of information for the position of the body.
Visual disturbances
The neck muscles are closely related to those of the eye. If the neck muscles are tense, it is mostly due to the eye muscles and vice versa. If there is ametropia, the head posture is automatically adjusted unnaturally. With uncorrected nearsightedness or farsightedness, the head is stretched forward or pulled back. The neck muscles suffer from this and tension can occur. These usually occur at noon, when the eyes have been moving for a few hours and are often caused by long monitor work. Tension can be avoided by taking more breaks in everyday office life.
If the neck tension arises otherwise, the ability to see can also be impaired by the pinching of vessels and nerve tracts in the neck area.
The vessels that run through the neck area often end in the head area. The following circulatory disturbance leads to visual disturbances. These can express themselves individually from person to person and range from flickering and flashes of light in the field of vision to impaired visual acuity.
If you have severe eye problems, it is advisable to consult an ophthalmologist to make sure that this is related to neck tension.
Tinnitus
People with tinnitus hear a sound that objectively usually does not exist. This noise can be a whistling, hissing or humming, which is either only perceptible in one ear or in both and partially temporarily or continuously for the patient.
The origins of tinnitus are varied and still not fully understood. There are approaches to explain it in psychological stress, constant noise exposure, various ear diseases and muscle tension. When there is tension in the neck muscles, the cause of the tinnitus lies in pinched or pinched vessels and irritated nerve tracts.
The hearing center and the neck muscles are anatomically very close to each other, which means that the reduced blood flow and the irritation of the nerve roots in the neck area can lead to a misdirection of hearing information from the nerves in the ear area.
Tinnitus, which is perceived in the rhythm of the beating heart, usually leads to tension in the head-turning muscle (Sternocleidomastoid muscle), which is in the immediate vicinity of the bilateral carotid artery (Common carotid artery) stands. If this is compressed, the heartbeat is perceived as noise in the ear.
difficulties swallowing
Difficulty swallowing can have numerous causes. A distinction is made between the Dysphagia (Complaints without further pain) and the Odynophagia (Complaints with accompanying sore throat). The process of swallowing is a complicated process that involves many nerves and muscles that have to work in unison. It is partly arbitrary and partly involuntary.
If the muscles in the neck become tight or if nerves are pinched or pinched, the swallowing process can suffer. Misalignments of the cervical spine, which are often associated with neck tension, can also have a negative effect on the swallowing process. Spondylosis deformans, a remodeling of individual vertebrae, is an example of this.
diagnosis
Since neck tension has a variety of causes, it can sometimes be difficult to make a diagnosis. In the case of stress-related causes and signs of wear and tear such as osteoporosis or arthrosis, a visit to the family doctor can be helpful.
Misalignments of the spine can best be visualized with imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
In most cases, a GP or orthopedic surgeon will be able to make a meaningful diagnosis.
therapy
There are a variety of approaches how to individually, at least partially, relieve neck tension.
- Warmth can often be helpful. Cherry stone pillows or hot showers can usually alleviate the symptoms. However, if there is additional inflammation in the neck area, heat is counterproductive.
- Movement is especially important so as not to keep the neck in an unnatural position. Here, however, care should be taken to exercise gently (e.g. swimming) and avoid jerky movements.
- Meditation and autogenic training serve to relieve stress so that the whole body and thus also the tense neck area can relax again.
- Regular physiotherapy massages are particularly helpful.
- Massages performed in-house can also alleviate the pain. For this purpose, so-called trigger points are sought by stroking the tense areas with your head tilted forward and both hands. These are individual muscle hardening that can be released with gentle but steady pressure. To do this, the hardenings are slowly circled with the fingers. This is uncomfortable at first, but much less painful after a while.
- Muscle exercises
- Oils
- Surgical procedures that relieve the neck tension by eliminating the cause are also possible with a specially made diagnosis.
It is important to prevent future tension through correct posture.
Which exercises can help?
Get into the habit of including neck exercises in your daily routine several times a day. To do this, it is best to choose several exercises that you find comfortable and that you can perform in everyday activities such as brushing your teeth.
Exercises:
- During the first exercise, place your hand one after the other on your forehead, then on both temples and the back of your head, and each time press lightly with your head for 10 seconds. This ensures a brief and gentle strain on the neck muscles, which is followed by a relaxation phase for the muscles. This also applies to the brief lifting of the shoulders on both sides. Repeat this 5 to 10 times.
- The next exercise describes the lateral stretching of the neck. To do this, reach over your head with one hand and gently pull it to one side for about 15 seconds until you feel a stretch on the other side. Be careful not to pull too hard and not to strain the neck too much. Hold this exercise for about 15 seconds, being careful not to pull too hard on the neck.
- To mobilize the spine, you can raise your hands at chest level and fold them while standing. One leg is raised at an angle and turned to one side while the hands pull to the other side of the body. Keep your upper body and hips as straight as possible and repeat this exercise 10 times before lifting the other leg and using the other side.
- The arms and shoulder circles also loosen the neck muscles. To do this, simply lift your arms and circle 20 times forwards and 20 times backwards or alternatively hold your arms against your body and, without much effort, circle your shoulders back and forth.
- Another exercise is the massage of the head turner muscle (Sternocleidomastoid muscle). To do this, turn the face in one direction until the head turner muscle protrudes visibly or palpably on the other side. Gently massage and rub this from the ear to the collarbone.
- So-called 'CAT-COWs' help to relax the back and neck area. To do this, keep pushing your back down while standing on four feet and make a 'cat hump' upwards. Repeat this 10-15 times.
Which sports can help?
With chronic neck tension, it is important to exercise regularly and build muscle. In this way, the pain is relieved, the tension partially relieved and new tension is prevented. However, it is important to choose the right type of exercise. Some sports are counterproductive, especially for people with chronic neck tension. These sports include, for example, tennis, squash and badminton.
Any sport that puts strain on the neck or one arm on one side makes the disease worse. You should make sure that the sport you choose involves your whole body.
- Swimming is one of those sports that gently train the whole body. However, breaststroke swimming, in which the head is held too far out of the water and the neck muscles are compressed, should be avoided here. Backstroke and crawl are suitable.
- Cycling, soccer, and inline skating are all sports that involve multiple muscle groups.
- Jogging, as a gentler endurance sport, ensures good blood circulation. This helps relieve tension.
- Dancing trains posture and the ability to move properly.
- Yoga and Pilates strengthen the whole body and at the same time help to relax.
An important additional factor is the stress reduction during sport, which can prevent further tension.
In all sports, it is essential to ensure that an appropriate warm-up phase is included, in which all muscles and ligaments are stretched before the stress occurs. This is an absolute must, especially for people with tension. A 'cool down' phase after exertion is also important.
Heat therapy
If the neck tension is not due to inflammation, heat will be effective in relieving tension.
If deep heat is generated, this ensures an expansion of the blood-supplying arteries, which leads to better blood circulation and oxygen supply to the hardened muscles.
This heat can be generated by a cherry stone pillow heated in the oven or microwave. Hot water bottles that are filled with hot water or rolled up towels that have been partially covered with hot water also provide short-term warming.
Long-term therapy with red light can also help. For this you need a red light lamp, which shines on the tense region at a distance of about 40 to 50 cm and an irradiation period of 10 to 15 minutes.
Ointments and heat patches, which are available in the pharmacy, can also help. Heat patches provide heat for up to 12 hours.
acupuncture
Acupuncture is a Chinese medicine. This is based on the belief that the body's energy, called QI, flows through the body on certain paths. If the flow of energy is disturbed, it can be restored with fine acupuncture needles that are pierced into the skin at certain points. The needles remain there for about 10 to 30 minutes to restore balance. During this time, heat may develop in the treated area. Except for a slight puncture pain, usually only slight pain is felt. The needles can be modified by heat or electrical stimulation to achieve better and more specific effects.
Side effects can be slight bleeding or bruising at the set site, but these occur only rarely and if only slightly, as the needles are very thin. The duration of a session varies from person to person, depending on how painful and persistent the neck tension is.
Acupuncture is an alternative healing method and has not yet been adequately proven scientifically. However, there are smaller studies that show less pain in patients treated with acupuncture compared to patients without this treatment. One explanation is that the needles placed in the nerve tracts release pain-relieving messenger substances, which lead to a decrease in pain.
Osteopathy
Osteopathy describes a complementary medicine that considers the body, mind and soul as a whole. This is influenced by the individual environment. If every single body structure is mobile, then the body as a whole with its nervous and vascular system is mobile and thus able to heal itself.
If an organ or muscle is restricted in its movement, the osteopath tries to find the cause and treat it.
During a session for the treatment of neck tension, the head and body posture is observed and assessed after taking an anamnesis. Then the spine as well as the back muscles and the neck are scanned. In this case, pain can often be spontaneously alleviated by just a few movements by the osteopath.
Read more about this under Osteopathy in cervical spine syndrome
Taping
The kinesiological tape, also called physio tape, is an elastic tape made of plastic, which is treated with polyacrylate adhesive, stuck to certain parts of the body and intended to achieve various therapeutic effects there. It can stick to the skin for between four and seven days and is waterproof.
The application should take place on dry and clean skin. Before doing this, it can make sense to depilate the respective part of the body.
The therapeutic effect is achieved by the fact that the tape moves and adapts itself to movements of the body, thus stretching and massaging the tissue and skin under the tape. This stimulates the blood circulation, the lymph flow and the nerve tracts in this region and tension can be released.
There are several ways to apply the tape. It makes sense not to do this yourself, especially in the neck and back regions, but to ask your partner or, at best, seek professional help who can choose and explain the best method of attachment.
The taping not only helps with tension in the neck, but also with muscle inflammation, osteoarthritis or migraines / headaches and can therefore be used in a variety of ways.
Medication
Gels, ointments, and tablets can help relieve symptoms for a shorter period of time. It should be noted that ointments and gels usually affect the organism far less, as they only have a local effect on the application site. However, in some cases they do not work as intensely as pain pills because they only penetrate into the upper layers of tissue.
Different ointments provide warmth, pain relief or a combination of both. The warming effect is mostly due to the active ingredient Capsaicin, which is obtained from chili peppers, triggered. Veins underneath the skin ensure better blood flow to the muscle parts by expanding them. In addition, the release of pain messenger substances is inhibited. These ointments usually work for a few hours. Well-known and helpful pain ointments are, for example Voltaren pain gel, Thermacare pain gel, Kytta ointment and the Traumel ointment.
Heat patches have a similar effect, their effect lasts for a similar time and which often use the same active ingredient.
If the choice falls on pain pills, there is also a large selection here.
Paracetamol Reliably relieves pain as the pain signals cannot be passed on to the brain. However, excessive doses of this can cause liver damage.
Ibuprofen is another option, but often combined with digestive tract and stomach intolerance. As well as Acetylsalicic acid, ASS or Aspirin® called which the production of tissue hormones (Prostaglandins) suppressed.
At night the pain medication can Naproxen help, which relieves pain for up to 12 hours. There are few known side effects with this pain reliever.
It is important not to resort to pain medication permanently, but to actively take action against the neck tension!
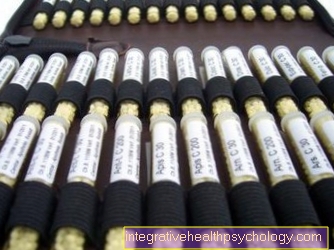
homeopathy
Homeopathy is an alternative treatment method. Natural substances made from plants or animals are used for therapy.
A homeopathic treatment consists of a conversation in which the symptoms are delimited as far as possible in order to find the right homeopathic remedy for the individual person.
There are also some remedies that can be helpful for neck tension. The remedy "Ruta" is often used for this. This works for neck tension due to bad posture, but can also be used for diseases such as broken bones, sprains and bruises. The "Cimicifuga" remedy is also effective for particularly strong tension, which radiates into the arms and back.
"Nux vomica" is recommended for tension, which is strongest especially at night and in the morning and becomes more painful through movement. "Bryonia" can treat those that are drawn more painful by warmth and movement.
The agents listed are just a few of the many alternatives. Therefore, it makes sense to seek professional advice.
Read more about this under Homeopathy for cervical spine syndrome
Which home remedies can help?
In some cases, neck tension can also be relieved or at least improved with the help of home remedies in order to alleviate the pain and to be able to undertake a normal everyday life.
- Heat is the most important and easiest measure here. A cherry stone pillow, which is heated in the oven or microwave, a warmed hay flower sack or a spelled pillow is suitable for this. A hot water bottle or a heating pad that you can sleep on are also warming alternatives. Warm clothing such as scarves and turtlenecks can also make a decisive contribution to improving tension.
Another option is the treatment with a warm quark wrap, which you place on the affected area. It can also be beneficial to take a sauna or steam bath.
However, it is important to ensure that the cause of the tension is not found in inflammation, on which heat would have a counterproductive effect!
- The next step is to choose a back-friendly mattress, especially with emphasis on the upper back and neck area. A suitable neck pillow also improves the sleeping position.
- Another tried and tested home remedy is St. John's wort oil, which is dripped onto a cotton pad and then placed on the painful area. This is covered with a foil and a cloth and left there for some time.
- Chamomile oil can also be helpful when used as a bath additive. The warmth of the water in combination with the chamomile oil has a stronger effect on the tense muscles.
- Tiger balm has a combination of various remedies and essential oils that promote blood circulation and warm you up. Tiger Balm RED in particular, which also contains cinnamon and cloves, is said to be helpful for muscle hardening.
When does my neck pain become chronic?
We speak of chronic neck pain when the tension persists for a period of at least three months and the pain severely affects your everyday life.
Chronic neck pain can be divided into specific and non-specific pain, with non-specific pain mostly caused by poor posture, stress, incorrect sleeping position or physical work. Specific ones usually go to joint wear (arthrosis) or other injuries.
What can I do with chronic neck tension?
In the case of chronic neck tension in particular, a visit to the doctor is unavoidable, as these are often based on a vertebral misalignment or other problems with the spine.
Therapeutic measures such as physiotherapy are often the right choice to relieve and prevent chronic tension. Regular stretching and movement of the muscles, as well as building muscle, are important to achieve better posture. A neck pillow, ergonomically shaped, can also improve symptoms.
If the chronic tension is increased or triggered by psychological factors such as stress, it is important to become aware of this and to reduce it. From stress reduction through sport to distraction through leisure activities and friends, there are different ways to reduce stress.
In the case of chronic neck pain, too, provided it is not an inflammation, that heat has a pain-relieving effect. As a preventive measure, it is important to reduce stress and take care of your own mental health.
Daily stretching as well as promoting natural muscle building in everyday life can achieve better posture. During office work, for example, short breaks in which you walk around can be built in.
What can be the consequences of chronic neck tension?
Neck tension can cause numerous consequential damage to the body:
- Inflammation in the shoulder area: The causes here are the permanent, unnatural posture and lack of movement.
- Cervicobrachial Syndrome: This syndrome describes the loss of sensitivity, symptoms of paralysis and radiation of pain from the neck to the arm.
- Herniated discs: Due to the tension, the muscles in the neck can no longer be stressed as they should be, and stronger forces act on the spine, which must be absorbed by the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. This leads to increased herniated discs.
- Migraines / headaches: Neck tension can promote migraines or severe headaches and spread to the respiratory muscles. This can lead to breathing problems and shallow breathing.
- Tinnitus
- Visual problems
- Dizziness / nausea