Kidney cysts
Synonyms in a broader sense
Cystic kidneys
possible medical condition: polycystic kidney degeneration
English: polycystic renal disease
definition
Under one Kidney cyst / kidney cysts one understands a cavity of the kidney which is mostly filled with fluid.
This cavity is reminiscent of a bladder, which can lie inside or outside the kidney, i.e. adjacent to it.
A special form of the cysts kidney represents the clinical picture of the cyst kidney. In this case almost the entire kidney consists of cysts.
It is a steadily progressive phenomenon. This disorder is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait.
This means that the predisposition to this disease lies in our genes. Inheritance is independent of gender and always occurs as soon as a gene with defective genetic material is passed on. The onset of this disease lies in the development of the child in the womb with the malposition of both kidneys.

Epidemiology
Common kidney cysts practically never appear before the age of 30 and become more common with age. Kidney cysts are detectable in around 20% of those over 60 years of age.
With a frequency of 1: 1000, the hereditary cyst kidney is the most common hereditary kidney disease in the general population.
The age of manifestation (age of occurrence), i.e. the age at which this disease develops most strongly and then prevails, is between the ages of 30 and 50.

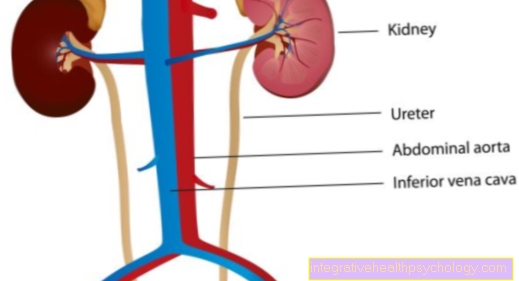
Illustration kidney cysts
- Kidney capsule
- Renal cortex
- Renal medulla
- Calyx
- Renal pelvis
- Renal artery
- Renal vein
- Ureter (Ureter)
- Kidney cysts
Causes of the kidney cyst
The root cause of common kidney cysts is mostly idiopathic, that is, of unknown cause.
In the case of the cyst kidneys, the cause is usually a mutation / change in the Chromosome 16. Chromosomes are the storage molecules of our body's genetic make-up. All of our features are encoded on 23 chromosomes plus 2 sex chromosomes. We have two of the 23 chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are divided into X and Y. There is also the autosomal recessive cyst kidney. The genetic defect must be present on both chromosomes in order for it to take effect.
Symptoms of the kidney cyst
Kidney cysts are usually asymptomatic, so they are not even noticed by those affected as they do not cause any symptoms. Mostly the cysts are incidentally one Ultrasound examination (Sonography) discovered and diagnosed. In rare cases, they can still cause discomfort in the form of complications such as infections.
In the case of the Kidney cyst can it to Blood in the urine, Pelvic inflammation and also Urinary tract infection come. Flank pain could possibly occur. Infection of a bleeding cyst can be dangerous.
Renal insufficiency, i.e. insufficient work up to Kidney failure, usually occurs in the 4th - 6th decade of life.
Read a lot more information on this topic at: Symptoms from kidney cysts
Complications
Here, too, the usual kidney cyst is again rather harmless, apart from possible inflammation of the same.
In the case of the kidney cyst, which is due to a defect within chromosome 16, further complications can arise.
The cysts can not only affect the kidney, but also:
- spleen
- pancreas
- lung
- Ovaries
- Testicles
- thyroid
- and also liver affect.
The heart valves are also often affected, which in the course of time become insufficient, i.e. no longer fulfill their function to the full. A Heart failure develops.
Other complications of a kidney cyst include arterial hypertension (high blood pressure) and Inguinal hernias (Inguinal hernia).
The high blood pressure is caused, among other things, by the fact that the kidneys are no longer able to do enough sodium to be eliminated. Sodium chloride, i.e. table salt, is retained in the blood together with water and thus creates a higher pressure due to the higher volume.
Diagnosis of kidney cyst

The diagnosis of kidney cysts is mainly made by the Ultrasonic. Here the cysts appear as dark cavities. Liquid always appears dark in the ultrasound. Behind these cysts there is a so-called sonic shadow in the ultrasound image.
In the case of the hereditary cyst kidney, there are often large, palpable kidneys. Here, too, the diagnosis is made with the help of ultrasound, whereby kidney and liver cysts must be detected. Gene analysis is rarely required.
Therapy / treatment
Therapy for a simple cyst is usually not necessary. Very large cysts can be punctured if necessary.
Puncture means that the fluid from the cyst can be sucked out with a needle that is inserted into the cyst. Samples of the punctured filtrate are then usually sent to a laboratory in order to have it examined for pathogens and other cells.
In the case of the cyst kidney, too, purely symptomatic therapy is usually given. For example, the common urinary tract infections are included Antibiotics treated.
Medicationwhich cause additional damage to the kidneys should be avoided. If a patient's kidneys are noticeably deteriorating, so can one dialysis (Washing of the blood outside the body by machines) or even one Kidney transplant become necessary. Genetic counseling is also part of a good therapy.
Read a lot more information on this topic at: Treatment of kidney cysts
prophylaxis
There is no prophylaxis, i.e. prevention, for kidney cysts.
Since the cyst kidney is congenital, no prophylaxis is possible here either. However, the risk of the disease recurring can be calculated as part of genetic counseling. Genetic advice can be obtained from doctors specializing in human genetics, usually at university hospitals.
forecast
In the case of hereditary (hereditary) cystic kidneys, around 50% of the carriers of traits become renal insufficiency by the age of 50 (chronic kidney failure).
Carrier means that they have the mutated gene on chromosome 16. But disease courses with normal kidney function are also possible. Are the Kidney values once bad, the disease progresses in the form of the Renal failure (Kidney failure) progressing rapidly.
The decisive factor here is the creatinine in the blood serum.
The higher this value, the worse the kidney works.
other topics
Other topics that might interest you:
- Kidney cyst symptoms
- Kidney cyst treatment
- kidney
- Lower urinary tract
- acute kidney failure
- Pelvic inflammation
- Kidney cancer
- Internal Medicine
All topics that have been published on the field of internal medicine can be found at:
- Internal medicine A-Z