Splint for an internal ligament tear in the knee
introduction
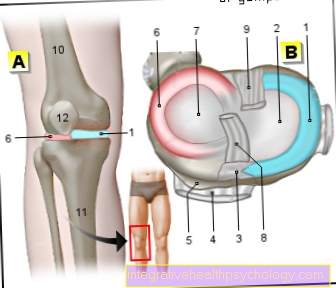
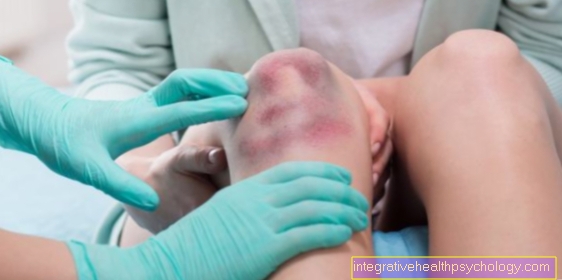
A Inner ligament tear in the knee joint usually requires splinting of this joint in order to stabilize it. This type of injury usually occurs during exercise combined with excessive movement of the knee joint.
The symptoms of the torn inner ligament are then pain in the area of the inside of the knee, possibly a Bruise in the knee at this point as well as the usual signs of inflammation such as redness, swelling and overheating (see also Inflammation of the knee).

Splint as a therapy concept for an internal ligament tear of the knee
If no other structures in the knee are injured and the knee joint is stable enough, conservative therapy with immobilization and splinting is usually sufficient. This initially restricts the mobility of the knee joint and thus prevents excessive / incorrect loading due to the lack of stabilization from the injured inner ligament. The radius of movement can then be adapted to the current degree of healing of the knee joint. The main thing is to prevent excessive flexion in the knee joint initially.
In the further course of therapy and in connection with physiotherapeutic measures, the maximum degree of flexion permitted by the splint can then be increased. There are various therapy concepts for this, but as a guideline you can initially assume a flexion of a maximum of 60 degrees and after a few weeks of a maximum of 90 degrees. The splint can usually be removed after about six weeks and in consultation with the attending physician.
But even after the splint treatment, special muscle building exercises should be performed to ensure permanent knee stability.
Surgical intervention should only be carried out if there are accompanying injuries or if there is instability in the knee joint.
Read more about this Ligament injuries in the knee joint
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Wearing the splint at night
If a splint has been prescribed by a doctor as part of a torn inner ligament, it should also be worn at night. Because especially at night there are many uncontrolled movements that can cause the knee to move very unfavorably. The splint is there to limit the range of motion of flexion in the knee joint. But it is precisely this that is often consumed by itself during sleep and can then have a negative effect on the healing process.If the splint is found to be a nuisance at night, additional padding with the help of cotton wool or soft clothing under the splint can help. The healing time is shortened with consistent adherence to the therapeutic measures.
Orthosis
At a Knee brace it is an aid in the form of an individually adapted support, which is used to immobilize, relieve and stabilize joints. This is usually prescribed by a doctor, for example in the context of a torn inner ligament, and produced and individually adjusted by an orthopedic technician.
On the one hand, the orthosis helps in the event of an inner ligament tear in the knee joint to restore the stability that has been lost and, on the other hand, to limit the range of motion in order to prevent incorrect loading. Above all, however, it is the protective function for the knee joint which orthoses mediate and which is decisive for the healing process of ligament injuries.
Knee orthoses can be made of different materials and should be selected individually in consultation with the attending physician.
If the course is uncomplicated, the orthosis should usually be worn for about six weeks after the injury and the knee should be loaded according to the stage during this time.
As an alternative to the orthosis or splint, there is the option of using a Knee brace to put on.
Summary
An isolated rupture of the inner ligament does not usually require surgery and can be treated with a conservative treatment regimen. On the one hand, the physiotherapeutic accompaniment is of great importance and, on the other hand, the support and relief of the joint by wearing a splint. This is usually for about six weeks and also required at night. Afterwards, tears in the inner ligament usually heal without any further restrictions and a full load is again easily possible.
If there are accompanying injuries, the extent of therapy depends on the type of injury and may take longer.