Tear duct
definition
Our eyes produce a film of fluid throughout the day so that the surface of the eye does not dry out. This also counteracts soiling of the eyes, as any dirt in the eye can flow away with the liquid.
As a logical consequence, there is therefore a need for a drainage system in the eye, the tear duct.
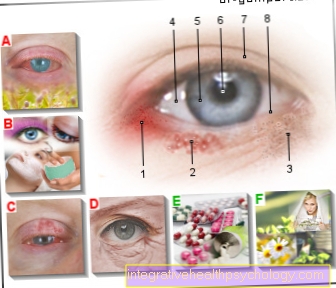
The tear duct is located at the nasal corner of the eye in the right and left eyes. It catches the fluid in the eye and creates a connection between the eye and nose.

Lacrimal canal anatomy
The tear system is a complex system made up of many small units that ensure the production and removal of tear fluid.
The lacrimal gland, which produces the tear fluid and then releases it into the respective eye, sits on the side above the eye at the outer corner of the eye. From there, every blink of the eye distributes the tear fluid as a uniform film of fluid over the eye.
In the following, the tears are collected in the teardrop points, which are located in the upper and lower eyelids just in front of the nasal corner of the eye.
If the tear film gets into the tear points, it is passed on into small tear ducts, which are located above and below the inner corner of the eye.
These tear ducts conduct the fluid further into the tear sac, which is still at the level of the right or left eye towards the nose.
From there, the tear fluid reaches the nasal tears and is drained into the nose. So this represents the connection between the eye and the nose.
Incidentally, the eye bags do not mean the "bags under the eyes" that are popularly referred to as "bags under the eyes". These describe drooping lower eyelids.
Are you interested in this topic? Then read our next article below: Tear ducts
Function of the tear duct
As complex as the structure of the tear system is, its function is just as varied. The tears produced ensure through permanent flow that the tear ducts do not clog. On the other hand, the tear ducts help drain the fluid produced in the tear glands.
The tears themselves wash away dirt that is in the eye and pass it on into the tear ducts.
In addition, there are certain substances in the tear fluid that kill bacteria and work against infections.
In addition, it also contains nutrients that are important for the cornea and the inside of the eye. Important nutrients for the eye itself are produced in the tear glands.
It has been found that tears also contain certain growth substances that accelerate the healing process for small wounds in the eye.
The fluid film in the eye also plays an important role in the visual function: unevenness in the cornea is evened out and thus a uniform surface is created. This is important so that the incoming light waves are refracted evenly.
The following topic may also be of interest to you: How does vision work?
Clogged tear duct - what is the cause?
The tear fluid is drained into the nose through the draining tear ducts, i.e. via tear points, tear duct, tear sac and tear-nasal duct. If one of these paths no longer works, the drainage is disturbed.
The fluid can no longer drain properly due to the blockage and infections can more easily affect the tear duct.
Signs of a blocked tear duct include:
- watery eyes
- reddened eyelids
- Pain or swelling in the eye
- blurred vision
The reasons for a flow obstruction in the tear duct can be a congenital malformation of the tear duct, a conventional inflammation in the eye, a glaucoma (glaucoma), an injury, or a tumor. In some cases, the tear ducts narrow with age and are therefore more susceptible to blockages. Chemotherapy or radiation can also narrow the tear ducts.
If there is a painless drainage obstruction of the tear duct over a longer period of time, a tumor should be ruled out by a doctor. If there is an acute inflammation, it usually heals itself after a few days or has to be treated with antibiotics.
You can find more information about this at: Clogged tear duct - symptoms and therapy
How can you irrigate the tear duct?
If the tear duct is blocked, the eyes will water excessively. In most cases, the obstacle can be removed.
In order to remedy the obstruction to drainage, one therapy option can be to have the tear ducts rinsed by an ophthalmologist. For this purpose, a short anesthetic can be performed in children and, if desired, anesthetic drops can be put in the eyes of adults.
First, the teardrop is widened with a thin, but front blunt instrument with twisting movements. Then a hollow needle with a rounded front is carefully inserted into the tear duct. To protect the structures, the opening of the hollow needle is on the side. This will flush a small amount of saline solution through the instrument into the tear ducts.
If the irrigation is successful and the draining tear ducts are clear again, this is shown by the irrigation solution being drained into the nose or throat.
If it is necessary to know exactly where the obstacle is, the doctor can carry out a further examination immediately afterwards. Contrast media is placed in the lacrimal duct and then an X-ray examination is performed. The ophthalmologist can then use the X-ray to determine where the narrowing is.
How to massage the tear duct
In newborns, the tear ducts are not yet well developed, which is why they can become blocked more often. To loosen the blockage, you can supportively massage the draining tear ducts.
In preparation for this, you take a cosmetic tissue and dampen it with lukewarm water. While you gently pull the lower lid down with one hand, you hold the cloth in the other hand. This is used to carefully clean the eye, once from the outer corner of the eye to the corner of the eye adjacent to the nose.
You can repeat the process as often as you like, but always with a clean cosmetic tissue. With your hands washed, place your index finger on the corner of your eye near the nose and apply gentle pressure for three seconds. Then let it go for a few seconds and repeat this a few times a day.
A warm washcloth or a warm tea bag on the eye also helps to widen the tear ducts a little.
What is tear duct stenosis?
A tear duct stenosis is a permanent narrowing of the tear duct. This can show up in excessively watery eyes and increased inflammation in the eye.
It is often noticeable in newborns that they wake up in the morning with crusty eyes and watery eyes even though they do not cry. Because immediately after birth, the draining tear ducts are often not yet fully developed, so that there are more frequent constrictions in the tear duct.
It is also possible that babies have a small protective skin on the entrance to the tear duct and make it impossible for the tears to drain away.
All of this usually improves in the course of the first year of life and usually does not require an operation. Nevertheless, parents should discuss the problems with the pediatrician and seek advice on how to get relief at home through massages and warm compresses.
In the case of purulent inflammation, you should see a doctor as soon as possible so that you can treat early and the inflammation does not spread.
In adults, in some cases, the tear ducts narrow with age.
Other reasons can be adhesions due to multiple inflammations or small stones that obstruct the corridor. A tumor, chemotherapy, or radiation can also narrow the tear ducts. Clarification by the doctor is also recommended here.
For more detailed information on this topic, see: Lacrimal Canal Stenosis - Causes, Symptoms and Therapy
Inflammation of the tear duct - what's behind it?
If germs get into the eye or if the tears cannot drain due to a narrowing of the tear duct, it can easily lead to an inflammation of the tear duct.
The typical symptoms are red, watery eyes with itching, swelling and pain. A general feeling of illness with a fever may also occur. Inflammation of the tear duct can be acute or chronic, but in both cases you should consult a doctor in good time.
Acute antibiotic therapy with eye drops or in tablet form may be necessary. Cooling compresses help.
In the case of chronic inflammations, which are usually associated with milder symptoms, the main focus is on eliminating the cause. This may require irrigation or X-ray examinations of the tear duct.
To prevent inflammation, for example, one should only look with washed hands and do so as rarely as possible. Cosmetic utensils such as mascara and eyeliner should be replaced regularly and not shared with other people.
Anyone who uses contact lenses should ensure that they are cleaned as recommended by the dealer and that they do not exceed the specified useful life.
You can read more helpful information on this topic under: Inflamed tear duct - causes, symptoms and therapy
Swelling of the tear duct - what's behind it?
A swelling of the tear duct is often based on an acute or chronic inflammation of the tear duct and the resulting blockage of the draining tear ducts. This can be accompanied by fever and general weakness, as well as purulent discharge in the eye.
Especially if there is a punctual, very painful swelling in the tear duct, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible if an abscess is suspected. In the case of an abscess, adequate therapy with local and systemic antibiotics must be started immediately to prevent it from spreading to adjacent structures (Phlegmon).
In addition, there is a fear of so-called fistula formation. This refers to the formation of a new small canal that leads into another tissue such as the skin and drains pus or secretion there.
Swelling of the tear duct can very rarely be caused by a benign or malignant tumor, which is why it is advisable to consult a doctor. In the case of a tumor with impaired function of the tear ducts, surgical therapy is very likely necessary.
Basically, the earlier treatment is started, the better the chances of healing a tumor in the tear duct.
Recommendations from the editorial team
Further general information may be of interest to you:
- Structure of the eye
- Vitreous
- Tear ducts
- Visual pathway
- Inflammation of the lacrimal gland















.jpg)