Urosepsis
Synonyms
Urinary poisoning, bacteremia, sepsis
definition
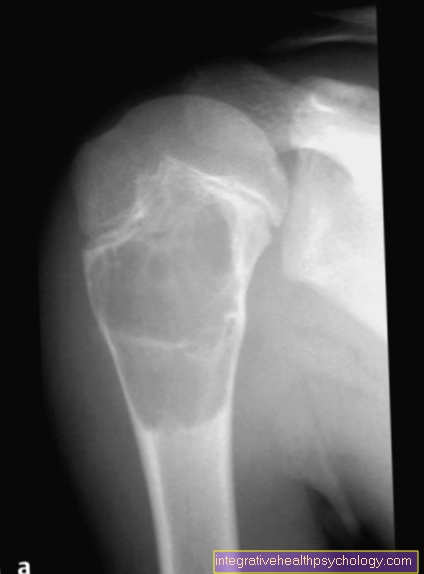
In urosepsis, toxin-forming germs pass from the kidneys into the bloodstream (blood poisoning). The main pathogens are E. coli (> 50%), as well as Klebsiella, Proteus or Enterobacter.
Also read the article on the topic: Urinary poisoning
causes
Risk factors for developing a Urosepsis are urinary flow disorders, one that immune system suppressive drug therapy (e.g. chemotherapy), an operation instead of a previous one (e.g. with the use of indwelling catheters) with the spread of highly antibiotic-resistant germs, Diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors or the Cirrhosis of the liver on de, bottom one Pelvic inflammation.
Illustration of the anatomy of the kidney
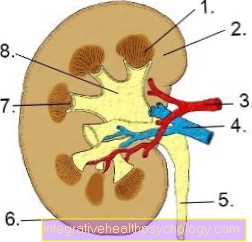
- Renal medulla
- Renal cortex
- Renal artery
- Renal vein
- Ureter
- Kidney capsule
- Calyx
- Renal pelvis
Symptoms
They are similar to septic shock (blood poisoning shock). In the initial stage, the skin is warm; only later, the narrowing of the vessels distant from the heart leads to cold acra (tips of fingers and toes, nose) and bluish (livid) discoloration.
Caution is advised with:
- Fever with chills
- Tachycardia (high pulse rate)
- Drop in blood pressure
- Tachypnea (high breathing rate)
- Clouding of consciousness
- and lack of urine excretion (oliguria to anuria).
When these symptoms occur, there is an acutely life-threatening condition.
diagnosis
The search for the cause (urinary congestion?, Kidney abscess?) Using ultrasound has the highest priority. The pathogens should be identified as quickly as possible using blood and urine cultures, also in order to identify any resistance to antibiotics.
The following can be detected in the blood:
- initially high number of white blood cells (leukocytosis), then very low number (leukocytopenia)
- Decrease in coagulation parameters (platelets, Quick value)
- Anemia
- Acid-base balance derailed
Read more information at: Kidney abscess
therapy
If there is an inflamed and congested kidney, this must be relieved immediately. This is done using a ureteral splint or renal fistula (nephrostomy). With renal fistula, the urine is artificially diverted to the outside through a tube that comes to rest in the renal pelvis
This is followed by broad antibiotic therapy, usually with a combination of aminoglycosides and penicillins or cephalosporins.
Of the Cycle is stabilized, e.g. B. by water-binding infusion solutions (plasma expanders), which replenish the lost blood volume. Infusion therapy should be initiated to balance the fluid balance and promote urine excretion.
The derailment of the acid-base balance can be neutralized by adding bicarbonate. It may be necessary to replace coagulation factors or even to perform hemofiltration (toxins are filtered out of the blood).
The most important measure is to remove the original hearth. In the worst case scenario, the kidney be lifesaving.
forecast
Despite intensive medical treatment, it is often very serious, especially if the therapy is started too late. The lethality (fatality) can be up to 50% because of the following multiple organ failure.