Vibration training indications, contraindications, risks
Indications of vibration training
In this topic I will focus on the areas of application of vibration training in the field of medical indications restrict. In the case of a wide variety of clinical pictures, damage and injuries it occurs primarily - directly through the damage - or secondarily through a reduction in the daily range of movement or training Deficits in the muscular Activation ability.
Relief postures and short periods of inactivity, caused by pain or damage to the musculoskeletal system lead in the long term to accelerated neurodegenerative changes. Especially with neurological diseases there is a correlating decline in performance in posture control, mobility and the restrictions on quality of life.
This vicious circle can neither be interrupted by strengthening the training units (insufficient energetic prerequisites!) Nor by influencing the underlying clinical picture.

At this point comes the possibility of Vibration training in the game. The external application of Vibration stimuli enables neural and muscular activity, which the patients with their individually different basic problems can no longer reach through independent training. In these cases, vibration training can not only be used as a supplement, but also exclusively.
Orthopedic indications
- Back pain of various causes
(Pain relief by improving muscle relaxation, stretching and coordination, inhibiting pain receptors)
- Posture damage
(Strength building and posture improvement)
- Scoliosis
(Improvement of stability)
- Foot malformations
(Strengthening of the arch muscles)
- Muscular Strength deficits after immobilization, accidents, injuries
(Improvement of muscle performance)
- Muscular hypertensiontoo much muscle tension
(Decrease in muscle tension)
- disc prolapse, in the non-acute phase
(Training of the local muscle system)
- Degenerative diseases of the spine
(Pain relief, stability)
- osteoporosis
(Improvement of bone strength and bone mass)
Sports medicine indications
- performance increase
(Muscle building, Improvement of coordination, speed and agility, parallel to the sport-specific training)
- Sports injuries
(Improvement of the metabolism, faster mobilization of the damaged tissue, earlier start of training)
Neurological indications
Spastic paralysis:
- Parkinson's
(Reduction of increased muscle tension and tremors (tremor), improvement of coordination and posture)
You can find more about this under our topic: Parkinson's disease
- multiple sclerosis
(Regulation of muscle tension, increase of muscle functions, improvement of posture, bladder and rectal control)
You can find more about this under our topic: multiple sclerosis
- stroke
(Reduction of spasticity, improved strength behavior, faster mobilization and rehabilitation)
You can find more about this under our topic: stroke
- Paraplegia
(Tension regulation, training of the arm and support muscles, coordination, relaxation, movement control and speed, support of treadmill training in cases of incomplete paraplegia, significant increase in performance and reduction of lateral differences in the gait pattern)
You can find more about this under our topic: Paraplegia
Flaccid paralysis:
- Ankle paralysis, e.g. to Herniated disc of the lumbar spine
(Improving motor control and increasing muscle performance) - Plexus palsy, Paralysis of the arm nerves e.g. after a motorcycle accident
Improving motor control and increasing muscle performance and muscle building) - Balance disorders
(Improvement of balance and fall prevention)
Internal Medicine
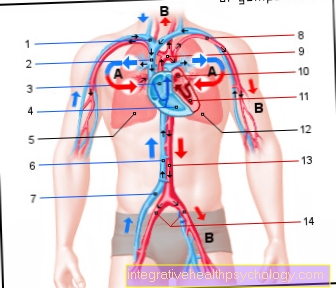
- Arterial and venous circulatory disorders (PAD)
(Improvement through increased blood flow, tension regulation of the vascular wall muscles)
You can find more about this under our topic: PAOD
Gerontological indications
-
Loss of muscle mass and performance
(Strength gain, strength building, coordination improvement, increase in muscle performance) - osteoporosis
(Increase in bone substance) - Sedentary lifestyle
(Improved mobility by increasing and building strength, improving coordination and balance) - Reduction of posture control
(Building muscle strength in the global and local Core muscles, posture improvement) - Urinary incontinence
(Improvement of Urinary and stool continence) - Balance disorders
(reduced tendency to fall by improving balance, strength and sensorimotor performance - motor control of posture and movement -)
- Incontinence
(improved bladder and rectal control)
- Pelvic floor weakness
(improved bladder and rectal control, lowering of back pain)
- Spine - pelvic instability after delivery
(Strength building and posture stability)
Contraindications to vibration training
especially in the frequency range above 15Hz!
- Pregnancies
- Acute inflammation, Rheumatoid arthritis
- Open wounds
- Inguinal hernia
- Acute migraine attacks
- Fresh implants such as Hip prosthesis or Knee prosthesis
- Fresh fractures
- Gallstones or Kidney stones
- Phlebitis, thrombosis
- epilepsy
- Tumors and metastases, bone cancer
- Pacemaker
Possible side effects of vibration training:
- Tingling in the Musculature
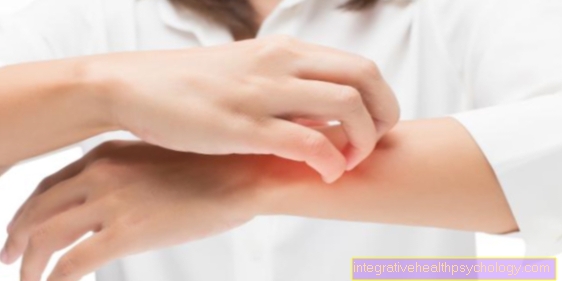
- Itching of the skin
- Pain intensification due to excessive training intensity
- Temporary Drop in blood pressure
- Short term Hypoglycaemia
Note
Possible side effects of vibration training can be prevented by slowly increasing the training intensity!