Lactate performance diagnostics
synonym
Lactate test
definition
Lactate performance diagnostics is a procedure that is primarily used when working with athletes. It is also used less frequently in everyday clinical practice.
It is used to determine performance, especially in the endurance area, for example in football.
It can also be used to check whether there has been an increase or decrease in performance over time.
The basis of the lactate performance diagnosis is the energy production of the muscle cells in an aerobic and anaerobic way and the lactate production, which gives an indication of the current mode of energy production.
Physiology of performance diagnostics

The body needs time at all times energy. He gains this to a large extent from the with sustained physical exertion Breakdown of sugars (Carbohydrates) how glucose.
The glucose is in a kind of storage form, the Glycogen, in muscle and liver in front.
As long as the body with enough oxygen is supplied, the glucose obtained from the glycogen is completely increased water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2) and energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) reduced.
One speaks of aerobic energy production.
Also in this area of energy generation arises Lactate, but significantly less than in the area of anerobic energy generation (see below).
With increasing stress, the body is no longer able to provide enough oxygen for energy metabolism at a certain point.
He now has to gain the necessary energy without oxygen.
This is also done glucose from the Glycogen degraded, but not as completely as in areobic energy production.
It arise Lactate and again Adenosine triphosphate.
In contrast to aerobic energy production, at the maximum 38 moles of ATP arise, arise at the anaerobic energy generation but only 2 moles of ATP per molecule of glucose.
The anaerobic energy generation is therefore significantly less productive. But your advantage is this Independence from oxygen.
That which occurs in larger quantities during anaerobic energy production Lactate leads to hyperacidity within a relatively short time, the so-called Acidosis, of the PH value the body is thus degraded.
Such acidification leads to an inhibition of the processes that are responsible for the breakdown of glycogen and the supply of energy slowly comes to a standstill.
The body is forced, so to speak, to stop the load for its own protection.
A distinction is made between the aerobic and anaerobic areas in energy production. The point at which the body changes from one mode to the other is known as anaerobic threshold or Lactate threshold.
The intensity of this threshold depends very much on the Training condition is very individual.
When providing a service below the anaerobic threshold, i.e. in the area of aerobic energy generation, the athlete can continue to provide this performance over a relatively long period of time, for example the marathon runner.
With a load above the anaerobic threshold, i.e. in the area of anaerobic energy generation, the body can only perform for a short time, for example during a sprint.
The anaerobic threshold has a lactate value of 4 mmol / l. However, this value is individually very variable and can only be used as a rough guide value, which is why the term `` is '' nowadays individual anaerobic threshold.
The lactate concentration at rest is usually around 1-2 mmol / l.
Procedure for lactate performance diagnostics
When working with (high-performance) athletes, the goal is to use lactate performance diagnostics as much as possible sport specific perform.
In this respect, physical strain does not always take place under standardized conditions on an ergometer or treadmill.
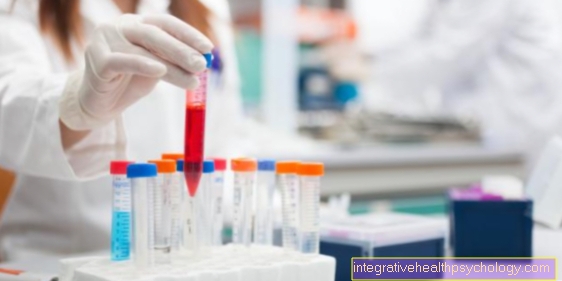
In football training, for example, you often see the footballers a little after running blood is removed from the earlobe, then the Lactate levels to be determined in the blood.
What is important, however, regardless of the type of stress, is the stress intensity gradually increased becomes.
Usually with a low stress level started and all 3-5 minutes the intensity increased.
At each stage, capillary blood is drawn, usually from the earlobe or fingertip. The earlobe is usually tested about 10 minutes before the first measurement with a blood circulation-increasing ointment (Finalgon®) rubbed in.
If the lactate test is carried out in a room provided for this purpose, a EKG derived, with which the Heart rate is taken into account.
The levels are increased until the Workload is reached.
What intensity of exercise is started with, how big the levels are and whether it is increased to full capacity, is decided individually based on the training and health status of the respective test person.
Based on the values determined for each level, a Lactate performance curve created. It usually sets the service provided (for example running speed or wattage, x-axis) with the measured lactate concentration (y-axis) in relationship.
This results in a curve whose Right shift for one Increase in performance speaks.
The point at which the lactate curve increases significantly is called individual anaerobic threshold designated.
Up to this point, if the load remains the same, there is a so-called Lactate steady state available. The formation and breakdown of lactate are maintained Libra so that there is no accumulation of lactate in the muscle.
A service in this area can therefore be provided over a longer period of time. This is why the individual anaerobic threshold is also known as Continuous output limit.
Indications
Nowadays, lactate performance diagnostics are primarily used when working with athletes, especially those in Endurance range, applied.
It provides information about the current training status and can show in the history whether a workout has become a Increase in efficiency could lead.
With the help of the lactate test, individual Training intensity ranges defined and Exercise recommendations for endurance training.
For certain questions it is advisable to use lactate performance diagnostics with a spiroergometric examination to combine, in which respiratory gases and volumes are also measured.
Such a combination is often useful, especially in everyday clinical practice far away from sports medicine.
Contraindications
Since the lactate performance diagnostics with a significant physical exertion goes hand in hand, there are some diseases for which implementation is contraindicated.
These include acute heart attack, an infection such as a lung infection (pneumonia), a strong Narrowing of the aortic valve (Aortic stenosis), one acute respiratory failure as well as a thrombosis, for example in the deep leg veins.
Termination criteria
To protect the test person, when performing the lactate test, attention should be paid to certain signs that indicate that the body overused is.
Which includes:
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- sign of Reduced blood flow (Ischemia) of the heart in EKG
- a Chest tightness (Angina pectoris)
- dizziness and Cold perspiration
- an insufficient increase or a sudden sharp decrease in the Blood pressure.













.jpg)