Calf lifter
introduction
Training the calf muscles (M. gastrocnemius) is not trained in isolation in conventional fitness and health training. Exercising on the leg press puts enough strain on the twin calf muscles so that this isolated calf lifting exercise appears to be ineffective and time-consuming. In bodybuilding and in specific sports, however, targeted training of this muscle group is necessary in order to optimize performance. In many running and jumping disciplines in athletics, optimally trained calf muscles are a prerequisite for maximum performance. Simply put, the calf muscles work when you stand on tiptoe. The antagonist that causes the ankle to stretch is called the anterior tibial muscle (M. tibialis anterior)
Trained muscles
- Calf twin (M. gastrocnemius)
- Longer fibula muscle (M. peroneus longus)
- Fibula short muscle (M. peroneus brevis)
- Clod muscle (Soleus muscle)
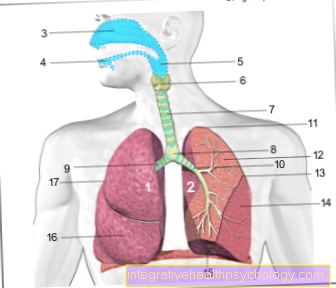
Figure calf muscles

Gastrocnemius muscle
Two-headed calf muscle - 1st + 2nd
(Twin calf muscle)
- External calf muscle -
Gastrocnemius muscle,
Caput laterale - Internal calf muscle -
Gastrocnemius muscle,
Caput mediale - Shin community -
Corpus tibiae - Heel bone - Calcaneus
- Calf community -
Corpus fibulae - Achilles tendon -
Tendo calcaneus - Femoral shaft -
Corpus femoris - External articular knot -
Lateral condyle - Inner joint gnar -
Medial condyle - Kneecap - patella
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Description calf lifter
The athlete sits on the device, the thighs are fixed below the lifting surface. The feet are on the support surface. The back is straight, the spine is not strained with this type of calf lifter. The athlete lifts his knees by stretching the ankle, thereby contracting the calf muscle. It is advisable not to remain seated on the device between the individual sets of this exercise, as otherwise it will be very difficult to loosen the muscles. Some devices allow a longer work path, in which the heel can be brought below the contact surface of the feet and the calf muscles are stretched. The weight and repetition of the calf lifter depend on the training goal.
Training without equipment
If you prefer to do your training without equipment, you can fix a barbell in the neck and slowly stand on your toes. Tip: Even without weight, this exercise can be very strenuous.
Modifications
The calf lifter does not necessarily have to be performed in a sitting position. Numerous devices enable calf raises with a straight posture. The calf lifter is usually used in this form, especially in jumping strength training, as the upper parts of the muscles can be trained more specifically. With this form of training, however, it should be noted that problems in the spine area can arise. Standing calf lifter is generally not recommended for back problems.