Resuscitation in the infant / child
Synonyms in the broader sense
Resuscitation, Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
English: resuscitation
Resuscitation in the infant / child

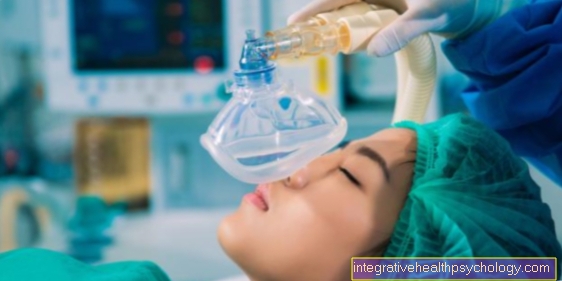
The resuscitation in children and infants is quite different from that in adults. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that an infant and children have a significantly higher need for oxygen. On the other hand, in children, the cause of the Cardiac arrest just very rarely in the heart.
Therefore, one starts the resuscitation of the infant / children with 5 ventilations. Only when there are no signs of life can you feel for your pulse. Usually the child's condition improves significantly after ventilation. The pulse is at the Arteriabrachialis, the humerus artery, palpated. With infants and children, the pressure massage is also performed much more gently. Depending on the age and size of the child, the chest is depressed accordingly. With infants, for example, only 2 fingers are used for chest compressions and the chest is only pressed in about 2 cm. Likewise, you must not overstretch the child's head, as this obstructs the airways. This is due to the anatomy of children. The head is brought into the so-called sniffing position, the head is slightly elevated (1-2cm). The drug dose is also adjusted based on body weight. Due to the oxygen demand mentioned above, the rhythm of resuscitation is also changed. Children are pressed 15 times and ventilated twice. When defibrillating, the Joule number is adjusted according to the body weight.
more information on this topic
- resuscitation
- Ventilation
- Forms of cardiac arrest
- Cardiovascular arrest
further interesting information from this area:
- Heart attack
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Racing heart
- coronary heart disease
- Amiodarone
You can find an overview of all published topics in this area at: Diseases of the heart