angina
introduction
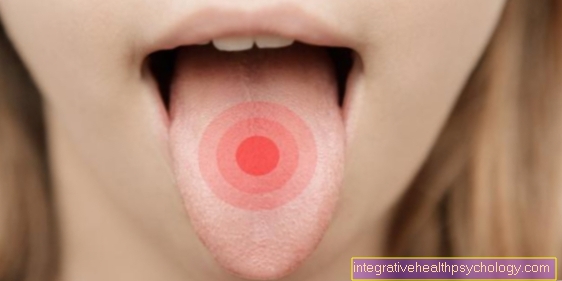
A tonsillitis is usually a description for the acute form of tonsillitis, which is also called acute tonsillitis or acute tonsillar angina. In this disease, the tonsils (tonsils) are inflamed. These tonsils are two elevations at the transition from the mouth to the throat and are part of the body's immune system.
Acute tonsillitis

School-age children in particular, but also toddlers and adults, develop acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis). The transmission takes place here via droplet infection, which can be highly contagious, especially before treatment with antibiotics.
Acute tonsillitis occurs most often in the winter months and in spring.
In addition to the acute form of tonsillitis, there is also the less common chronic form of tonsillitis. Here, the tonsils have been inflamed for over 3 months.
This chronic disease can occur after one or more tonsillitis and is characterized by an obstruction of the depressions (crypts) of the tonsil tissue. Often the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis are smaller than in acute tonsillitis.
A so-called lateral cord angina, in which the lymphatic tissue in the throat area is affected, is also possible.
Read more on the topic: Acute tonsillar angina
causes
The acute tonsillitis is transmitted over Droplet infection, so through saliva or at Sneeze. Most often the causative agents of tonsillitis are tonsillitis Viruses, but there are also those bacterial Tonsillitis, mainly due to beta-hemolytic streptococci of group A.
In addition, there are other bacteria (e.g. pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae) or also Mushrooms considering causing the acute tonsillitis.
Most of the time you are just already with weakened Immune system prone to tonsillitis.
Also as an accompanying symptom to other diseases, such as for Scarlet fever, inflammation of the tonsils can occur.
Other diseases that can be associated with tonsillitis include:
- Pfeiffer's glandular fever (Eppstein-Barr virus)
- Herpangina (Coxackie A virus)
- Thrushangina (fungal infection caused by Candida albicans)
- specific angina in syphilis (syphilis)
- Angina as part of a tuberculosis
- Angina Plaut-Vincent
- Angina agranulocytotica (lack of granulocytes in the bone marrow)
- Angina as part of a diphtheria
- Angina as part of a leukemia
Symptoms

The typical symptoms of tonsil disease are sudden onset difficulties swallowing, high fever and decreased general well-being.
The tonsils are inflammatory swollen, strong reddened and have a whitish, greyish or yellowish color Topping. This covering can look like stripes, punctiform or continuous.
Most of them are Lymph nodes in the corner of the jaw and the lymph nodes on the neck painful swollen (see also: Lymph node swelling in the neck), the patient's speech lumpy / slurred.
On top of that comes stronger Bad breath as another typical symptom.
Diagnosis
By looking closely at the tonsils, the doctor can identify the tonsil surface and the coating and thus roughly assess the pathogen causing the disease.
Based on the appearance and color, as well as the size and spread of the coating on the tonsils, it can be narrowed down which pathogen is most likely:
- Streptococcal angina: white-yellowish, punctiform coating, then confluent to form a dense coating
- Angina Plaut-Vincenti: unilateral small ulcer
- Angina agranulocytotica: dirty, dead melts
- Lues / syphilis: small spots, possibly slightly raised on the tonsils and oral mucosa
- Tuberculosis: small ulcers with a thickened edge
- Scarlet angina: dark red almonds
- Diphtheria: whitish-greyish coherent coating, when the coating is detached, the almond underneath bleeds
- Herpangina: small ulcers on the palatal arches
- Pfeiffer's glandular fever: confluent, gray-whitish deposits
In practice it is irrelevant whether it is a so-called “purulent angina”, since pus is simply dead, white blood cells that have arisen from a bacterial infection. However, the white-yellowish coating in the event of a virus infection can also be understood as a purulent inflammation, so that the disease is not differentiated into purulent and not purulent, but bacterial and viral.
To determine this precisely, a throat swab is examined for bacteria. Laboratory results can also be helpful in distinguishing between bacterial and viral tonsillitis.
A bacterial infection leads to an increase in white blood cells (granulocytes) and an increase in the inflammation values (especially an increase in the CRP value) in the blood count.
If an infection with group A streptococci is suspected, the doctor can use the throat swab to perform a rapid test or a bacterial culture in order to arrive at a reliable diagnosis.
Read more on the topic: Pus on tonsils
therapy
The most difficult thing about the therapy of acute tonsillitis is that much liquid should be drunk, however extreme Pain when swallowing consist. Children in particular suffer from you so quickly Dehydration.
Bed rest, lozenges, and mouthwashes are recommended as general measures.
The medication used in acute tonsillitis with fever pain reliever and anti-inflammatory Medicines such as acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), Ibuprofen and Paracetamol in question. Aspirin should be avoided, especially in children and asthmatics.
Is there a Streptococcal angina before, so should with Antibiotics treated so that the emergence of a rheumatic fever or one chronic inflammation of the kidneys is prevented. Antibiotics are recommended here penicillin and cephalosporins.
When taking antibiotics, it is always important to take the medication for as long as the doctor has ordered it and not to stop taking the antibiotic as soon as the pain and fever have improved, as this leads to a recurrence of tonsillitis Formation of resistance can occur in the bacteria, which makes renewed treatment much more difficult.
Common side effects of antibiotics are Gastrointestinal complaints (for example: diarrhea and nausea). Vaginal yeast infections can occur in women during and after taking antibiotics.
Home remedies for tonsillar angina
There are some home remedies that are recommended for angina:
- Envelopes with cottage cheese
- Envelopes with mixed healing earth
- Fresh ginger tea with honey and lemon
- Gargle with sage tea, chamomile tea or salt water (caution, gag reflex!)
- Oil pulling
surgery
If tonsillitis is very common, surgical removal (Tonsillectomy) of the tonsils should be considered.
The prerequisite for the operation is at least one four times a year Occurring tonsillitis with fever over 38,3 Degree and enlarged mandibular angle lymph nodes. In addition, the previous tonsillitis must have been confirmed by a doctor and well treated with antibiotics.
The main risks involved in surgery on the tonsils are Secondary bleedingthat can occur up to three weeks after surgery.
Complications
Peritonsillar abscess
A possible complication with bacterial angina is one Accumulation of pus in the tissue around the tonsils, the so-called Peritonsillar abscess. This abscess then has to be split open and removed, whereby the tonsils are usually also removed during the operation. Then is a Antibiotic therapy against streptococci, staphylococci or Haemophilus influenzae bacteria.
Blood poisoning
The bacteria of tonsillitis can cause blood poisoning (sepsis).
Autoimmune reaction
Beta-hemolytic streptococci can cause acute disease Kidney disease (acute Glomerulonephritis) or the rheumatic fever come. This is caused by an autoimmune reaction antibodywhich are falsely active not only against the strep, but also against the endogenous Adjust tissue that is actually healthy.
Risk of infection with tonsillitis
The tonsillitis is due to its transmission through droplets of saliva very contagious, since appropriate amounts can be distributed even when speaking normally. Sick people should go to school, kindergarten, public transport and open-plan offices stay away, as larger crowds in particular encourage infection.
The duration of infection depends on the pathogen. Streptococcal angina, for example, is no longer contagious after just one day of antibiotic treatment, while viral tonsillitis can be contagious for much longer.
Freedom from fever and symptoms serve as a rough guide.
Chronic tonsillitis
The chronic form of tonsillitis (Tonsillitis) arises from a complete or even partial Clasp the depressions in the almond tissue (crypts). The tonsils are in contrast to acute tonsillitis scaled down.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
In addition to permanent, unpleasant Bad breath it sometimes occurs in chronic tonsillitis Foci formation. This means that it also appears as a result of existing foci of inflammation in the tonsils other Organs or in the Joints inflammation can occur. However, this theory is currently under discussion.
Therapy of chronic tonsillitis
In the chronic form of tonsillitis, the only remaining therapeutic option is operational distance the tonsils with subsequent more antibiotic treatment.










.jpg)