Rib pain
General
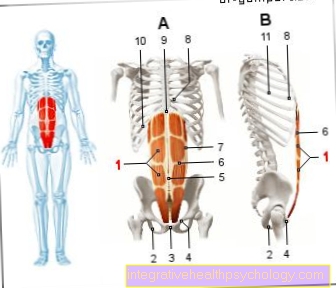
Humans have a total of 12 pairs of ribs, of which the top seven pairs are each directly connected to the sternum via a costal cartilage. On the spine, the ribs are connected to the vertebral bodies via the costal joints. Nerves and vessels run along the inside of the lower edge of the ribs.
Find out more about the topic here: Pinched nerve on the ribs
Rib pain can come either from the ribs or from their cartilaginous part. The cause of rib pain can therefore come from the joints and the ligaments there, or it can be triggered by the nerves that run very close to the ribs.
However, since pain is usually very uncharacteristic, inflammatory or other diseases can also be considered as causes in addition to the orthopedic causes. Other symptoms are indications of non-orthopedic causes of rib pain.
Are you interested in this topic? Read more about this at: Pain between the ribs

Causes of Rib Pain
Rib pain after a broken rib
The most common disease and cause of rib pain is a broken rib (Rib fracture).
The broken rib is a common injury in the chest area. One or more rib bones are injured. A series of ribs fractures is when more than three ribs are broken.
In most cases, a rib fracture occurs as a result of a fall with direct impact.
Typical symptoms are pain over the affected rib, which gets worse when you inhale and exhale deeply, cough and move. In addition to rib pain, skin emphysema is often seen over the fracture and occasionally a crunch can be heard when pressure is applied to the fracture.
Bruised ribs can also have similar symptoms (Rib contusion) which in most cases was more likely to be caused by blunt trauma.
Simple rib fractures are usually treated conservatively and heal without complications.
Read more on the topic: Pain when the rib breaks
Rib pain after a diaphragmatic hernia
The diaphragm is a respiratory muscle and anatomically separates the chest (thorax) from the abdomen. In the case of a diaphragmatic hernia (Diaphragmatic hernia) there is an enlarged opening in the diaphragm through which - depending on the location of the hernia - abdominal organs push into the chest.
Most often, the diaphragmatic hernia is found where the esophagus (Esophagus) leads into the abdomen or stomach. So there is naturally an opening there. If this expands, the stomach, for example, if it is very full, can slide through the enlarged opening into the chest.
Since the stomach lies below the left costal arch, pain can be felt in this area in the case of a diaphragmatic hernia if the stomach is trapped in the gap.
Depending on the size of the break and the proportion of abdominal organs in the chest, the lungs can be displaced, so that, in addition to pressure and rib pain, symptoms such as shortness of breath can occur.
An operation on the diaphragmatic hernia is only carried out if it causes considerable discomfort.
You can read more information on this topic here: Diaphragmatic hernia
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Rib pain during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the abdominal muscles that attach to the ribs are stretched further and further due to the increasing space requirements of the unborn child. This stretch exerts a permanent, increasing pull on the ribs, especially in the area of the costal arch.
The pain that arises in this way usually occurs suddenly and repeatedly throughout the day.
From around the eighth month of pregnancy, the top pole of the uterus is often in the area of the costal arch and thus exerts pressure on the chest, which can cause pain in the ribs.
Are you interested in this topic? Read more about this at: Pain in the ribs during pregnancy
Rib pain when coughing
When coughing, air is expelled from the lungs like an explosion, for example to remove foreign bodies or mucus from the airways. During this process, the muscles of the chest wall are used to "express" the chest and thus the lungs. Since a cough is the fastest movement a person can make, many different muscle groups in the chest are involved.
The muscle groups involved have to perform a great deal of strength in order to achieve the necessary speed of tension. Patients with a chronic or prolonged cough, which can occur in the context of bronchitis, for example, often have pain in the chest because the muscles of the chest wall are overloaded by the constant coughing.
This muscular pain can easily be mistaken for rib pain because the muscle fibers used for coughing run along the chest wall between the ribs. Other muscle groups such as the chest muscles or the back muscles are also required for coughing and sometimes start on the ribs.
It is difficult to clearly differentiate between rib pain and muscle pain at the point where the muscle attaches to the rib. In rarer cases, in patients with osteoporosis or in cancer patients with metastases in the ribs, a strong cough can also lead to a broken rib.
Read more on this topic:
- to cough
- Pain in the costal arch from coughing
- Pneumonia pain
Metastases as a possible cause of rib pain
There are some malignant tumors that can cause bone metases when cancer cells spread. Examples are breast cancer, prostate cancer, bronchial carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma.
In addition to other bones, the tumor cells can also affect the ribs and lead to changes in the bone structure there.
Bone metastases in the ribs cause various symptoms, particularly pain. Those affected often describe the rib pain as deeply drilling. The pain is typically permanent and does not improve with rest. This leads to a significant decrease in the quality of life.
Furthermore, bone metastases can cause pathological fractures, i.e. the formation of bone fractures without force on the bones. Metastases in the ribs often cause great suffering for the patient, so that adequate pain therapy is urgently indicated to alleviate the symptoms as much as possible.
Inflammatory causes
Shingles
Shingles (Herpes zoster) is caused by the reactivation of varicella viruses. These viruses are responsible for chickenpox in childhood and can linger in the nerves of the spinal cord after infection. If the immune system is weakened (e.g. in old age, through cancer, HIV etc.), these viruses can be reactivated and cause inflammation of the nerve endings.
This manifests itself in severe pain and usually only occurs on one half of the body. The pain is accompanied by spread skin rashes and blisters, which often appear in the area from the 5th to 7th ribs.
As a result, the pain of shingles is often misperceived as pain in the ribs. Therapy should definitely be given with ibuprofen for the pain and with extensive shingles with an antiviral drug such as acyclovir.
You can read more information on this topic here: Shingles
pleurisy
The pleura (Parietal pleura) and the lung membrane (Visceral pleura) are thin skins and are separated by a small, liquid-filled gap. Everything together is called the pleura. The pleura lines the inside of the rib cage, the pleura is around the outside of the lungs.
These skins are primarily used for breathing and ensure that the skins slide against each other without problems, for example when the chest and lungs expand during inhalation. With pleurisy (pleurisy) these skins become inflamed.
Pleurisy usually occurs as a result of other diseases such as viral or bacterial pneumonia, bronchitis, tuberculosis or lung cancer.
Since the inflamed pleura lies against the chest, symptoms such as fever, cough and fatigue can also occur in the ribs, which can be felt over the entire chest. The pain in the ribs is usually aggravated during breathing. Treatment for pleurisy depends on the cause.
You can read more information on this topic here: pleurisy
ankylosing spondylitis
In patients with ankylosing spondylitis, the rib joints ossify as part of their disease. This can cause breathing problems and rib pain.
For more detailed information, see: Bechterew's disease - causes, symptoms and therapy
Illnesses as further causes
Tietze syndrome
In rare cases, rib pain occurs due to an inflammation of the rib-sternum joint (Sternocostal joint) the 2nd-4th Rib of unknown cause.
The disease manifests itself as pain in the joints. This disorder is also called Tietze syndrome or Chondroosteopathia costalis designated. A regional circulatory disorder or mechanical irritation factors are suspected.
Treatment is with painkillers, the prognosis is good: the swellings heal on their own over a period of several days to months.
Read more on this topic at: Tietze syndrome
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
In rare cases a cervical rib can be fully developed. This can cause nerves and blood vessels in the arm to become trapped when the arm is raised. The consequences are sensory disturbances, circulatory disorders, possibly also paralysis of the arm when moving overhead. This clinical picture is called Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS).
Read more on this topic at: Thoracic outlet syndrome
Can that also be an indication of lung cancer?
Rib pain in isolation is not a symptom of lung cancer and should not cause panic.
Symptoms such as coughing, breathing noises, chest pain and difficulty breathing are significant indications of a disease of the respiratory system.
Regardless, rib pain can be a symptom of metastatic lung cancer (malignant growth in the lungs) be. Skeletal metastases can settle in the ribs and cause rib pain and pathological rib fractures.
With the next article, you will be well educated about the signs of lung cancer. Read more about this under: How do you recognize lung cancer?
Rib pain by localization
Front
Pain in the upper pairs of ribs one to four in the area of their attachment point on the sternum can be accompanied by swelling and is then referred to as Tietze syndrome. The cause of this rare form of precisely localized rib pain in the front of the sternum (sternum) is an inflammation of one or more rib-sternum joints (Sternocostal joints).
Sudden pain in the front ribs after an accident or fall may indicate a fracture of the sternum or rib or a bruised rib.
Pregnancy can also cause rib pain.
Right vs. Left
Rib pain on the right or left side of the chest (thorax) can be triggered by a torn muscle fiber between the ribs in a chronic cough, which permanently stresses and overloads the muscles of the chest wall.
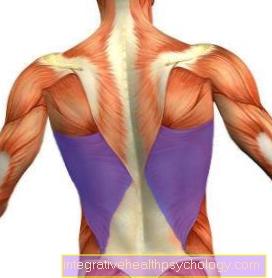
Poor posture or incorrect loading during sport can also trigger muscle pain in the ribs. The right and left sides of the chest can be affected Latissimus dorsi muscle (widest back muscle), which is often to be increased in a special form through strength training, or the Serratus anterior muscle (anterior sawtooth muscle).
After an accident with a collision on the now painful side, rib pain on one side of the chest should also include bruised ribs or a broken rib. A broken rib should be ruled out by an X-ray if it is suspected, and a bruised rib is treated by taking painkillers.
This topic could also be of interest to you: Right Rib Pain - What Do I Have?
Back
In many cases, the cause of rib pain at the back of the back is a blockage of the costal vertebrae. The costal vertebral joints can be blocked by incorrect loading or incorrect posture of the chest and their mobility restricted.
Triggers for a rib blockage can be carrying a heavy bag on one side, incorrect posture when working at a desk, tense back or chest muscles, rotating the upper body too quickly during exercise or blocking a thoracic vertebra.
Absence of the spine its own curvatures (Lordosis and kyphosis) or if they are too flat, this can also lead to a blockage of the ribs or thoracic vertebrae.
The pain with a rib block is mainly in the area of the transition to the spine, but can also radiate into the sides of the chest or even stretch forward to the sternum. Other symptoms may include pain in the cervical spine, shoulder, or arm, depending on the blocked rib.
The pain of a rib block is always dependent on the breath, as the ribs in the two costal vertebrae are rotated with each breath to allow the chest and lungs to expand. Coughing, sneezing, moving the arm on the affected side, or putting pressure on the chest may increase the pain of a rib block.
The treatment of a rib block consists of so-called "straightening" and subsequent movement exercises that are intended to promote mobility and strengthen the muscles. At times it can be useful to take painkillers.
It is important to know that the symptoms of a rib block can be similar to the blockage of a thoracic vertebra, which is why a detailed physical examination should have taken place before the straightening.
Please also read our topic: This is the correct way to resolve a rib block
Under the chest
Pain just below the chest can be rib pain, which in turn can be triggered by various causes (Rib block, vertebral block, muscle tension, rib bruise, etc.). Chest pain can also be caused by inflammation of the mammary gland (mastitis) caused.
Pain that is not felt under the chest but below the chest is often caused by a disease in the abdomen. The stomach contents may flow back into the esophagus (Esophagus), which can be felt as heartburn in the area between the costal arches.
Read more on this topic at: Pain under the chest
Situations where the rib pain occurs
While breathing
In addition to direct injuries to the ribs, rib pain when breathing can also result from irritation or injury to muscles and nerves that are involved in raising and lowering the chest. Therefore, it is often difficult for the layperson to differentiate the origin of the pain.
In addition to rib pain, there are also coughs (with or without expectoration), Sore throat, tiredness and fever, bronchitis or pneumonia are possible causes.
Further information on this topic can be found at: Pain under the ribs when breathing
When moving
If rib pain occurs when moving, there can be various causes. On the one hand, a wrong movement that leads to a muscle strain is a possible reason. Ribs and thoracic vertebrae can also jam due to incorrect lifting, for example, which can manifest itself in rib pain.
On the other hand, injuries such as bruises or breaks on the ribs can be responsible for rib pain during movement.
If rib pain occurs repeatedly when moving, especially behind the sternum and on the left side, which disappears again at rest, a doctor should be consulted. This could be a circulatory disorder of the coronary arteries (Coronary heart disease) that must be dealt with.
After the sport
Pain in the ribs after exercise is mostly caused by muscular tension. Either the muscles between the ribs or the abdominal muscles can cause rib pain.
Overloading the muscles during sport due to strenuous training and a lack of breathing technique can lead to pain that persists after sport. The pain is particularly felt when inhaling, as the tense muscles do not allow the chest to widen.
Therefore, one should make sure to adapt the training to the respective fitness level so that the muscles do not cramp during the sport. It is also possible that insufficient stretching after exercise leads to tension and sore muscles.
In weight training, it can happen that an intercostal nerve is irritated or pinched due to incorrect movement or excessive stress. One then speaks of an intercostal neuralgia, in which there is pain in the ribs that persist after exercise and possibly for several days to weeks afterwards.
More symptoms
Rib pain is generally expressed in chest pain. This pain can either be permanent (chronic) or suddenly (acute) occur.
Recurrent pain that lasts longer than six months is referred to as chronic rib pain. They can also vary in intensity.
Rib pain that comes directly from the ribs is usually caused by a bruise or a break. This means that the pain is easy to localize and can usually be felt at a specific point.
Rib bruises or fractures are particularly painful when inhaling deeply or coughing or when external pressure is exerted on the painful area. If surrounding structures such as muscles or nerves are affected, a sharp, localized pain can usually be identified here as well.
If the pain in the ribs originates from internal organs such as the heart, lungs or upper abdominal organs, the pain is usually dull and diffuse, so it cannot be precisely localized.
In general, rib pain is often accompanied by a feeling of oppression or tightness, which can be felt especially when inhaling.
But even with a severe cold, constant coughing can cause sore muscles in the muscles in the chest area. This can also cause pain during coughing.
More about this on our website: Rib pain when coughing
Rib pain with back pain
Rib pain can be accompanied by back pain. The rib pain can be triggered, among other things, by back problems, for example if a rib-vertebral joint is dislocated.
Other possible causes in the area of the back are acute diseases such as a herniated disc, malformations such as scoliosis, and muscular causes.
Pulled muscles in the back can cause both back and rib pain. Muscle strain is a common clinical picture that typically arises as part of excessive exercise.
For rib and back pain, a visit to the orthopedic surgeon is recommended to find the right diagnosis.
Shortness of breath with rib pain
Occasionally, rib pain can go along with shortness of breath.
One possible cause for the occurrence of both complaints is the so-called Tietze syndrome - a chondropathy of the costal cartilage at the base of the breastbone.
With this disease of unknown cause, those affected suffer from severe pressure painful swelling in the area of the anterior chest. The pain in the ribs comes suddenly, can spread to the arms and cause shortness of breath.
Another possible cause of rib pain and shortness of breath is pleurisy. Severe pleurisy causes excessive build-up of fluid in the chest, which can even cause shortness of breath. Shortness of breath is a serious symptom that definitely needs clarification.
You can read more about this topic in the next article: Causes of shortness of breath
Rib pain with tension
Tension typically occurs when the muscles are overloaded.
Many different muscle groups have their insertion in whole or in part on the ribs. Mention should be made of the chest and back muscles, but the abdominal muscles are also attached to the ribs.
These muscles can tense up and shorten as a result of incorrect loading or an incorrect posture, which exerts a permanent pull on the attachment point on the rib. This pull can cause pain in the area of the affected rib, but it can also radiate into the course of the muscle and therefore make the exact localization more difficult.
Other possible causes are blockages in the spine or in the rib joints, excessive strain on the muscles during exercise and poor posture.
Tension in the rib and back muscles can cause severe pain in the ribs, which usually get worse when you breathe in and out, cough and strain.
Are you more interested in this topic? Read more about this at: Tension
Stomach pain as a possible accompanying symptom
Left rib pain, in particular, can be accompanied by stomach pain.
The symptoms can be an indication of a stomach disease, pancreatic disease or a heart attack, as a heart attack is not always associated with the typical symptoms. Especially in women, a heart problem can manifest itself with pain in the upper abdomen.
If stomach pain and rib pain occur together, one should see a doctor to find and treat the cause.
For more information on this topic, see: Stomach Pain - Symptoms, Causes and Therapy
Diagnosis of rib pain
In order to find out where the rib pain is coming from, it is necessary to rule out various causes. External palpation of the ribs can lead away if the rib is broken. An inspection of the body can also provide information if the rib pain is triggered, for example, by a bad posture or tension.
On the one hand, X-rays can show a broken rib, on the other hand, pneumonia, for example, which can cause rib pain especially when coughing and inhaling, can be seen in the X-ray image.
Most important, however, is a precise anamnesis from which many causes can be ruled out. As detailed below, information on the localization of the pain and any accompanying symptoms can be used to narrow down the causes of the pain.
Treatment of rib pain
Depending on which disease is underlying the pain in the ribs, it must be treated accordingly. If there is a broken rib, the focus is on pain therapy, if it is a complicated fracture, surgery may be necessary.
Intercostal neuralgia, tension and strains are also treated with pain relievers such as NSAIDs (Ibuprofen or Diclofenac) treated. In addition, a gentle strengthening of the muscles and physiotherapy should take place.
If the pain is caused by bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are usually prescribed.
Taping
With the taping a bandage can be attached to painful parts of the body, which supports the healing and symptoms of orthopedic injuries.
Taping on the torso and ribs can be used for muscle tension, but also for bruised ribs and is intended to relieve rib pain by relieving the affected rib or muscles through tensile forces. To do this, the tape is affixed along the ribs or muscles.
The tape can be attached by the orthopedic surgeon at home independently or, better, by someone else, following appropriate instructions.
If you have any further interest in this topic, then read our next article below: Tape bandage
Duration of rib pain
The duration of the rib pain depends on the cause. If the rib pain is a symptom of bronchitis or pneumonia, it will be gone about one to two weeks after it has healed.
If the rib is broken, the pain can take up to six weeks for the fracture to heal.
Intercostal neuralgia, in which a nerve is irritated or inflamed, can still be noticeable after months and cause pain, especially when inhaling, even if the nerve is no longer pinched.
Which doctor treats rib pain?
Basically, rib pain can have various causes. The family doctor is suitable as the first doctor contact to have a detailed discussion about the complaints and to do a physical examination.
Then, depending on the suspected diagnosis, a visit to the orthopedic surgeon may be indicated, especially if there are problems with the muscles and the skeletal system.
Anatomical excursus for those particularly interested

I-XII ribs 1-12 -
Costa I-XII
(I-VII) True ribs -
Costae verae
(VIII-X) false ribs -
Costae spuriae
(XI-XII) rudimentary ribs -
Cost. fluctuantes
- Rib head - Caput costae
- Rib neck - Collun costae
- Rib humps -
Tuberculum costae - Rib body - Corpus costae
- Rib head joint -
Articulatio capitis costae - Sternum - sternum
- Vertebral bodies -
Corpus vertebrae - Costal cartilage -
Cartilago costalis - Rib-sternum joint -
(Sternocostal joint) - Rib-vertebral body joint -
(= Point 5.)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations