Abdominal pain before your period
introduction
Pre-period abdominal pain can occur throughout the second half of your cycle and is counted as premenstrual syndrome. The cause of the pain is not fully understood, but hormones are believed to play a role.
The pain usually subsides with the start of your period and disappears completely by the next ovulation. In addition to abdominal pain, pain in other parts of the body and a variety of other symptoms can occur during this time.

Causes of abdominal pain
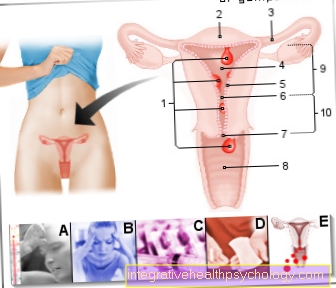
Abdominal pain before your period typically only occurs in the second half of your cycle, i.e. after ovulation. The exact causes have not yet been fully clarified, but there are explanations that start from hormonal causes.
In the second half of the cycle, the hormone progesterone dominates. Progesterone effects among other things Fluid displacements in the body. It also explains why the chest and feet swell during this phase. These changes in fluid balance can also potentially be the cause of abdominal pain.
Another explanation suggests that interactions between progesterone and other messenger substances in the brain could be the reason for the pain. Such interactions are not perceived by everyone, which explains why not every woman suffers from pain and, more specifically, abdominal pain before the period.
Finally, it is also suspected that women with abdominal pain before their period may react more sensitively to degradation products of progesterone and that this can trigger the pain.
Other factors that can lead to abdominal pain and other symptoms of PMS are, for example, an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), smoking or an unbalanced diet. But psychological factors such as stress can also be a cause.
Abdominal pain despite the pill
The pill is regularly used as a therapeutic measure against PMS in order to better regulate the hormonal balance during the cycle. In the period after starting the pill, abdominal pain and other pain can still occur, as the body first has to adjust to the changed hormones. After that, the pain should usually get better.
However, there are also pills that make the pain worse without any relief after a while. The exact cause behind this phenomenon has not yet been sufficiently clarified.
Read also: Abdominal pain from the pill
Concomitant symptoms
In addition to abdominal pain, premenstrual syndrome includes a number of other both physical and psychological symptoms:
- The progesterone in the second half of the cycle leads to water retention in various parts of the body. This can cause tenderness in the chest lead, as well as edema in the Legs and Feet.
- Muscle, joint or headaches are also possible.
- Neurological accompanying symptoms are, for example, migraines or an increased sensitivity to external stimuli.
- In addition to abdominal pain, other symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract occur, such as diarrhea, nausea, cravings, but also loss of appetite.
- However, PMS also encompasses a number of psychiatric symptoms. Mood swings, particularly depressive moods, are typical. In this context can also Listlessness, fatigue and Symptoms of exhaustion occur.
All of these symptoms can occur individually or in combination, so that PMS can be a severe burden.
Read more on the topic: Premenstrual syndrome despite taking the pill
Nausea and periods
Hormone fluctuations and muscle contractions in the uterus can lead to pain. In some women, the movements of the uterus also affect the gastrointestinal tract. It can Nausea, vomiting and also diarrhea occur. The nausea is not limited to the period before your period. It can also occur during menstruation, when the uterus contracts to shed the excess lining.
Nausea can also occur as part of premenstrual syndrome. Find out more about this topic at: Premenstrual Syndrome and Nausea
Back pain and periods
It has not yet been fully understood why back pain can occur before your period. But back pain belongs to the symptom complex, which is called premenstrual syndrome. If the back pain occurs at regular intervals, which can be explained by the cycle, gynecological diseases such as endometriosis or fibroids should also be considered by the gynecologist in the diagnostic work-up. Both of these diseases show cycle-dependent symptoms, which reach their maximum especially shortly before the period.
Diagnosis of abdominal pain
First of all, the chronological course of the pain is discussed in a consultation with a doctor and is related to the cycle. For this it can be helpful to keep a symptom diary over a period of a few weeks. There must also be other causes, such as a Hypothyroidism or a Irritable bowel syndrome be excluded. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical symptoms, without the need for diagnostic equipment.
Can that also be a sign of pregnancy?
Abdominal pain is not one of the uncertain signs of pregnancy. Nausea and vomiting are more typical. As a rule, implantation cannot be felt either. Abdominal pain does not appear until later in pregnancy, when the uterus is growing and the uterine ligaments are under tension.
You might also be interested in: Signs of pregnancy
The stomach ache is then called pulling or stabbing felt. A pregnancy test should always be carried out to determine whether or not you are pregnant.
In contrast to a regular pregnancy, an ectopic pregnancy can cause severe bulging pain. These clearly exceed the intensity of the pain caused by the cycle. In addition, with an ectopic pregnancy, there would be no regular menstruation, but rather irregular spotting.
Find out more about the topic here: Ectopic pregnancy
Treatment of abdominal pain
First of all, avoid substances that are known to worsen abdominal pain, but also all other symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. These include alcohol, caffeine and also nicotinecontained in cigarettes.
If this does not relieve the abdominal pain, an oral contraceptive can be used ("the pill") used to regulate hormone levels. At first, the symptoms can get worse because the body first has to adjust to the hormones. After a few weeks, however, there should be improvement.
Learn more about the topic on the main page: The pill
If the abdominal pain cannot be controlled by the pill or if hormones cannot be taken for other reasons, pain killers can also be used. The pain medication should be discussed with the gynecologist, as physical addictions can quickly arise.
An alternative to the classic painkillers is an antidepressant. There is one at a dose that is only pain relief and has no effect on mood. Although this may seem counterintuitive at first, antidepressants are now an important and widely used drug in pain management.
Duration of abdominal pain
The abdominal pain and the accompanying symptoms begin in the second half of the cycle after ovulation. They can increase over a period of two weeks until menstruation. When your period begins, the pain should subside again and should be gone after the period at the latest.
Recommendations from our editorial team
- Pain in the abdomen
- Period pain - what to do?
- Pain during menstruation
- Abdominal pain when ovulating
- The middle pain