These are the typical symptoms of vocal cord inflammation
introduction
The inflammation of the vocal cords is due to different factors and therefore manifests itself through different symptoms. A distinction is made between acute and chronic vocal cord inflammation. The chronic form is defined if the symptoms persist for more than three weeks.
While coughing, swallowing difficulties and a sore throat are in the foreground in acute vocal cord inflammation, chronic inflammation is more likely to be expressed by a dry throat, a foreign body sensation and an obsession with throat clearing.

These are the typical symptoms of vocal cord inflammation
Symptoms of acute vocal cord inflammation:
- Sore throat
- Larynx pain
- Scratchy throat
- Throat irritation and / or painful cough
- difficulties swallowing
- hoarseness
- rough, scratchy voice
- no voice
- mucus
- salivation
Symptoms of chronic vocal cord inflammation:
- Persistent hoarseness for more than three weeks
- Nodules on the vocal cords
- Coughing force
- Less sore throat than the acute form
- Dry throat
- Foreign body sensation in the throat
The hoarseness
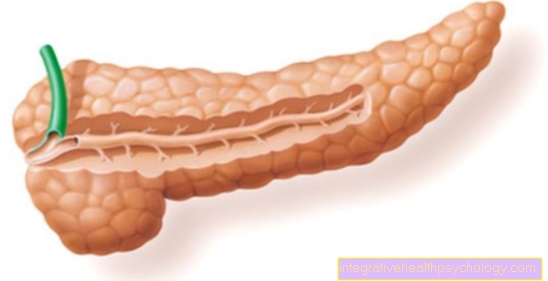
The vocal cords are two very fine muscle layers that sit in the larynx and are used to train the voice. Usually they can vibrate freely. When the vocal cords become inflamed, their structure changes, which limits their ability to vibrate. Otherwise normal tones suddenly sound rougher and scratchy.
Depending on the severity of the inflammation, the ability of the vocal cords to vibrate can be so impaired that affected people can no longer hear any sound. You can often only whisper for a few days. Persistent overstimulation of the vocal cords can lead to chronic changes, resulting in chronic hoarseness. If it is overused for too long, small nodules can also develop on the vocal cords. These prevent the vocal cords from vibrating normally and contribute to chronic hoarseness.
Read more about the topic here: The hoarseness.
Sore throat
With a vocal cord inflammation, there is often an additional sore throat. In most cases, the pain occurs even before the vocal cords actually become inflamed.
The sore throat is usually caused by an upper respiratory tract infection. Viruses or bacteria settle in the throat. The mucous membranes become inflamed, causing the sore throat. The inflammation usually begins in the throat, but can reach the vocal cords. A sign that the vocal cords are also inflamed is pain when swallowing.
Find out all about the topic here: The inflammation of the vocal cords.
The larynx
Vocal cord inflammation is usually associated with larynx pain. Usually the trigger is a viral or bacterial infection. When this travels through the throat to the vocal cords, the entire larynx is usually also affected. This causes discomfort in the area, especially when swallowing and speaking.
However, inflammation of the vocal cords can also be caused by chronic reflux (belching of stomach acid). In this case there is a strong urge to cough in addition to the larynx. This occurs more often at night because the reflux is stronger when lying down.
Find out more about the topic here: Larynx pain.
The throat clearing
Having to clear the throat is a sign of chronic inflammation of the vocal cords and / or larynx. As a rule, symptoms such as hoarseness and a feeling of dryness in the throat that persist for more than three weeks are added. In contrast to acute vocal cord inflammation, there is often little or no sore throat.
The inflammation changes the structure of the vocal cords. This can make it feel like there is a foreign object (such as a crumb) in the larynx area. The body's normal reflex is to "clear out" this foreign body.
Increased salivation
When the vocal cords are inflamed, there is often a feeling of dryness in the throat. This causes the body to produce more saliva. The inflammation of the vocal cords also changes their surface. This can make it feel like a small foreign object (such as a crumb) is in your throat. This can also trigger increased salivation.
The increased saliva production also has a health effect: The body's own defense cells are in the saliva. These are needed to fight bacteria or viruses that cause vocal cord inflammation. An increased release of immune cells also leads to an increased flow of saliva.
The difficulty swallowing
Inflammation of the vocal cords often causes difficulty swallowing. Mostly the reason for this is an extensive inflammation of the throat. The throat and larynx are usually also affected when germs such as viruses and bacteria are the trigger for the inflammation. The inflammation leads to irritation of the mucous membranes in the vocal cords as well as in the throat and larynx. As a result, they react much more sensitively than usual to mechanical stimuli. When swallowing, chyme or liquid is transported along the inflamed mucous membrane. Due to the increased sensitivity, even such a touch can lead to pain.
However, it is not just contact with what is swallowed that irritates the mucous membranes. Even the act of swallowing itself can cause pain. The larynx is moved with each swallow. This movement alone causes additional irritation of the inflamed nerve endings and thereby triggers a painful stimulus. Since the larynx in particular is moved when swallowing, an inflammation of the vocal cords including the larynx usually leads to greater swallowing difficulties than an inflammation of the throat or throat alone.
Read more about the topic here: The difficulty swallowing.
The slime
In the case of vocal cord inflammation, bacteria and / or viruses are often involved in the development of the inflammation. The airways can also be affected. In order to get rid of the germs better and to protect itself from them, the body has a simple defense mechanism: It packs the germs in mucus. This makes it harder for the dangerous bacteria and viruses to adhere to the mucous membrane. It also makes it easier to cough up the germs.
An inflammation of the vocal cords suggests that the pathogens have not only settled in the throat but also a little deeper in the throat. That is why the body uses all of its defense mechanisms to protect itself from further spread of the germs.
What home remedies can help with vocal cord inflammation? You can find more information here.
The typical symptoms of chronic inflammation of the vocal cords
The most typical symptoms of vocal cord inflammation are coughing and hoarseness, and sometimes even complete voice failure. Chronic inflammation of the vocal cords is defined as lasting more than three weeks. Chronic vocal cord inflammation can therefore be assumed if the hoarseness persists for three weeks.
In contrast to the acute inflammation, the chronic form is significantly less painful. In addition, the urge to cough in chronic inflammation of the vocal cords is usually triggered by a dry throat or the feeling of a small foreign body.
In chronic inflammation, the vocal cords are thickened over a long period of time. This can cause a throat compulsion. While an acute inflammation of the vocal cords is triggered in most cases by infectious pathogens such as viruses and bacteria, the mechanisms underlying chronic inflammation of the vocal cords are different. Therefore, there are no additional symptoms such as fever or a runny nose with chronic inflammation. Rather, symptoms that indicate reflux disease are indicative of chronic inflammation of the vocal cords.
The backflow of acidic gastric juice leads to burning pain behind the breastbone, which is usually most pronounced when lying down. If the stomach acid reaches the vocal cords, the mucous membrane there is irritated, which can lead to chronic inflammation of the vocal cords.
Also read the article: Duration of the vocal cord inflammation
What are the typical symptoms in children?
Diseases and symptoms in children are often more difficult to interpret than they are in adults. Small children in particular are not yet able to express themselves verbally, so that they cannot communicate that they have a sore throat, for example.
The first sign of a vocal cord inflammation is therefore increased crying of the children. Affected children can become very restless, especially when they are fed. Since swallowing is often painful in the case of vocal cord inflammation, the children usually eat and drink less than usual.
Older children will usually have a sore throat. One symptom that is particularly indicative of vocal cord inflammation is hoarseness. This hoarseness can of course also be noticed in babies as soon as they cry. Since vocal cord inflammation, especially in children, is usually accompanied by inflammation of the pharynx, it is worth taking a look into the throat. If this is red, there is a certain probability that the vocal cords are also affected by the inflammation.

.jpg)