Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes
definition
The lymph nodes are the Filter stations of the human lymphatic system. The lymphatic system transports the lymph fluid, which arises outside of the body cells as a filtrate of the blood and thus transports nutrients or metabolic end products but also pathogens. The lymph nodes as filter stations can use these pathogens on the one hand eat and thus render harmlessOn the other hand, they can immune system also activate.
Lymph node swelling can be either under a local inflammation or because of a threatening systemic disease occur.

In general, you can tell if a lymph node acutely painful enlarged and there is also evidence of a local infection or infection in the body that is usually a benign process acts. The lymph gland swelling occurs creeping and without pain on and can also no connection to an infection should be sent to a more threatening illness be thought.
In most cases, chronic lymph node swelling develops slowly and progressively. In comparison to acute lymph node swelling, a starting point for the underlying disease is usually not immediately recognizable; it usually progresses slowly over a longer period of time.
Please also read our page Lymph node swelling- How dangerous is it?
causes
Chronic lymph node swelling can have various causes. On the one hand, local infections such as chronic tonsillitis can be the cause. On the other hand, generalized infections, such as Pfeiffer's glandular fever (infectious mononucleosis), HIV, or parasitic diseases such as toxoplasmosis, can be causal.
Long-term use of certain drugs can also lead to chronic enlargement of the lymph nodes. Examples are the anti-epileptic phenytoin, allopurinol (a drug for gout) and the antiarrhythmic agent procainamide.
Diseases of the lymphatic system such as leukemia, Hodgkin's disease or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma are malignant causes.
Storage diseases of the body are also causes of chronic lymph node swelling. Most of these are hereditary and cause certain substances to accumulate in the body's cells. For example, Gaucher's disease or Niemann-Pick's disease should be mentioned here. In infancy and toddlerhood, Kawasaki syndrome, a febrile illness, is the reason for the lymph node swelling.
Read more on the topic:
Lymph node swelling after surgery
Duration of lymph node swelling
Chronic lymph node swelling in EBV
The abbreviation EBV denotes that Epstein-Barr Virus (also Human Herpes Virus-4), the cause of Pfeiffer's glandular fever (also infectious mononucleosis). In the English-speaking world, the disease is also called "Kissing Disease“Because the infection usually spreads via the highly infectious saliva.
After an incubation period of one to several weeks, an tonsillitis accompanied by fever With greyish-white coverings and one generalized lymph node swelling.
This lymph node swelling is typical symmetrical and especially on the neck to observe. Accompanying it can be massive Swelling of the spleen up to the risk of rupturing the spleen. Also the liver may be affected by swelling.
The therapy of Pfeiffer's glandular fever consists in a purely symptomatic treatment with physical protection, Hydration and Painkillers. The administration of a penicillin to treat tonsillitis can lead to a drug eruption.
Please also read our page Pfeiffer's glandular fever.
Chronic lymph node swelling in toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a disease that from animals to humans transmitted - a so-called parasitic zoonosis. Typically the pathogens Toxoplasma gondii, in contact with Cats transmitted, which the sporozoa (unicellular parasites) in a meat meal and then excrete it with the faeces. The infection rate in Germany is with 30-50% relatively high, but a very large part of the infections run without symptoms.
However, immunosuppressed people and pregnant women with a primary infection are particularly at risk of developing toxoplasmosis. This brings in light fever, fatigue, Headache and body aches for several weeks and also Lymph node swelling with himself.
Once the infection is over, there is one lifelong immunity. However, are immunocompromised people particularly endangered by the reactivation of the inadequately controlled pathogens on one Involvement of the brain with hemiplegia, sensory disorders, speech disorders and possible epileptic seizures.
Please also read our page Toxoplasmosis.
Chronic lymph node swelling in HIV
An infection with the HI virus is a complex disease that is associated with numerous symptoms, complications and secondary diseases and is fatal if left untreated.
HIV is the abbreviation for the human immunodeficiency virus, which leads to an immune deficiency and a very complex clinical picture. The virus is mainly transmitted sexually through unprotected intercourse or from the pregnant mother to the child. The clinical picture of the infectious disease is divided into three stages.
Read more on this topic: Lymph Node Swelling - What Evidence Is There It Is HIV?
A few weeks after the initial infection with the virus, symptoms similar to those of a conventional viral disease with runny nose and swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck region can occur.
Stage A includes the acute infection with flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache and body aches, and generalized lymph node swelling.
Stage B is characterized by an increased number of infections. These are referred to as non-AIDS defining. Fungal infections, chronic diarrhea, shingles and many more play a role here.
Stage C is called AIDS (English: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) designates and includes AIDS-defining diseases such as various parasitic, bacterial, viral or fungal diseases. In addition, some malignant diseases such as lymphoma can occur, which can also cause chronic lymph node swelling.
Read more about this on our website HIV.
Chronic lymph node swelling in leukemia
In rare cases, swelling of the lymph nodes can indicate a malignant cancer such as leukemia of the lymph cells. The most important distinguishing features from the much more frequent reactive lymph node swellings due to infections or other body processes are a significantly longer period of illness and the painlessness of the swollen lymph nodes.
The lymphatic cells in the lymph nodes can degenerate in a malignant manner or other cancers can settle in the lymph nodes as metastases. If such a painless lymph node swelling persists over a period of several weeks to months with additional symptoms such as weight loss and fatigue, without a previous infection, a sample of the lymph node should be taken by the doctor for clarification.
The various malignant diseases that can be associated with such a swelling of the lymph nodes sometimes have very different disease courses with widely varying therapies and prognoses.
Here you can find out more about the topic: Lymph node pain
Chronic lymph node swelling due to sinusitis
Sinus infection is a very common disease that accompanies seasonal respiratory infections. The paranasal sinuses include, for example, the frontal sinuses or the ethmoid sinuses. However, the maxillary sinuses are most commonly affected by the inflammation. This is usually due to infections with typical cold viruses, and bacterial infections can also follow in the course of the disease.
Sinusitis is often associated with an exacerbation of symptoms and an increase in the duration of the illness. Typical accompanying symptoms are a heavy head, headache, pain when pressure or knocking on the maxillary sinuses from the outside, a strong feeling of illness with a runny nose and a blocked nose, as well as reactive, severely swollen lymph nodes.
Find out more about maxillary sinus infections
Chronic lymph node swelling in tonsillitis
The tonsillitis is also a typical complication of harmless colds of the upper respiratory tract. It occurs especially in school-age children and leads to swelling, difficulty swallowing, pain and a stronger feeling of illness with a sore throat and fever. In response to the harmful pathogens, the lymph nodes can swell painfully. Lymph nodes in the neck, lower jaw or collarbone are particularly affected.
Tonsillitis usually goes away on its own; antibiotic therapy is rarely necessary for bacterial inflammation. If the tonsils are so deformed and scarred after numerous inflammations that tonsillitis can easily develop, surgical removal of the tonsils can be considered.
Read more about the topic here:
- Symptoms of tonsillitis
- Swelling on the side of the neck
diagnosis
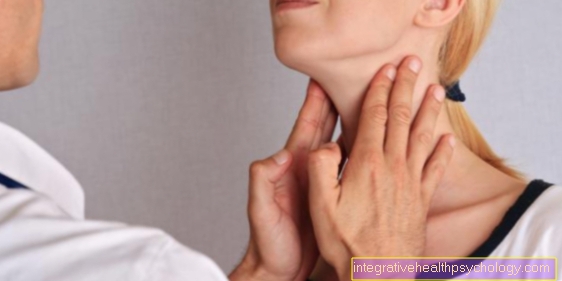
The diagnosis of chronic lymph node swelling is made by the attending physician as part of the physical exam posed. The tactile findings of the superficially palpable lymph nodes on the neck, armpits and groin play a decisive role here. Furthermore, the anamnese one of the most important means of diagnosis.
It will be the Duration of the swelling, Painfulness and eventual Concomitant symptoms such as fever, skin changes or injuries in the lymph stream area. Furthermore are the knowledge about Underlying diseases, one regular medication use, the Travel and vaccination history, Sexual and drug history as well as the Contact with animals important diagnostic landmarks to determine the cause of the lymph gland swelling.
In addition, it is possible through imaging procedures such as the Computed Tomography, Magnetic resonance imaging or the Ultrasonic to prove enlarged lymph nodes. On too X-rays For example, in the chest, enlarged lymph nodes are quite visible.If the above measures cannot be used to determine with certainty whether the cause of the lymph gland swelling is benign or malignant, suspicious lymph nodes can be identified surgically remove and histologically examine under the microscope.
Concomitant symptoms
Concomitant symptoms of chronic lymph node swelling are as extensive as their causes. For one, a general feeling of illness with headaches and body aches as well fever occur. Additionally can local redness or overheat lead to discomfort.
As part of a generalized infection such as Pfeiffer's glandular fever, there is not only tonsillitis but also fever, and swelling of the spleen can also be an accompanying symptom.
The Kawasaki syndrome in childhood brings not only lymph node swelling but also one Conjunctivitis, one Reddening of the skin as a result of increased blood flow, or a trunk-dominated rash with himself.
It can also be used in the context of cancer, such as lymph gland cancer Night sweatsmultiple changes of bed linen or night clothes, unexplained fever over 38 ° C and a Weight loss greater than 10 percent of the starting weight within half a year. These three are called the so-called B symptoms and can also occur individually. In Hodgkin's lymphoma, a so-called Alcohol pain accompanying symptoms count. This occurs in the affected lymph nodes after consuming alcohol.
Treatment / therapy
Treating chronic lymph node swelling always means that Treatment of the underlying condition, since this is mostly just a symptom and not a disease. So you should first look carefully for the cause. It is important that a doctor should definitely be consulted if anything is unclear.
Ambiguities are next to one painless swelling also a swelling that has existed over a long period of time, i.e. chronic lymph node swelling. With one of the underlying lymph node swelling Cancer systemic therapy in the form of a Radiation and chemotherapy required.
In general, after successful treatment of the underlying disease, a Size reduction of the affected lymph nodes to be determined. The removal of individual lymph nodes for diagnostic confirmation makes sense, but generally makes little sense in a therapeutic context.
Duration
The general duration of a lymph gland swelling is usually directly related to the duration of the underlying disease connected. If, for example, the primary infection has been treated and regressed, the swelling should also subside. From a diagnostic point of view it can be said that slowly and over a longer period of time (over several weeks) swollen, non-painful lymph nodes are more likely to be attributed to a more serious disease.
At the Early stages of HIV infection for example, lymph node swelling occurs from more than two lymph node stations outside the groin region, generalized for more than three months on. If the swelling occurs acutely, i.e. within a few days, it is more likely to be benign.
Classification of chronic lymph node swelling according to location
Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck
The groups become the lymph glands of the neck regions in front of and behind the auricle, below the lower jaw and chin, in the Area of the neck and back of the head, the upper shoulder as well as the groups above the collarbones counted. The chronic lymph node swelling in these groups can have various causes.
For example, a Tonsillar angina (Tonsillitis) recur and thus also cause chronic swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck area. Also Tumor diseases in the head and neck area causes swelling of the lymph glands in the areas mentioned above.
At Tumors in the mouth region swelling of the lymph nodes in the area of the angle of the jaw, below the chin and the area in between can occur. With swelling of the lymph glands above the collarbone should also always be involved in cancers Bronchi, of the esophagus and des Gastrointestinal tract be thought.
Please also read our topics Lymph node swelling in the neck - dangerous? and Lymph node swelling in the neck - dangerous?
Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin
The lymph nodes in the groin region can be anatomically divided into a vertical and a horizontal group. They run in the vicinity of the large vessels and filter the lymph of the legs, of the Abdominal wall, of Back and part of the outer genital region.
The vertical groups of lymph nodes are located on the inner side of the thigh and filter the lymph fluid of the legs. The horizontal group of lymph nodes is below the inguinal ligament palpable, which pulls from the upper part of the hipbone towards the groin. This group of lymph nodes collects the lymph fluid from the abdominal wall, back and parts of the external genitals.
Swelling can be due to some STDs which are transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse. Examples here are infections caused by pathogens such as Chlamydia, Genital herpes viruses or pathogen of syphilis.
On the other hand, generalized infections such as Pfeiffer's glandular fever, infections with the Cytomegaly virus, mumps, measles or rubella Lymph node swellings also appear in the groin region.
Lymph node swellings in the groin in general are very palpable, and checking them is part of the doctor's standardized physical examination.
Please also read our topic Lymph node swelling in the groin- dangerous?
Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes in the armpit
The armpit lymph nodes can be divided into several groups. A central group, a front group lying on the chest, a group lying behind the axillary fold and a group below the collarbone are distinguished. They collect the lymph fluid of the Armpit, of the chest and the Chest wall and the Most of the arm. The group lying under the collarbone then collects all of the above groups before the lymph flows into the venous angle of the large vessels.
A chronic swelling of these lymph nodes can be systemic Infections, but also through one Cancer, such as. Breast cancer be conditional.
Please also read our topic Recognize breast cancer.
Also read our topic Lymph node swelling in the armpit - dangerous?
Lymph node swelling in chronic tonsillitis
In the throat area, humans have several lymphatic structures that can be assigned to the immune system, which we call Almonds describe. You are on Throat entrance, at the palate, at the tongue and at the Eustachian tube. In addition, the so-called Side strands counted among them. If almonds come into contact with pathogens, they activate the immune system and are also able to eat the pathogens that have entered. As part of this activation it comes to Increase in size.
The concept of chronic tonsillitis is actually no longer used because it can be misleadingly understood. It is more of a repeated acute inflammation, as the tonsils deal with pathogens around the clock. It is the term of repeated acute tonsillitis (Tonsillitis) So recurring tonsillitis with symptom-free or low-symptom intervals. Lymph node swellings typically occur in the area of the tonsillitis Jaw angle on.
Read more on the subject here Chronic tonsillitis.
Lymph node swelling in chronic sinusitis
The paranasal sinuses mainly serve the Language education, for example the formation of the nasal sounds. In addition, they are to be understood as resonance spaces when speaking and singing and also reduce the total weight of the skull because they are hollow spaces. At Colds for example, the ethmoid cells can become inflamed, which prevents secretions from draining from the sinuses. Thus it is possible for germs to lodge there and trigger an inflammation.
Keeps sinuses from becoming inflamed longer than 12 weeks on it is called chronic. Symptoms such as purulent runny nose and a movement-dependent facial pain, especially when bending the head forward.
Viruses are the most common pathogens of this disease, which is why in most cases the administration of antibiotics does not make sense. Therapeutically, one tries to proceed first with cortisone-containing nasal sprays. In the case of long-term suffering, a surgical procedure to widen the drainage ducts is indicated. In the case of sinusitis you can Lymph node swelling in the area in front of the auricle occur.
Sinus infection.