Supinatorlous syndrome
definition
The supinatorlogic syndrome is a bottleneck syndrome of the radial nerve in the area of the elbow joint. The name supinator lodge comes from the fact that the radial nerve divides just below the elbow joint and its motor part, which is damaged in the syndrome, runs through the supinator muscle.

Synonyms
Other names for the supinatorlogic syndrome include "supinator syndrome, radial compression syndrome or supinator tunnel syndrome".
In supinatorlogic syndrome, similar to the much more common and well-known carpal tunnel syndrome, a nerve is pinched, constricted or compressed. This affects the so-called deep branch of the radial nerve. This branch is purely motor-driven, which means that certain muscles are weakened or paralyzed, but not sensitivity or loss of sensitivity.
neurology
The radial nerve, also called the radial nerve, is a so-called mixed nerve. It contains both motor fibers and sensitive fibers. In the area of the elbow joint, it divides into the two fiber parts.
The sensitive part runs superficially towards the back of the hand and the motor part runs down through the supinator muscle to supply the muscles there for hand extension. The pattern of symptoms also differs depending on where the nerve is damaged.
If only the superficial part is damaged, only sensory disorders are evident. If only the motor part is damaged, as is the case with supinatorlogic syndrome, then the main symptoms are muscle deficits. If the nerve is damaged further up in the direction of the upper arm, both sensory disorders and motor failures can be observed.
causes
The causes of supinatorlous syndrome can be total different genesis be. What they have in common is the constricting the motor branch of the radial nerve and thus damaging it.
A possible cause of compression syndrome can be a Breakage of the ulna or radius in the area of the elbow joint be. Here is a possible Bone displacement or an educated one bruise to a Bruising of the nerve and an associated Nerve damage to lead.
Also one Dislocation / dislocation of the radial head (also Radius head called) out of its ligament guide can lead to a constriction of the nerve in the area of the entry point into the muscle.
Inflammation, tumors or Adipose growths in the area of the nerve penetration can also lead to a bottleneck. Supinatorlogic syndrome can also be caused by a Increase in the muscles of the supinator muscle which is built up by repetitive exercises such as playing tennis or playing the piano, which can also lead to a constriction of the nerves.
The bottleneck syndrome can also be another cause constant external pressure arise, for example, when carrying heavy objects on one side or small children.
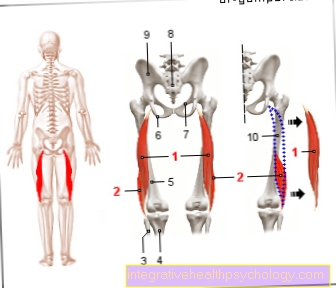
Figure elbow joint

- Upper arm head -
Capitulum humeri - Outer femoral knot -
Lateral epycondilus - Inner femoral knot -
Epycondilus medialis - Upper arm roll - Trochlea humeri
- Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri - Spoke head - Caput radii
- Spoke neck - Collum radii
- Roughness of the spoke -
Radial tuberosity - Roughness of cubit -
Ulna tuberosity - Spoke shaft -
Corpus radii - Ellschaft -
Corpus ulnae - Articular cartilage
- Joint capsule -
Articular capsule - Ellen's nerve -
Ulnar nerve - Arm extensor -
Triceps brachii muscle - Upper arm muscle -
Biceps brachii muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Symptoms
The main symptom of supinatorlous syndrome is a weakness in the extension of the fingers. The weakness can develop to such an extent that the fingers can no longer be stretched. What is important here is that it is a purely motor problem, since supinatorlogic syndrome only affects the motor part of the radial nerve. The sensitive part is completely intact, so there is no disturbance of sensation on the fingers or arms.
Additional impairments in sensitivity indicate an injury to the radial nerve before it divides into its motor and sensory parts. Such an injury would then be in the direction of the upper arm. However, the back of the hand, unlike the fingers, can be raised all the time. So, so to speak, there are only “falling fingers”, not a “falling hand”.
Pain
Another symptom of supinatorlogic syndrome is a so-called load-dependent pain in the area of the outer elbow joint. There is the so-called radius head, which is a spherical structure of the radial bone. The pain mainly occurs when turning movements, i.e. when the patient turns the palm upwards.
Repetitive twisting of the forearm may lead to a feeling of muscle fatigue. You know this feeling after repeating the same exercise a few times in sport. The patient with supinatorlogic syndrome can also have pain that radiates into the wrist of the affected side.
In supinatorlous syndrome there is pain that is described by most people as "dull". They often occur spontaneously and are mainly found in the area of the forearm below the elbow. Pressure on the affected area increases the pain.
Occasionally, the pain can also appear down the forearm to the wrist. This depends on the severity of the nerve damage.
Symptoms in the forearm
In supinatorlogic syndrome, only the lower part of the arm is affected, as the nerve damage only occurs in the forearm. The resulting symptoms therefore only affect the forearm, not the upper arm. Since supinatorlogic syndrome only affects the motor fibers of the radial nerves on the arm, there are no sensory disorders in the arm. The damage to the motor nerve fibers leads to weakness of the fingers and pain when rotating the forearm.
How is supinatorlogic syndrome different from tennis elbow?
In a supinatorlogic syndrome there is damage (lesion) to a part of the radial nerve (the so-called Ramus profundus, literally "deep branch"). As a result, if this nerve is completely severed, the muscles supplied by the nerve, which are responsible for stretching the 3rd and 4th fingers, can suddenly no longer be used properly.
There is also a rather dull pain. In the case of a tennis elbow, on the other hand, improper or overloading leads to minor injuries in the area of the muscle attachments on the elbow and thus to severe pain. The muscles initially still work here and can only be actively moved to a lesser extent as the process progresses.
diagnosis

The diagnosis of supinatorlogic syndrome is made up of the anamnese and the physical examination of the patient. This gives a first impression of where the cause of the problem can possibly be found.
Next can be through a Neurologist (neurologist) the Conduction velocity of the affected nerve to be determined. Does pressure lead to one significant damage to the nerve sheath and nerveso can that Line speed significantly reduced be.
As part of the diagnosis, you can also Ultrasound examinations as well as other imaging procedures such as roentgen or MRI are used. Ultrasound can be possible Lipomas (Fatty growths) or ganglia (benign soft tissue tumor), which lead to constant pressure on the nerves, can be found. X-ray examinations can possibly reveal existing Fractures of the ulna and radius be excluded.
MRI elbow and forearm
The MRI of the elbow and forearm can be used as a component in diagnostics. It serves primarily to to represent constricting structures.
In the MRI images, for example Bruising, Inflammation or small fatty growthsthat the Radial nerves squeeze, be represented.
However, damage to the nerve function or the radial nerve itself cannot be shown in the MRI.
Read more on this topic at: MRI of the elbow
therapy
Both supinatorlogic syndrome can be treated conservative, for example by means of Painkiller or Physiotherapy, as well as operational.
Since the operative treatment of supinatorlous syndrome no comparably high chances of success like the operative treatment for a bottleneck within the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome you should try conservative non-surgical therapy first.
With the non-surgical approach one tries with the help of pain medication that to reduce the pain in the forearm area. The so-called above all come here non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for use. This group includes, for example Diclofenac or Ibuprofen. They not only relieve the pain, but also fight possible inflammation in this area. Likewise can Medicines that relax muscles serve, come into play. Supinatorlogic syndrome can also be treated with Cold and heat applications or pure physiotherapy.
How can physiotherapy help?
As a conservative therapeutic measure, physiotherapy can have a particularly supportive effect in the treatment of supinatorlogic syndrome. The severity of the damage to the nerve is crucial. Adapted to this, in physiotherapy the focus can be placed on a supportive development of the surrounding muscles and / or the muscles affected by active exercises can be strengthened again.
Special procedures, such as lymphatic drainage or direct stimulation of the affected nerve (electrical stimulation), can also be helpful.
OP
If the non-surgical treatments for supinatorlogic syndrome do not respond or respond only insufficiently, surgical treatment can be carried out. An operation should take place quickly, especially if there is paralysis. During the operation, one tries to expose the deep, purely motoric branch of the radial nerve.
Since this is very fine, special care is required. At the point of entry of the radial nerve into the muscle, it is covered by a connective tissue fiber. This can run very tight and thereby pinch the nerve. During the operation, an attempt is therefore made to widen the entry point of the nerve into the muscle. The expansion takes place by cutting through the restricting structures such as fiber strands or connective tissue.
How is supinatorlogic syndrome different from tennis elbow?
It can be difficult to tell the difference between tennis elbow and supinatorlogic syndrome.
As a result, supinatorlous syndrome is often confused with tennis elbow symptoms, especially when the pain is the main focus.
The occurrence of pain on the outer upper arm is clearly to be found in the muscle area in supinatorlogic syndrome, while tennis elbow pain can be triggered on the upper arm bone (lateral epicondyle).
The typical tests for a tennis elbow can also be positive for supinatorlous syndrome, which can easily confuse the clinical pictures.
Read a lot more information at: Symptoms of tennis elbow
forecast
A prognosis in the context of supinatorlogic syndrome is difficult to poseas they are mainly from the Duration and severity of nerve damage depends. A damaged nerve that has already started to appear Paralysis has led, can not completely healed immediately as soon as the pressure is gone. The healing of such a damaged nerve may possibly Months to complete to take.








-operation.jpg)