Treatment of Bartholinitis
introduction
Bartholinitis is a very painful inflammation of the Bartholin's gland (or “large vaginal atrial gland” translated from Latin) that is perceived as unpleasant by affected women. Usually only the ducts of the gland located in the area of the labia minora are affected. These can then be recognized as smaller reddish points in the vaginal vestibule. However, bartholinitis always needs treatment. Different treatment steps are recommended depending on how the inflammation progresses.
Read more on the topic: Bartholinitis and Bartholinitis Symptoms
Early stage
In the case of early-stage Bartholinitis, only the ducts of the gland are initially affected. It would be advisable to start anti-inflammatory treatment early on. This can reduce the cell response to the respective pathogen, i.e. all signs of inflammation, such as Swelling, redness, overheating are reduced and the Bartholinitis is prevented from spreading even further to the glands themselves. In this way, the tissue concerned has the opportunity to recover by swelling and the bartholinitis with all its discomfort goes back. Another important point in the treatment of bartholinitis is pain relief medication. Since the inflammation affects a very pain-sensitive area of the female sex, it is perceived as extremely uncomfortable. Cooling the affected areas can also have a pleasant effect against the pain.
Advanced bartholinitis
Should the Bartholinitis be more advanced, i.e. should a "abscess“(= An encapsulated collection of pus) at the location of the gland outlets, it would make sense to have one Relief of the boil to undertake. This should always be done by a doctor, by a cut in the encapsulation is carried out in the course of the gland duct. Of the pus should be completely removed. Afterwards, when the encapsulation has been opened, the walls of this artificial body cavity can be sutured to the surrounding tissue so that it is kept open in the future. Further accumulations of pus as a result of Bartholinitis can flow away and do not immediately form a new so-called "Bartholin's cyst“ (Bartholinitis cyst). This treatment process is also called "Marsupialization". In the following it is helpful to open cyst With Hip baths keep clean to minimize the number of exciters in this area. Furthermore, a relocation of the opening or a re-closure should be counteracted. Even with the help of a Tamponade closure can be prevented. In the further course, the opened cyst contracts and forms a new duct. However, this is only recommended for "mature" abscesses. If they are not ripe enough, the whole thing can be conservative by using red light and Pull ointment (e.g. Ilon® ointment) be helped. A pain relieving treatment, as described above, is recommended during this time.
Complications
However, if bartholinitis recurs with renewed formation of a boil, which incidentally happens very often, the entire gland should be surgically removed. If the "Bartholin's cyst" is not addressed with one of the above treatments, it can burst spontaneously, that is, without any external influence. Then, too, becomes a operative treatment recommended. The burst Bartholin's cyst should be cut open further, completely freed of pus and kept open by sewing the cyst walls. Without treatment it can get worse Complications come. The pathogens could spread beyond the gland and affect the whole body. In the worst case this can lead to a life-threatening blood poisoning that absolutely urgently needs medical attention.
trigger
It is also important that one smear the opened cyst is made, the following microbiological should be investigated. This provides information about which pathogen was responsible for the Bartholinitis. Are typical Staphylococci, Escherichia coli, Streptococci, Anaerobes. Also Gonococcithat are, for example, sexually transmitted (also known as gonorrhea), can be the cause. If these are demonstrable, a targeted one must be provided antibiotic treatment against the relevant pathogen. This procedure is also recommended if the condition does not improve despite appropriate treatment, but there is also a general deterioration in the state of the body.
Alternative treatments
Of course there is alternative methods to treat bartholinitis. The homeopathy also offers treatment options, for example. Certain homeopathic remedies are recommended, such as Mercurius solubilis, Hepar sulfurius, Acidum silicicum and Thuja. These are used depending on the stage of bartholinitis and dosed accordingly.
Alternatively, Bartholinitis can also be treated with the Herbal medicine to treat. Are a means of choice warm hip baths with special additives like Oak bark, Chamomile flowers, Witch hazel or Witch hazel. These counteract the inflammation. In addition, so-called retuning therapy can take place. This can be done either with medication or with stimulation therapy. This is supposed to body's defense system be stimulated and strengthened so that it can fight the inflammation independently and defend itself earlier against a colonization of germs.
Although these alternatives seem gentler, they should be used with care and with professional support. If the desired effect does not occur, a medical evaluation would be advisable.
Sitz baths for the treatment of bartholinitis
In the early phase or later as a supplement to surgical and antibiotic therapy, hip baths can have a positive influence on the course of bartholinitis.
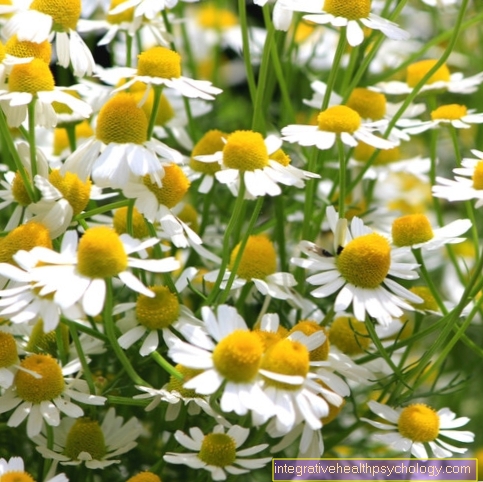
To do this, a bathtub or a special hip bath attachment for the toilet is filled with water and disinfecting additives. Then you should stay in the water for 15-30 minutes. Various substances are suitable as additives to warm water. Chamomile is a popular and long-known additive. In a hip bath, chamomile penetrates deeper layers of the skin and develops anti-inflammatory effects there, which is why the Sitz bath with chamomile is also suitable as a measure for early symptoms of Bartholinitis. In addition, chamomile promotes wound healing, which is why it is wonderfully suitable as an accompanying measure after surgical therapy. The effect of chamomile has been proven by scientific studies.
Another possibility is the addition of potassium permanganate. This has a disinfecting and astringent effect. This means that it leads to a "dehydration" of the inflammation. When using it, you should make sure that it is diluted in the correct ratio, as in extreme cases it can cause burns to the skin. It should also not be used for too long, as it can lead to undesirable drying out of the skin.
Furthermore, polyvidone iodine, which also has a disinfecting effect, can be used.
Home remedies to treat bartholinitis
The home remedies for Bartholinitis are usually plants or products that have anti-inflammatory, antibiotic or emollient effects.
At the very front is the chamomile hip bath. It has been scientifically proven that chamomile has a local anti-inflammatory effect and promotes wound healing, which is why the Sitz bath with chamomile is suitable both in the early stage of the inflammation and later as an accompanying measure in addition to the medically initiated therapy.
Ginger is also one of the commonly recommended home remedies. There is no scientific analysis specifically for bartholinitis, but it is known that ginger generally has anti-inflammatory properties, which is why it can be taken as a supportive measure.
The ginger can, for example, be cut into slices and poured over with hot water and then enjoyed as a tea. Other home remedies such as aloe vera, vermouth, lemongrass, gentian, dandelion or garlic have not yet been specifically investigated for their effectiveness against Bartholinitis. However, scientific studies have proven their anti-inflammatory, partly antibacterial and partly pain-relieving effects. If the symptoms do not go away with home remedies, a doctor should be consulted.
Homeopathy to treat Bartholinitis
Homeopathic therapy for bartholinitis consists of two pillars.
On the one hand, it consists of acute therapy and, on the other hand, constitutional therapy.
The acute treatment depends on the nature of the symptoms. If the pain is pulsating and the abscess is red and hot, we recommend taking Belladonna.
If the pain is sharp to the touch and the abscess is shiny and the skin is swollen all around, Apis is particularly suitable.
If you suffer from splinter-like pain and also have a desire for acidic food, Hepar Sulfuris is suitable, which is known as a "homeopathic scalpel" because it is supposed to lead to an opening of the abscess.
The splintered pains come and go quickly, the sweat smells foul and if genital condylomas are present at the same time, Nitricum Acidum can be used.
Lachesis, on the other hand, is recommended for jealous young women who cannot tolerate tight necks and who suffer from a bluish-red abscess.
Since, according to homeopathic doctrine, it is a disease from the field of "sycosis" (a non-limiting miasm that can lead to chronic diseases), a mere suppression of the abscess would possibly lead to a shift of the problem to the internal organs .
Therefore, in addition to acute therapy, constitutional therapy is recommended. There is no scientific basis for the homeopathic therapy of Bartholinitis according to the criteria of modern medicine.
Ointments for treating bartholinitis
Ointments have different meanings in the treatment of bartholinitis. First of all, in the case of a simple inflammation of Bartholinitis, ointments containing antibiotics can help to contain the inflammation. Ointments that contain active ingredients such as fusidic acid, nebacetin or bacitracin are best suited.
If an abscess has already formed, but it is not yet fully developed, an ichtholan ointment can be used to help. The ointment causes the abscess to ripen more quickly and can subsequently be surgically treated more quickly. Other ointments that promote abscess maturation can also be used for this purpose.
When is the use of antibiotics necessary?
If the bartholinitis does not improve with general measures, such as Sitz baths or one or the other home remedy, or the symptoms increase, you should consult a doctor in good time, who will then decide on how to proceed depending on the extent of the inflammation.
The first warning signs are fever and fatigue as well as unbearable pain when sitting and walking.
In mild cases, antibiotic ointments are suitable for therapy with antibiotics. Most often, however, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets. If the inflammation is not yet so advanced, therapy with antibiotics alone may be sufficient. Usually, preparations such as ceftriaxone are prescribed, which cover the spectrum of the most common pathogens. If an abscess has already formed, the usual procedure is surgical opening. In addition to rapid relief, this offers the possibility of searching for the causative agent. As a result, an antibiotic can be specifically selected that works optimally against the pathogen found.
If the antibiotic and / or surgical therapy is not carried out in good time, there is in rare cases the risk that the germs enter the bloodstream. This can lead to life-threatening blood poisoning.
When do you have to be operational?
If the outlet of the inflamed Bartholin's gland sticks together, an abscess can develop, i.e. an accumulation of pus within the inflamed gland. Once this development has taken place, it is usually necessary to surgically drain the abscess. Many women shy away from surgical therapy at the beginning.
Since the formation of an abscess is usually associated with very severe discomfort when sitting and walking, most women find the surgical opening of the abscess a great relief in the end. The procedure is usually carried out on an outpatient basis. Local anesthesia is usually sufficient. The most commonly used surgical technique is called marsipulation. The abscess is opened with a scalpel. The walls of the abscess cavity are then sutured to the skin so that the cavity remains open to the outside.
This is necessary as the Bartholin's abscess tends to recur otherwise. The secretion obtained in this way is used to determine which germ is responsible for the inflammation in order to be able to begin targeted antibiotic therapy. If the inflammation recurs frequently, consideration may be given to removing the affected Bartholin's gland as a whole.
Other surgical procedures, such as suctioning the secretion from the abscess with a needle, creating an artificial fistula using a catheter or rinsing the wound with alcohol or silver nitrate, no longer meet today's medical standards.
Duration of treatment
Surgical therapy for bartholinitis is an outpatient procedure that only takes a few minutes. The duration of the antibiotic therapy depends on the germ, the extent of the inflammation and the chosen antibiotic. As a rule, however, this does not take longer than a few days.
However, it should be noted that the antibiotic should not be discontinued earlier than discussed with the doctor, since antibiotic-resistant germs can develop if antibiotic therapy is not carried out correctly. In rare cases, chronic inflammation of the Bartholin's glands can develop, resulting in longer treatment times.
Bartholinitis prevention
If you want to prevent bartholinitis, the first and easiest measure is adequate hygiene of the genital area. This also includes protected sexual intercourse. The aim is to keep the number of pathogens that lead to bartholinitis as low as possible while maintaining the natural and protective flora of the genital area. However, one should be careful when choosing a product. Many hygiene articles from the drugstore can irritate the very sensitive area more than protect it, i.e. the body's own protective barrier of the mucous membranes can be attacked. Therefore, the following applies here: less is more - it is better to work with gentler means - water and a little pH-neutral soap are completely sufficient.