ganglion
Synonyms
Upper leg, synovial cyst, ganglion cyst
Further meaning: In medical terminology, “ganglion” is also an anatomical term for a collection of nerve cell bodies. This is not discussed in this article.
introduction
A ganglion is a fluid-filled protrusion of the synovium that often occurs in the area of the wrist.
Since it appears as a firm, mostly painless swelling that looks similar to a protruding bony protrusion, the ganglion is also known as the overbone in lay language.
Because of its similarity to a tumor, the ganglion is also referred to medically as a pseudotumor, although strictly speaking it is a cyst, i.e. a fluid-filled cavity.
In most cases, a ganglion is harmless and does not require treatment. Removal by surgery is only necessary if symptoms occur - for example because the ganglion is pressing on nerves or blood vessels.

Causes: How does a ganglion arise?
All Joints of the body are surrounded by a joint capsule, the out connective tissue exists and with a clear liquid (Synovia) filled is.
This makes the joint on the one hand stabilized and on the other hand prevents the synovial fluid as Sliding layerthat the articular cartilages rub directly against each other.
At a Irritation of the joint, about through Overload or at one arthrosis, it can become a excessive production of synovial fluid come. This creates a Overpressure in the joint.
There is now one general weakness of the connective tissue or if the joint capsule is overstretched due to a previous injury, the Evert synovial membrane. Then it imagines cavity, which is connected to the joint space and above it is filled with synovial fluid. So can change the size of the ganglion depending on the amount of fluid contained - most of time it increases with movement of the joint.
In rare cases the synovium bulges inward instead of outward, so that a Ganglion in the joint space arises (intraosseous ganglion).
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Symptoms of a ganglion
Often times, sufferers have a ganglion no complaints, because it mostly not painful is.
In some cases, however, a Pressure sensitivity exist because there are pain receptors in the joint capsule that can be activated when the ganglion is irritated or when it grows.
Since ganglia have a Reach size of over eight centimeters can, sometimes the Limited mobility of the joint become.
Mostly, however, patients have first symptomswhen the ganglion on nerves or blood vessels around it presses. Then can Pain, Numbness, tingle or one Muscle weakness occur in the affected area. A ganglion grows in the area of a tendon, it can also become a painful tendonitis come.
What kind of pain does a ganglion cause?
Most ganglia cause no pain and hardly any other discomfort. However, depending on its size and anatomical position, a ganglion can cause pain of varying degrees. For example, a large ganglion can impair the mobility of muscles and joints and cause movement-dependent pain. At the same time, it can be very painful to lean on the ganglion.
When a ganglion presses on a tendon, it can cause painful tendinitis and, if a nerve is clamped, cause paresthesia. In addition, very small ganglia can also cause pain.
Occasionally there are tiny ganglia that are located deeper under the skin and are only noticeable through pain. Such ganglia are often diagnosed late or not at all. The pain can have different pain characteristics depending on where it is, how big it is and what structures it is pressing on.
Can a ganglion press on a nerve?
Depending on where the ganglion is anatomically located, it can cause various complaints. In addition to vessels and tendons, larger ganglia can also press on a nerve. If a large ganglion presses on a nerve, unpleasant symptoms can arise. Those affected may experience unpleasant symptoms such as tingling, pins and needles or numbness in the area where the nerve is supplied.
How can a ganglion be distinguished from a tumor?
Any form of tissue growth or swelling is defined as a tumor. A distinction is made between benign and malignant tumors, which are colloquially known as cancer. A ganglion is by definition a benign tissue tumor that lies under the skin and is usually palpable and easy to move. Malignant tumors, such as giant cell tumors, which can also occur in the area of the finger joints, are very rare.
With the help of an ultrasound examination, the doctor can determine whether a tumor shows signs of benign or malignant changes and, if necessary, initiate further examinations. Ganglia are very common findings and can usually be quickly diagnosed and differentiated from a malignant tumor.
localization
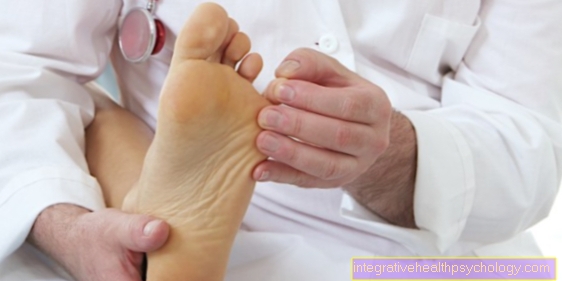
Ganglion on the foot or dorsum of the foot
The foot is a possible location for a ganglion to appear. Typically, the over-legs occur in the area of the back of the foot. They are usually found on joints (arthrogenic). These are mechanically stressed areas. A ganglion on the dorsum of the foot can be symptom-free or press on tendons and affect them. Tendonitis can result from long-term pressure from a ganglion on a tendon.
In addition, a ganglion on the foot can put pressure on a nerve and cause paresthesias such as tingling or numbness.
Ganglion at the knee (meniscus ganglion)
A ganglion on the knee is a benign tumor. It is also known colloquially as an overleg. However, this term is somewhat misleading, as a ganglion is not a bony structure, but rather a tumor formation in the area of the joint capsule. A ganglion always represents a connection to the joint. In principle, fluid can also be exchanged between the joint, e.g. with inflammation of the joint and ganglion. An inundation of fluid would cause the ganglion to swell.
A ganglion can also develop inside the knee, namely on the menisci.
Read more on the topic: Meniscal ganglion
Ganglia, depending on their size and location, can lead to more or less discomfort. Tense ganglia e.g.can cause pain in the knee as well as mechanical impairment when moving the knee.
The treatment of a ganglion is usually conservative. Only when it increases in size so much that either severe pain is caused or that mechanical impairments take place, an operative approach must be considered.
Ganglion on the finger
Ganglia on the finger are relatively common. The main reason is that the fingers represent a mechanically very stressed area. Here, the tendons in the vagina move up and down with every finger movement, creating friction effects that can then lead to the formation of small tumors known as ganglia.
In the area of the heavily mechanically stressed fingers, there are very often painful ganglia. In addition to the pain in the finger joint, mechanical movement impairments of the finger can also occur.
The treatment of small ganglia is mostly conservative, i.e. through anti-inflammatory or cooling measures.
If these treatment methods are not sufficient, it must be considered whether the ganglia are not removed surgically. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia.
After the procedure, the restorative physiotherapy is started immediately after a short rest period. This is important because if the finger is held still for a long time, irreversible stiffening of the joint can occur.
Read more on this topic at: Ganglion on the finger
Ganglion on the wrist
Ganglion formation can also occur in the area of the wrist. With every movement of the hand, numerous muscles and tendons are passed through narrow tendon sheaths, which can lead to severe mechanical stress. There is always a very high risk of ganglion formation at these points.
Ganglia in the area of the wrist can be found either on the back of the hand or towards the palm of the hand, in the area of the wrist.
Sometimes a ganglion does not need to be treated, but only needs to be watched while waiting.
If it increases in size and if there is pain (pain in the wrist), especially when performing movements, surgical rehabilitation should be considered.
Sometimes a ganglion can become so large and poorly located that it puts great pressure on the nerves that run through it. In this case, patients complain of numbness, mostly of the little finger and the ring finger.
A ganglion can only be treated conservatively to a limited extent. Cooling and anti-inflammatory measures are used, which can alleviate the symptoms caused by a ganglion.
More about this on our website Ganglion on the wrist
therapy
When a ganglion no complaints caused, it usually has to not treated be - in many cases it even regresses on its own.
However, kick Pain on or presses the ganglion on nerves or blood vesselstherapy is necessary.
Then the following treatment options come into question:
- Conservative therapy:
If a new ganglion has emerged, it can be temporary Immobilization and Protection of the joint in connection with the Taking anti-inflammatory pain relievers or Cortisone lead to regression. - Operative removal:
If the ganglion has existed for a long time, conservative treatment often does not lead to success. Then the therapy of choice is the one Removal of the ganglion in one operation, mostly under local anesthesia. As a rule, the joint can then be moved again immediately after the operation. An operation can at the request of the patient, also for aesthetic reasons be performed. - Puncture:
There the doctor pricks the ganglion, to drain the contained liquid. Then will Cortisone into the resulting cavity injected to reduce the likelihood of the ganglion forming again. Still it is The risk of relapse with this therapy is relatively high.
Can an ointment help?
Ointments are not drugs that can heal a ganglion and its cause. Pain relieving ointments can be used when a ganglion causes pain from pressure on joints.
Products such as horse ointment and arnica products are often used. These can alleviate any inflammatory processes, but do not lead to healing or shrinking of the ganglion.
Again and again Voltaren-Emulgel® is recommended against the irritation. Unfortunately, we have not been able to research any data regarding the effectiveness.
Can you crush a ganglion?
A ganglion is a benign soft tissue tumor that is filled with fluid. If a ganglion causes discomfort, the family doctor should be seen and possibly a referral to a surgeon should be made. You should never crush a ganglion yourself. It is not a simple pimple, but a more complex form of a cyst.
If a ganglion is to be removed, this must be done under sterile conditions, i.e. surgically, as otherwise inflammation can occur in the affected area.
Which doctor treats a ganglion?
If you discover a nodular change under the skin on your hand or foot, you should first consult your doctor so that he can examine the structure beforehand. If the general practitioner suspects or confirms a ganglion, an orthopedic surgeon and surgeon can be considered as specialists.
The family doctor issues the relevant referrals for the specialists. In particular, if the patient wishes to have the ganglion removed, a presentation to a surgeon is indicated.
What to do if a ganglion has burst
If a ganglion bursts, inflammation, bleeding and renewed swelling can develop in the affected area. Most often, sudden ganglion rupture is harmless and does not cause discomfort. However, if signs of inflammation such as reddening, warming, swelling and impaired mobility in the ganglion area occur, a doctor should be consulted.
A doctor's visit is also indicated if pain or bleeding occurs after a ganglion burst.
These home remedies can help with a ganglion
If a ganglion is causing pain or showing signs of inflammation, conservative home remedies can be used to relieve the discomfort. Comfrey ointments and creams or tinctures that contain arnica are popular. Many older patients report a positive effect of horse ointment and arnica. Healing clay paste, ginger and potato slices can also be placed on the ganglion to alleviate possible swelling.
If there is a ganglion on the dorsum of the foot, baths can improve possible symptoms.
Healing clay for treating a ganglion
Healing clay is a popular alternative remedy that has numerous uses. In the case of ganglia, healing clay paste or compresses can be placed on the ganglion or wrapped around the area to relieve the symptoms.
If the person concerned has pain or signs of inflammation, the applications can lead to an improvement in the symptoms.
Further information is available under our topic: Healing earth
Application of horse ointment
In addition to herbal extracts and arnica creams, horse ointment is a popular herbal remedy for treating a ganglion. Horse ointment does not heal or disappear the ganglion. However, horse ointment can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Horse ointment contains rosemary, camphor, arnica, fennel and ginger oil, which are some valuable anti-inflammatory agents. In particular, if a ganglion is pressing on joints or tendons, the anti-inflammatory ointment can be used so that those affected can continue to actively move their hands or feet.
Further information is available under our topic: Horse ointment
forecast
A ganglion is not a dangerous disease. However, some sufferers have Struggling with recurring ganglia for years, because none of the treatments can guarantee a permanent removal: after a puncture, a ganglion recurs in half of the patients after some time, After surgery, the likelihood of relapse is still 10 to 20%.
diagnosis
Often times, the doctor can already pass a ganglion through a Palpation examination diagnose after seeing the Patient's complaints and medical history (anamnese) asked Has.
If there are other possible causes for the swelling, a Ultrasound examination beeing confirmed. In the ultrasound can also one possible osteoarthritis or injuries can be made visible as a trigger for the ganglion.
If, however, the Suspicion is that a real tumor could be present, will usually be a Tissue sample (biopsy) removed.
Before surgical removal of the ganglion, a MRI of the respective region (e.g. hand, knee, foot, etc.) to determine the exact location and extent.
When does an MRI need to be performed on a ganglion?
The basic diagnosis of a ganglion is a physical exam and an ultrasound scan. An x-ray can also be done to detect joint damage from the ganglion.
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is not a standard imaging method for ganglia, since most ganglia are easily recognizable from the outside and easily palpable. An MRI is basically only needed if the attending physician suspects further joint damage or if it is a very small ganglion in the joint.
frequency
A ganglion usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 40 on, but it can
also occur in children. Women are affected about twice as often how
Men.
The most common is an over leg at the wrist before, preferably at the
Outside of the hand on the back of the hand. Ganglia are somewhat less common
on the flexor side of the hand in the area of the Saddle thumb joint or to the
Finger joints.
In rare cases, a ganglion also occurs on Back of the foot or on knee on.