Treatment of the herniated disc
therapy
As with many diseases, the disc prolapse a conservative and operational Treatment (OP) open.
Which Form of therapy (what can be done) should be used, must always be decided individually. At this point both will Forms of therapy briefly presented.
Which treatment is best for you should not depend on your sympathy for a form of therapy. Together with your doctor, you should work out the best way to treat your herniated disc.
Most herniated discs can be completely healed by conservative measures. Today, an operation is only used in a smaller proportion of cases.
You can find more extensive information about the OP under our topic: OP of a herniated disc

Conservative treatment of herniated disc
Except for acute, median incidents that lead to major impairments and can imply motor and sensory failures, the herniated disc is generally initially treated conservatively.
First, the Spine relieved by bed rest. This immobilization can last for four to six weeks. Bed rest may cause discomfort (Back pain) in the field of Lumbar spine occur by something called a Stepbed can be softened.
Is the Cervical spine Affected by a herniated disc, the immobilization can be about a Neck seal.
Please also read our topic: Treatment of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
Physiotherapy / physiotherapy
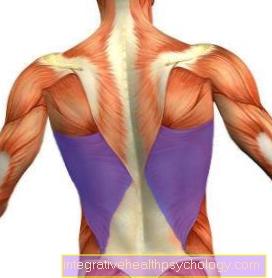
Through the Strengthening the back muscles As part of physiotherapeutic measures, improved muscular guidance of the spine is achieved, which ultimately also results in less stress on the Intervertebral disc causes. The physiotherapeutic measures in the context of the conservative treatment of the herniated disc represent a very important area.
For this we have developed a completely separate area with our physiotherapist in the team:
More on the subject: Physiotherapy for a herniated disc
Kinesio tapes can also be used for a herniated disc. Tapes help relieve tense muscles in the event of a herniated disc.
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Medication for a herniated disc

Drug therapy does not only play a role in spinal diseases - such as a herniated disc (Pharmacotherapy) play a significant role in the so-called Pain therapy.
With regard to the herniated disc, these are especially the ones not-steroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs, the NSAIDs, like for example:
- Ibuprofen
- Diclofenac (e.g. Voltaren®)
- Indomethacin
or - COX-2 inhibitors
- Celebrex®
- Arcoxia®,
which are used and are usually administered as tablets, capsules or suppositories or in the form of intramuscular injections or intravenous infusions in the case of a herniated disc.
An anti-inflammatory, decongestant (= anti-inflammatory) Have an effect in a special way Corticosteroids (cortisone). They should only be taken under medical supervision and only prescribed by the doctor if the individual requirements are met. Cortisone can also be used by a doctor Cortisone syringe be injected.
Find out more about the topic here: Cortisone therapy for a herniated disc
For the above-mentioned drug treatment of the herniated disc, drugs for muscle relaxation (Muscle relaxantse.g. Sirdalud®), which can potentiate the analgesic effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Relaxants alleviate some of the symptoms by releasing muscle tension.
If the herniated disc has progressed so far that the damage has already spread to the peripheral annoy aligns, as is the case, for example, in the context of a nerve root impairment Antidepressants or anticonvulsants raise the pain threshold.
Chronic pain that is constantly present and no longer fulfills the actual function of the pain, the warning function, can be caused by a doctor administered Opiates or opioids, for example in the form of a so-called pain plaster, are prescribed.
Taking medication over a certain period of time can lead to sometimes considerable side effects. Self-therapy should therefore be avoided in any case.
Pain therapy for herniated discs always belongs in the hands of a doctor. Only he can prescribe the correct treatment by assessing the individual extent of the disease.
Cortisone
Cortisone is a commonly used drug for back pain. For this, it is usually injected intramuscularly in the area of the hips / buttocks, which is also done by the family doctor in many places when patients come with severe back problems. Cortisone also plays a crucial role in the treatment of herniated discs. Cortisone is one of the so-called glucocorticoids, which among other things have an anti-inflammatory effect. Since inflammation also provokes pain, cortisone can prevent or alleviate the occurrence of pain. In addition to reducing inflammation, cortisone causes the tissue to decongest so that less pressure is exerted on the nerve root and the symptoms of the herniated disc are reduced. Cortisone does not necessarily have to be used as a syringe, but can also be used in the form of tablets or infusions.
Exercises and physiotherapy

The conservative therapy options are now indicated in 90% of cases. Only 10% of herniated disc patients ultimately have to undergo surgery because of its severity or failure to respond to conservative treatment. This is why physiotherapy with appropriate exercises is very important.
In general, all exercises that stabilize posture, improve coordination and are gentle on the spine are suitable. Since the herniated disc is a sign of wear and tear, it is also important to counteract wear and tear by relieving the strain on the intervertebral discs by loosening tension. The relief of the intervertebral discs also plays an important role. The intervertebral disc is like a kind of sponge that can soak itself up with water and nutrients in a healthy state. This is no longer possible due to compression, which also results in a herniated disc, so that special exercises in the case of a herniated disc are designed to ensure the supply of nutrients for part of the intervertebral disc through relief.
Special massages, water aerobics, endurance sports, Pilates exercises, special back exercises and muscle building exercises can achieve this effect.
Mobility is improved through the stretching and stretching exercises. In order to strengthen the muscular apparatus and thereby give the spine more stabilization, it is important to train both the abdomen and the back. Endurance sports include hiking, Nordic walking, swimming, cross-country skiing and long-term cycling. When swimming, you should only avoid backstroke or crawl and breaststroke. The advantage, as with underwater gymnastics, is the fact that the joints and spine are less stressed under water.
Please also read our topic: Exercise after a herniated disc
In general, the purpose of sporting exercises is to build up the muscles and release tension. Furthermore, the aim of physiotherapy is to stimulate the metabolism and circulation. On the one hand, this also promotes the nutrition of the intervertebral disc and regeneration processes and, on the other hand, the body can offer more resistance to tiring work through strengthened muscles and endurance, so that the physical overload does not have a damaging effect on our spine. The perception training should be integrated into the therapy in addition to strength training against the background that you gain awareness of what is good for your back and which movements or activities are not beneficial in the healing process of a herniated disc.
Often the patients are treated with painkillers in the initial phase of physiotherapy. But not only the exercises are important, but also the consideration of whether something should be changed in everyday conditions. It can be very helpful to have a desk chair, desk, keyboard, etc. adjusted to improve posture. In addition, patients must be aware that they should no longer be lifting heavy loads in everyday life.
Read more about the topic here: The ideal office chair after a herniated disc.
Sports that exert compression or strong pressure on the spine (e.g. horse riding) are contraindicated in the case of a herniated disc. Rapid turning movements or abrupt hyperextension should also be avoided. This includes, for example, playing tennis or squash. It used to be the assumption that after a herniated disc one should take it easy by resting. However, this attitude has long been outdated, because it has been proven that active muscle strengthening and relaxation of tension can alleviate the symptoms of the herniated disc and have a positive effect on the recovery phase. In addition, one's own activity promotes nutrition for the intervertebral disc; Sitting for long periods of time or the outdated assumption of calm rest, on the other hand, have a negative impact on disc nutrition and thus healing.
In conclusion, it can be said that physiotherapy with a variety of approaches and exercises enables individual conservative treatment of a herniated disc.
Because the topic is so extensive, we have set up a completely independent topic that deals with physiotherapy and exercises after a herniated disc.
Read more about this under our topic:
- Physiotherapy for a herniated disc
- Exercises for a herniated disc
General information on exercises for a herniated disc
Sport plays in the Therapy of herniated disc an important role. The following shows which exercises are suitable for strengthening the back muscles. In general, regular breathing and calm execution should be ensured.
The exercises are repeated daily, whereby the pain threshold is not exceeded.
Exercises for the cervical spine
A relaxed sitting position is assumed on a stool. The arms hang down on both sides, the sternum is moved forward and the navel is drawn in. The gaze is directed forward and a slight double chin is made. Then the shoulder blades rotate backwards or forwards in a slow, circular motion.
The exercise is repeated ten times in both directions. In this way, blockages in the cervical spine can be released and the muscles can relax.
Another Exercise for a herniated disc of the cervical spine serves to strengthen and mobilize. The right palm covers the auricle, while the left palm lies relaxed on the left thigh. The head now actively presses against the right hand for five to ten seconds.
The same is repeated with the left side.
The exercise can also be done forwards and backwards. To do this, one hand exerts counter pressure on the forehead or both hands exert counter pressure on the back of the head while the head pushes backwards or forwards.
Exercises for the lumbar spine
To relieve and relax the back, the upper body is placed on a thin surface and the lower legs are placed on a large exercise ball or on the seat of a chair.
A right angle is formed between the upper body and thigh and between the thigh and lower leg. The exercise should be done for about ten minutes.
- The following exercise serves to mobilize the lumbar spine. At the same time, the abdominal muscles are trained.
In the supine position, the legs are in the 45 degree angle angled and feet resting on the floor. First, the navel is moved inwards for about five seconds and the lumbar spine is pressed to the floor. Then the countermovement takes place, also for five seconds. While the navel is moved outwards, the lumbar spine goes slightly into the hollow back. Each movement is repeated five times. - In the next exercise, the lumbar spine is also mobilized. This also has the side effect of an improved supply of nutrients. The feet are repositioned on their back at a 45-degree angle on the floor. Both knees are now tilted to the right as far as possible towards the floor. The position is held for five seconds. Then the same movement to the left takes place. This movement is also repeated five times.
laser

Treatment of a herniated disc under the Use of a laser device is a minimally invasive procedure, the under local anesthesia can be carried out and about 25-35 minutes lasts.
The indication for laser therapy is that the herniated disc fresh must be and not too complicated should be.
The goal of this therapy option is Volume reduction of the intervertebral disc around the pain symptoms, which i.a. caused by compression of the surrounding nerves caused by the prolapse of the intervertebral disc. The principle is with one special diode laser implemented.
The procedure is as follows: First the corresponding intervertebral disc must be over Puncture of laser technology be made accessible. This puncture will under CT control performed to ensure that the right intervertebral disc punctured has been. The intervertebral disc consists of one fibrous ring structure (lat. Annulus fibrosus), in the middle of which a gelatinous core (lat. Nucleus pulposus) lies. The laser device is up in the Nucleus pulposus advanced; get there Flash-like rays in the infrared range submitted. At very high temperatures, these laser beams vaporize the gelatinous core, so that the whole intervertebral disc shrinks. The effect is also called in medicine "Shrinking Effect" designated. In principle, the laser beams can also be used in Annulus fibrosus release. The main thing is that due to the shrinkage the Compression of the surrounding nerves will be annulled.
In addition to reducing pain, laser treatment can also provide a Stabilization of the fiber ring structure the intervertebral disc can be restored, as small tears in the fiber ring can close again. The pain reduction is based on the Destruction of the pain fibers. In addition, certain areas can be affected by the heat Transmitter substances (Glutamate, substance-P etc.) no longer manufactured so that the transmission of pain stimuli no longer works.
Peridural Infiltration (PDI) and Periradicular Therapy (PRT)
In the peridural infiltration (PDI) or periradicular therapy (PRT) of the herniated disc analgesic, anti-inflammatory and tissue-sclerosing drugs are administered to the painful nerve root with millimeter precision under computed tomographic control. Thereby it comes to a containment of the taking place around the nerve root "mechanical inflammation"and to a decongestion of the nerves. In the case of herniated discs, a shrinkage of the displaced disc tissue can sometimes be observed.
While we the PDI in the case of a herniated disc, preferably in the lumbar spine area, the PRT rather for them Cervical spine.
The intervention does not provide a replacement operative therapy but in the case of pain resistant to other conservative treatment, if there is no or only minor neurological pain Symptoms from the herniated disc can be used as an alternative to surgery.
Even after pain Intervertebral disc surgery In many cases, PRT can achieve freedom from symptoms or symptoms. The use of computed tomography is not absolutely necessary for this type of surgery in the lumbar spine area.
Such treatments have recently become possible in an open MRI.
PDI
PDI is one of the conservative treatment a herniated disc and stands for "Peridural Injection".
The indication for a PDI is made if either other conservative methods do not work or if the patient is after an operation still in pain. The PDI is generally not only used in the treatment of a herniated disc, but also in the Therapy of nerve root irritationthat are independent of a herniated disc.
Before the Lumbar region about a Local anesthetic the skin must be numbed thoroughly disinfected and covered in sterile conditions become. The PDI is usually while sitting, in the so-called "Hunchback" posture, or in side position carried out. The needle will between the spinous processes of the Vertebral bodies stabbed. The spinous processes must be palpated beforehand.
It is also important to know that the spinous processes are consecutive vertebral bodies depending on the height The spine stand different to each other. They are in the lumbar area approximately horizontal; in the Thoracic area however, rather roof tile-like sloping. In any case, the hollow needle must be used carefully up to the epidural space, the space between Dura mater and periosteum (Periosteum), be advanced. It will Ligamentum flavum ("Yellow ribbon") pierced, which spans between the spinous processes of the vertebral bodies. The whole thing goes under CT control to make sure that the needle is really in the right place. Now that the needle is in the epidural space, you can Injected drug and spread out in the same room.
The drug is mostly a Mixed narcotics out cortisone and salt. That includes cortisone works anti-inflammatoryi.e. decongestant and anti-inflammatory. The salt, on the other hand, dries out the prolapse, i.e. the protruding intervertebral disc, so that it becomes shrinks and the Relieves nerve compression. That reversible nerve compression was the cause of the pain symptoms and the paresthesia, which decreased by the PDI are. Until freedom from pain occurs, you have to up to 6 injections take place even if the effect is sometimes sometimes even after the first injection of the local anesthetic is noticeable. The whole thing can be used as a "Single" can administered or one lays a catheter.
Complications are with a PDI rather seldom; nevertheless, there are potential risks. Through the Sympathetic block can it to one Drop in blood pressure come, the injection area may become ignite and the Spinal cord can be injured when puncturing above L2. Since in Epidural space / peridural space next to fat and connective tissue a Venous plexus there is a risk of this puncture. In the case of an intravenous location, intoxication (poisoning) can result from the local anesthetic. Duroperfusion with the needle can cause a increased loss of cerebrospinal fluid lead which is clinically proven to be Headache expresses. In addition, is a allergic reaction possible.
In general, it remains to be said that the peridural injection no replacement for surgery is, but can possibly lead to freedom from symptoms that a Surgery is no longer absolutely necessary is.
PRT

PRT is a "periradicular therapy" that is similar to the procedure of peridural injection.It is also used when patients suffer from a herniated disc, but also when they complain of other back pain that mainly radiates into the extremities. PRT is the most common method used to treat herniated discs. It is of great importance, among other things because studies show that the conservative PRT procedure is in no way inferior to the surgical procedure, especially in terms of sustainability.
A drug is injected onto the nerve root under computed tomography control (lat. radix = Root). The drug is a mixture of a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory drug.
Bupivavain or Scandicain can be used as a local anesthetic and Triamcinolon or Lipotalon® as a corticosteroid. As an alternative to the CT check, the PRT can also be monitored by magnetic resonance imaging. The needle can be positioned even more precisely, in the millimeter range. Since the needle has to be very fine for this, the drug can only be injected in small doses. Recently, due to the lack of radiation exposure, the MRI has also been used for control. The advantage is that the organs are less irradiated and thus stressed. However, the time required is greater and you have to use other material so that metal-containing objects must under no circumstances be in the immediate vicinity of an MRT device.
In PRT, the drug is injected directly onto the nerve root, where it unfolds its effect, which is very similar to that of PDI: decongestant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic. The irritated and compressed nerve has space again due to decongestion and the symptoms are reduced. In addition, thanks to the local anesthetic, the nerve irritated by a herniated disc no longer responds as strongly to the mechanical irritation, which also results in pain relief.
Ideally, a total of 2 to 4 treatments should be carried out with an interval of one week.
By then, there should have been an improvement. If this is not the case, you can inject a few more injections if necessary, but surgery should generally be considered under this aspect, as the herniated disc is too strong for PRT therapy or the location is too unfavorable.
Read more about this under: PRT
Infusions for a herniated disc
With the infusion become two primary goals pursued: firstly, the pain should be relieved and, secondly, the inflammation should be reduced. In general, conservative drug treatment of a herniated disc can be applied diverse ways respectively. In addition to taking tablets or injecting i.m. (= intramuscular) intravenous infusion is an often chosen variant.
Get routine Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (= NSAID) used. These include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin or COX-2 inhibitor (COX = cyclooxygenase enzyme). Corticosteroids are used for anti-inflammatory effects administered by infusion. Because a herniated disc is common with muscular tension Muscle relaxants such as Siralud are used to relieve tension. You can also use the infusion Vitamin preparations can be added.
The infusion is usually associated with inpatient treatment.
Cure / rehab after a herniated disc

The Cure or rehab (Abbreviation for rehabilitation) is one established therapy option after a herniated disc. There are many clinicswho have specialized in the treatment of the disease that has become very common.
As a rule, the cure begins after one Herniated disc surgery; about 4 to 6 weeks after that. It is among doctors, however partly discussedwhether to start rehabilitation earlier. Depending on the clinic in which a patient begins his rehabilitation, the exact timing of the start and course of the cure / rehab vary.
First and foremost, as with physiotherapy Strength, endurance, flexibility and awareness training on the therapy plan. It is important to have the muscular apparatus in the body after the operation Abdomen and back to rebuild and strengthen in order to regain adequate stabilization, which also with a good one Body - especially Back posture goes hand in hand. A cure includes several measures and can individually adapted to the patient become. On the one hand, physical therapy exercises are also the Back school makes sense. But water and relaxation therapy are also proven rehabilitation therapy approaches. The water aerobics has the advantage that underwater the Joints and also the Spine relieved are and therefore all muscle building exercises performed at the same time gentle are. It is also common Everyday training integrated into a cure. This means the fact that patients conscious movement, no longer lifting heavy loads or avoiding jerky movements in the back area.
The corresponding exercises of the cure / rehab should be provided 3 to 4 times a week for 30-60 minutes be performed. Usually you get an individual schedule with your own "cure program" for the time of your rehab.
The goal of rehab is that Pain relief, one better stability and agility to attain and on a back-friendly posture to pay attention. In addition, the return to everyday life plays a more or less important role depending on the patient's condition.
Studies have one on this definite short-term improvement proven symptoms. Also that the Return to everyday life is relieved, has been proven in studies.
For more information on this, read our topic: Rehabilitation after a herniated disc
Duration of treatment
The duration of the treatment of a herniated disc cannot be given across the board, as this depends largely on the severity of the herniated disc, the constitution of the patient and the type of treatment.
The treatment usually takes place over a period of several weeks. In the conservative therapy that is mostly used, injection therapies or the like are usually used in the acute phase of the herniated disc. The acute phase usually lasts at least a week, but can also extend over six weeks. Beyond the acute phase, regular physiotherapy is essential, which should be continued for several weeks after the herniated disc in order to strengthen the back muscles and thus relieve the intervertebral disc.
What else can you do?
What to do with a disc prolapse everything else you can do is very diverse and start with physiotherapy, medication, sport and end with the operation.
Each treatment is not "off the shelf", but has to be tailored to the individual case and what you can do in particular depends crucially on the leading symptoms of the person concerned.
We have everything on this topic under "Herniated disc - what to do?" summarized.
Taping for a herniated disc
The so-called Kinesio tapes when treating a Herniated disc. Even if you are not able to heal a herniated disc, the tapes help to relax the muscles and thus the Lumbar spine pain to lower.
Operation of a herniated disc

Surgical therapy is always carried out when the herniated disc is so advanced that it causes massive discomfort, especially when neurological symptoms such as paralysis or incontinence occur.
Surgery is usually performed in neurosurgery or orthopedics departments. Operations on the spine can be carried out either openly or in a minimally invasive manner. The latter method is gentler on the patient, but takes a little longer but shows a better cosmetic result because only small skin incisions are necessary.
The minimally invasive procedure requires certain anatomical conditions. If visibility does not allow such an operation, an open back operation must be performed. The aim of every operation is to eliminate the herniated disc. As a rule, the intervertebral disc is removed or the part that has emerged between the vertebral bodies. In most cases, the two vertebral bodies have to be stiffened afterwards, as there is no longer sufficient protection between them and bone friction between the two vertebral bodies is prevented by stiffening.
As a rule, the patient does not notice much of this stiffening after the intervertebral disc operation in his everyday movements, since the other vertebral bodies can take over the movement of the stiffened joint. The stiffening is usually carried out with plates or screws attached to the side of the vertebral bodies. The operation is performed frequently, but due to its location and proximity to nerves and spinal cord, it is always risky. Postoperative swellings in the area of the vertebral bodies can lead to compression of the spinal cord with symptoms of paralysis.
Furthermore, an injury to the structures accompanying the spine can occur during the operation and make corresponding extended operations necessary. After the operation, the patient should first wear a corset to protect the joints and restrict heavy lifting and bending in the first few weeks.
Every spinal surgery is followed by a physiotherapeutic treatment stage, which can be carried out for different lengths of time. There are now approaches to completely replace the intervertebral disc. For this purpose, cartilage cells are grown and multiplied outside the body. Then, in a second surgical procedure, the replacement intervertebral disc is reinserted between the corresponding vertebral bodies.
Both this and the stiffening process show varying degrees of success. As a rule, neurological symptoms can be alleviated. However, patients rarely become completely pain-free, so that supplementary pain therapy is often indicated.
Read more on the topic:
- When should a herniated disc be operated on?
- Operation of a herniated disc
- Operation of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
- Operation of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine










.jpg)