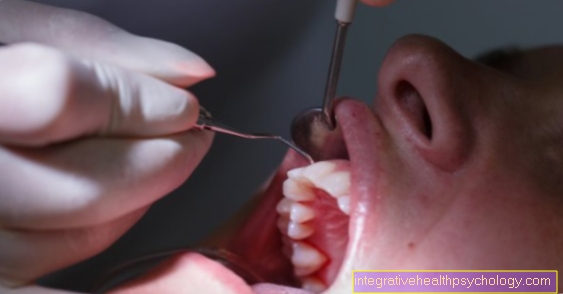
Teeth whitening
synonym
Teeth whitening, bleaching
English: whitening
definition
Bleaching is the artificial whitening of the tooth surface using various technical and chemical processes. Discolored teeth are thus given a brilliant white again.

Causes of tooth discoloration
The older a tooth gets, the longer it is exposed to external influences such as coloring foods. So a tooth goes through a natural darkening process. This darkening can be accelerated accordingly with food and drinks. Frequent drinking of coffee and tea can discolour your teeth. Smoking also stains teeth darker.
But teeth can also be discolored through caries and tooth inflammation. The color of the teeth is then mostly yellowish-brownish. As a rule, all teeth of the dentition discolor the same, so that the discoloration is initially not noticeable to the viewer. Only a comparison with the natural tooth color (e.g. by placing a sample color palette next to the tooth) makes the severity of the discoloration clear.
Furthermore, discoloration can also occur if the tooth pulp dies (e.g. in the case of nerve inflammation and subsequent root canal treatment). Most of the time, the resulting discoloration cannot be seen in the entire dentition, but only on the affected tooth.
Whitening products
In many cases, a hydrogen peroxide base is used for bleaching.
Hydrogen peroxide molecules can get into the tooth structure (Tooth enamel and dentin) penetrate and release oxygen radicals there. Radicals are molecules that are very reactive and quickly bond with other molecules.
The oxygen radicals released in the tooth substance tend to react chemically with color particles. The consequence of this chemical reaction is that the properties of these particles are changed and they therefore appear colorless.
In the dental practice, much higher doses of tooth whitening products are used. Since they have a particularly corrosive effect on the gums and the oral mucosa, they may only be applied by the dentist himself or his trained specialist staff.
Most of these agents are applied to the tooth and then irradiated with short-wave light. This intensifies the lightening effect.
There are several products that can whiten teeth, the simplest of which can be used by the patient at home.
The variety of whitening products offered can be found in the following overview:
Whitening set
In addition to the dentist's whitening, there are also over-the-counter whitening kits. The principle is comparable to the dentist's set, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide is variable, which is significantly lower with the over-the-counter bleaching kits.
The set also includes a plastic splint for the upper and lower jaw, which, however, were not made individually and therefore may not fit well or not at all. The danger here is that the splint closes so poorly that the gums come into contact with the hydrogen peroxide preparation and are irritated or injured as a result.
Therefore, special care must be taken when using it. In order to use a suitable preparation individually, a consultation with the treating dentist can clarify and thereby reduce the risk of complications.
Whitening strips:
Handling: Strips are glued to the front of the teeth.
Comment: Complicated handling of the plastic strips and thus they seem to be less suitable for domestic use.
Whitening gel:
Handling: Gels are brushed on
Every whitening gel offered works in principle in the same way, they only differ in the concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2o2).
Because of the different high concentration of hydrogen peroxide, whitening gels are divided into two main groups:
- One is for use at home
- the other may only be used in the dental practice by trained staff.
For home use, whitening gel is offered, which has an oxidative or reductive effect on the color particles within the tooth substance. This means that the gel either releases or absorbs oxygen. In general, an oxidative whitening gel has a stronger and longer-lasting effect on the teeth, it is more effective. The user can independently apply the gel to the rows of teeth and decide for himself how often the procedure is repeated.
Since the chemical processes of teeth whitening take time, the gel should take effect for a few hours before it can be wiped off.
In order to avoid damage to the gums and / or the oral mucosa, it is recommended to place a splint made in the dental laboratory over the rows of teeth.
In the dental practice, much higher doses of bleaching products are used. The high concentration of hydrogen peroxide in the gel ensures that the product has a strong corrosive effect on the tissue around the tooth. For this reason, it may only be applied by a dentist or his specialist staff.
In addition, a laser or a light source that enhances the whitening effect of the whitening gel is often used.
Lightening pens:
Handling: Various marker pens similar to highlighting pens. The teeth are "painted".
Comment: The highlight pens all do well in relevant tests.
A whitening pen is a whitening product that can be used on the go. In terms of shape and size, the pen is reminiscent of a lipstick, which is why it fits in every handbag or pocket. The structure of the pen consists of an applicator brush and a reservoir in which a gel containing hydrogen peroxide is contained. The concentration of the bleach is 0.1%, which is why it is freely available and falls under cosmetic products.
You don't even have to clean your teeth in advance to use the pen. They are simply dried with a handkerchief so that the gel can be applied with the pen. Only when the gel has dried on can the lips be closed again so that the hydrogen peroxide does not come into contact with the gums and damage them.
The mouth should be rinsed after use.
Whitening aligners:
Handling: The whitening product is poured into the splint.
Comment: The rails impress with their ease of use and their comparatively good results. They do best on the tests.
The splint is made individually from plastic in a dental laboratory and is optimally adapted by taking impressions and making plaster models. A hydrogen peroxide preparation in gel form is inserted into these splints and applied to the teeth. After a certain exposure time, strictly following the instructions of the dentist, the teeth can be lightened sustainably.
Care should be taken that the hydrogen peroxide does not come into contact with the gums, as it damages them. After inserting the splint, excess should be removed quickly. The recommendation for use with the splint is around 1 - 2 times a year and should not be carried out more often in order not to damage the teeth.
If the application is carried out more often, the teeth can become very sensitive to pain and cause symptoms due to cold stimuli that did not cause any symptoms before the treatment.
Bleaching (tooth) cream:
There are some whitening toothpastes on the market that promise to whiten teeth. But how gently can a toothpaste whiten teeth?
The mechanism of all whitening toothpastes is to use a certain particle size to remove the upper layer of the discoloration and thus to whiten the teeth. The problem here is that the particles in the toothpaste are so large that, in addition to the discoloration, they also remove the tooth enamel and thereby weaken the tooth. If this toothpaste is used too often, the enamel layer becomes thinner and thinner and the teeth become sensitive. The sensitivity of the teeth increases because the protective coating in the form of enamel is removed and the dentin layer comes to the surface.
Read correspondingly: How can you rebuild tooth enamel?
To avoid this, you should pay attention to the RDA value when buying toothpaste, which indicates the particle size within the toothpaste. Unfortunately, only very few manufacturers give the RDA value on the packaging today. Internet research and consultation with the dentist can help in this case.
A value of 0-40 is considered to be slightly erosive, between 40 and 60 as an average value, from 60 and up the toothpastes are very erosive. Toothpastes with an RDA value above 60 are therefore not recommended.
The frequency of once a week for a toothpaste that is moderately abrasive and once every two weeks for a toothpaste that is highly abrasive should not be exceeded.
The use of the whitening toothpaste is not recommended for patients with very thin enamel, as they are more sensitive and less protected than with a thick layer of enamel. A consultation with the treating dentist makes sense to use the optimal product for the individual situation.
Bleaching lamp:
A relatively new way to whiten teeth is with the whitening lamp. The lamps emit bluish, cool light. First, a whitening agent is applied to the teeth to be bleached. The light from the lamp then activates the gel and should thereby achieve a more efficient result.
However, the gel consists of hydrogen peroxide, which has been proven not to be activated by light (regardless of the wavelength). Furthermore, these lamps produce a lot of heat that acts on the teeth and can damage them. At the latest from a temperature of 42 degrees Celsius, the blood and nerve vessels inside the pulp marrow perish and the tooth dies. We therefore advise against using the whitening lamps.
Home whitening:
Home bleaching is a popular variant of many patients in order to whiten their teeth about 1 to 2 times a year. Before that, a special plastic splint was made in the dental practice by taking an impression, into which the bleaching preparation is inserted without the rest of the oral cavity coming into contact with the agent. The preparation that is mostly used is not hydrogen peroxide, but carbamide peroxide, which is much milder and carries fewer risks. Hydrogen peroxide is about three times as strong as carbamide peroxide, which is why the wearing time of the splint with the preparation is longer with carbamide peroxide.
In the case of teeth that have already been bleached, there should be about a year until the next use so as not to strain or damage the teeth. Too frequent use of home bleaching can make the teeth much more sensitive, so that cold stimuli in particular tend to lead to pain.
Home bleaching can whiten teeth by a maximum of two tooth shades. Larger jumps are not possible with the carbamide preparations.
How does bleaching with hydrogen peroxide work?
Regardless of whether it is about bleaching clothes, hair or teeth, hydrogen peroxide is the agent of choice in each of these cases.
Hydrogen peroxide is made up of a compound of hydrogen and oxygen. In the dental field, products with a concentration that does not exceed 0.1% are freely available. These belong to cosmetic products.
All higher concentrated preparations are subject to dental use. The dentist uses concentrations between 10% and 40%, at which the gums must be protected in order not to come into contact with the hydrogen peroxide. Ingestion of the preparations can lead to vomiting and burns to the esophagus. Therefore, these concentrations are far too dangerous for home users and should be carried out under medical guidance and supervision.
The dentist distinguishes between in-office bleaching, in which a specially made bleaching tray is used in the practice under supervision, and home bleaching, in which the patient carries out the application at home.
Bleaching sticks, toothpaste and the like, which are among the cosmetic products, are commercially available. The low concentration of these products does not mean that they can be used excessively, as these can also damage the teeth. The instructions for use must therefore be strictly followed; if anything is unclear, the attending dentist should be consulted.
What should be considered before whitening?

It is important to have a whitening performed by a dentist and first to have the health of the teeth to be bleached checked. The dentist should check that the teeth to be bleached do not have caries and that the surrounding gums are not irritated, inflamed or affected by periodontal disease. In addition, the dentist should be able to assess what is causing the tooth discoloration (normal age-related discoloration, metabolic-related, discoloration from food). Only healthy teeth should be bleached. Before the teeth are bleached, the teeth to be bleached are first cleaned. To do this, the tooth surfaces and the adjacent gum areas are cleaned with a powerful water jet. For this purpose, the gums are lifted slightly with an instrument in the regions adjacent to the tooth and the gum pockets are washed under. Whitening can only begin after cleaning and following a health check.
Is teeth whitening bad for your teeth?
In general, using hydrogen peroxide is a cosmetic treatment that involves risks. Regardless of the product and its concentration, hydrogen peroxide causes the fluid contained in the teeth to be withdrawn. This dehydration implies that the teeth are more sensitive to thermal stimuli. Cold and heat stimuli, which did not present any problem before the treatment, can lead to pain stimuli after the application.
In the case of insensitive teeth, the infrequent use about once a year does not result in any subsequent symptoms, while the treatment of pain-sensitive teeth is not advisable. Whether a tooth is robust against external stimuli depends on the thickness of the top layer of the hard tooth substance, the enamel. If the enamel is particularly thick, bleaching usually does not cause any problems; with thin layers of enamel, a single application can lead to severe pain.
Hence, it cannot generally be said that whitening is healthy or unhealthy. Nevertheless, the application should be weighed with caution. In order to be sure that the application is suitable, an informative discussion should be carried out beforehand with the treating dentist so that he can select the optimal preparation and the appropriate application for the patient so that a sustainable, gentle whitening is achieved.
Risks / side effects of teeth whitening
Shortly after bleaching, the teeth may become uncomfortably sensitive, which is particularly noticeable when eating hot or cold food and drinks.
The reason is that water is withdrawn from the tooth during the whitening treatment. Only later is more water stored again, the hypersensitivity then decreases.
Furthermore, allergic reactions of the gums to the applied gel can occur during the treatment. In this case, the treatment should be stopped and the gel that has got onto the gums should be rinsed off immediately. Alternatively, another chemical substance can be used for whitening.
Furthermore, it must be noted that during treatment with the chemical in the mouth, a not inconsiderable proportion is swallowed by the patient with the saliva during and after the treatment and thus gets into the stomach. This can lead to irritation and inflammation of the stomach lining, nausea and vomiting, and allergic hypersensitivity reactions.
How much does whitening cost?
In the dental practice, care must be taken to ensure that the gums, tongue and oral mucosa are not affected by the agent containing hydrogen peroxide.
The preparation for teeth whitening is therefore very extensive, and the whitening costs are accordingly high.
Furthermore, a distinction is made between different methods in dental accounting:
- The so-called in-office (or power) bleaching causes costs of around 250 to 600 euros for the patient. In "power bleaching" high doses are used. In order to protect the gums from possible damage, a cofferdam must be placed before the actual treatment. Then the whitening agent is applied to the teeth and irradiated with short-wave light.
The application takes between 15 and 45 minutes and can be repeated if the result is insufficient.
- In order to achieve faster whitening effects, it is possible to irradiate the teeth with a laser during the bleaching, this is referred to as laser bleaching. The cost is around 600 euros.
- With so-called “home bleaching”, a splint that is individually adapted to the patient's jaw is produced in the dental laboratory. This dental splint is coated at home with a gel containing hydrogen peroxide and placed on the rows of teeth.
As a rule, around seven applications, even five hours, are sufficient to remove slight discoloration.
The costs for a visible result with home bleaching (usually several applications are necessary) are around 250 to 400 euros. Depending on the product chosen, the purchase can be more or less expensive.
In addition, as already mentioned, a dental splint has to be made in the laboratory.
Alternative whitening methods
Not every whitening has to be done by the dentist. Nowadays there are numerous products in pharmacies and drugstores that promise to whiten teeth using very different methods. An important factor, especially with toothpastes, is an abrasion mechanism, which is based on the assumption that the discolored surface of the tooth is removed by daily brushing due to abrasive additives in the toothpaste. If anything, brushing your teeth has to be done with the same product for weeks and months to achieve a slight effect.
There are also toothpastes and gels that have to be applied to the teeth and work on the same principle as dentist bleaching. Here, substances are added to the toothpaste that remove the coloring agents from the tooth. The effectiveness is limited, however, since the concentration of chemical substances is limited in over-the-counter products.
Here, too, it must be noted that the effects, if they occur, are not permanent and must be repeated at regular intervals. If the user is a wearer of implants or crowns, it must also be noted that the whitening effects between real and artificial teeth are not necessarily identical and that there can be cosmetically unsightly differences.
Also read:
- Home remedies for white teeth
- Diet for healthy teeth
- White teeth from whitening
- White teeth from baking soda
Summary
Bleaching refers to various methods for whitening a tooth or the entire set of teeth.
Teeth become discolored for a variety of reasons. The most common cause is the natural age of the teeth. In the rarest of cases, a young person's tooth color is as white as that of an older person. The intensity of the discoloration can also be influenced.
Excessive consumption of tea or coffee leads to faster darkening of the teeth. Regular consumption of black tea in particular leads to a yellowish-brown discoloration of the tooth enamel. Another important factor is nicotine consumption. Smoking for years makes teeth extremely yellow. In addition, inadequate oral and dental hygiene leads to increasing yellowing and the presence of diseases of the teeth (caries, periodontal disease). If a tooth has to be killed after a nerve inflammation and before a root canal treatment, the tooth enamel usually also turns yellowish-brown and is thus visually different from the neighboring teeth.
Numerous different types of bleaching have now been invented and also tested. The most common methods are chemical bleaching, which involves applying gel to the teeth. The bleaching ingredient is hydrogen peroxide. The reaction between the gel and the surface of the tooth creates hydrogen radicals that strip the tooth of its color and make it appear lighter (oxidative process).
In the reductive procedure, a gel that contains sulfur-containing molecules is also applied to the tooth. These remove oxygen from the tooth, which leads to an apparent light color. With laser bleaching, the chemical process on the teeth is accelerated by a laser beam that is held on the tooth to be treated.
So-called home bleaching is carried out independently by patients at home over a longer period of time. First, an impression of the dentition is made, which serves as a template for a dental splint. This aligner is then filled with chemical gels. The patient has to wear the splint regularly for several hours a day so that a corresponding effect becomes apparent.
With the walking bleach technique, dead teeth are filled with a chemical substance before the final closure and the tooth is then closed. After a day or two, the tooth is opened again and the substance is removed. During this time, the chemical has worked its way through the tooth wall from the inside out and bleached it.
The shelf life of the bleaching result depends on the method chosen, lifestyle and teeth cleaning. If patients limit their consumption of tea and coffee, refrain from smoking, practice regular dental care and have their teeth cleaned professionally by the dentist from time to time, a whitening time of up to 2 years can be expected. This should be followed by re-whitening, which can then be carried out more quickly, less expensively and at lower prices, as the large amount of bleaching agent usually no longer has to be used as with primary whitening.
Bleaching also has risks and side effects. This can lead to irritation of the gums after applying the gel. Treatment of the superficial enamel can also lead to a temporary over-sensitivity reaction of the teeth. Some of the bleaching agent is swallowed by the patient during and after use and, in rare cases, can cause irritation of the gastric mucosa or allergic reactions.
Depending on the method chosen, the cost of bleaching is between 60 and 700 EUR and is not covered by health insurance.