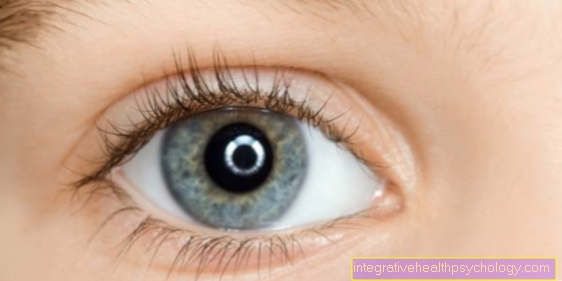
Bruised eyeball
Synonyms
Bruised eyes, blunt bulb trauma, contusio bulbi
definition
By blunt force in the area of the eyeball (Globe) or the eye socket (Orbit) the eyeball bruises.
How common is an eyeball bruise?
Subdivision into slight, more severe, severe eyeball bruises and eyeball tears (Eyeball rupture). However, this is very rare.

Recognizing a bruise in the eyeball
What are the symptoms of a bruised eyeball?
There is pain and, depending on the severity of the bruise, deterioration in vision. Double images are temporarily possible.
The eyelids are reddened and swollen and there is swelling around the eyes, known as "violet".
The conjunctiva (Conjugatives) can be affected so that it is sometimes no longer possible to open the eyes. Bleeding inside the eye can lead to an increase in intraocular pressure, a tear in the iris, detachment of the retina, clouding of the lens or a displacement of the lens.
A contusion of the eyeball can also lead to broken bones (Fractures) the bony eye socket (Orbit) come.
Most often the floor of the eye socket is affected, which is very thin and therefore breaks the easiest ("Blow-out fracture"). In this fracture, the mobility of the eyeball is restricted and double vision can be seen. Often the pupil is no longer round because the muscle that is responsible for the narrowing of the pupil (iris sphincter) is damaged and no longer functional. This means that it is no longer possible to fully adapt to different incidence of light. If the lens is involved, a bruised eye can lead to a so-called contusion rosette. This can be recognized by a star-shaped cortical opacity of the lens. It is also possible to twist the lens from its normal position (lens dislocation).
Does a bruised eyeball cause pain?
Since the bruise of the eyeball is usually the result of a direct or indirect blow to the eye itself or the area around the face, pain cannot be avoided. Depending on which parts of the eyes are affected and how severe, the pain is also differently pronounced.
However, the eyelids almost always swell, which in itself causes severe pain. The conjunctiva also swells and becomes red and itchy due to the increased blood flow, which is also sometimes accompanied by severe pain.
The development of corneal edema increases intraocular pressure, which can also be very uncomfortable and painful for the patient. In summary, the stronger the bruise is and the more structures have been damaged, the stronger and longer the pain will be.
You might also be interested in: Eyelid swelling and Pain behind the eye
Treat a bruise in the eyeball
How is a bruised eyeball treated?
The increased intraocular pressure is lowered with medication and controlled through constant follow-up examinations. Retinal injuries are usually treated with laser surgery.
The smallest injuries to the fundus of the eye sometimes only occur after a few days, so a follow-up examination is necessary 7 to 10 days after the accident.
To do this, the pupil is dilated with medication in order to examine the retina (retina) to facilitate. The most severe form of eyeball bruise, the eyeball rupture (Eyeball tear), must be surgically treated and treated with antibiotics as soon as possible to prevent an eye infection (inflammation) to prevent. In the case of broken bones in the eye socket, a clarification with an X-ray and usually a subsequent operation with the insertion of metal bone plates is necessary.
Which homeopathic remedies help with a bruised eyeball?
If a bruise of the eyeball is so severe and pronounced that it is dangerous to the eye itself and thus to the ability to see, a homeopathic approach is not advisable.
You should therefore always go to an ophthalmologist and have the bruise professionally clarified before relying on alternative healing methods.
However, there are some natural medicinal herbs here that have proven themselves in cases of bruises and bruises on the eyeball.
First of all there is Symphytum, in German comfrey.
Hamamelis, the Virginia witch hazel, also has a vasoconstricting effect and can thus support the natural healing process of the eye.
Arnica also helps against bruises and sprains of all kinds. Applied externally, it relieves pain and inhibits the release of inflammatory substances.
Preventing eyeball bruising
What are the causes of a bruised eyeball?
The bruise of the eyeball occurs, for example, through punching a fist, throwing a snowball, corking champagne, in agriculture through beating the horn, when chopping wood through jumping logs or when mowing the lawn through stones, falling in an alcoholic state (due to lack of protective reflexes), but also through sports injuries such as one Tennis ball, golf ball or squash ball.
How can you prevent a bruised eyeball?
Consistent wearing of protective goggles (even in sports), Seat belts and airbags in the car, keep champagne bottles away from your face when opening them, avoid violence.
Course of a bruise in the eyeball
How long does an eyeball bruise last?
Since a bruise of the eyeball is caused in the majority of cases by a blow to the eye itself or the skull, it is almost always an acute occurrence.
This also makes rapid and immediate treatment necessary. Under no circumstances should the affected patient postpone the visit to the doctor longer than absolutely necessary, since structures on and in the eye are permanently damaged and can no longer be reconstructed as time passes.
The development of edema in the eye must be contained as a priority so that the increased intraocular pressure does not pinch the optic nerve and cause it to die.
Depending on how the severity of the injury to the eye can then be determined by the doctor, appropriate treatment must be initiated.
Injuries to the retina are corrected, for example, using laser technology. Any broken bones must be treated surgically. If there are only minor injuries to the eyeball, a check-up after about seven days is usually sufficient to identify possible consequential damage or to diagnose late damage.
Depending on the individual case, the doctor must then decide how to proceed and adapt the therapy accordingly. How quickly the eye heals itself then depends entirely on the age and general condition as well as the severity and extent of the damage to the structures and is difficult to estimate.
What is the prognosis for a bruised eyeball?
A presentation as soon as possible to an eye clinic or ophthalmologist's practice is crucial for the success of the bruise treatment.
In most cases, eyesight can be at least partially or even completely preserved and blindness or severe visual impairment can only be expected in the event of very severe injuries despite surgery. In some cases, further surgical interventions may be necessary in order to optimize the eyesight in the course of the process.
Bleeding or tears in the macular area (Center of vision, point of sharpest vision, at the fundus) and an injury to the optic nerve usually cause a significant permanent visual impairment. The intraocular pressure must also be checked regularly in the years after the accident, as this can increase after a delay.
Detachment of the retina or opacity of the lens (cataracts, cataracts) is possible after the accident. Possible consequential damage from a bruised eyeball are also reading difficulties and related headaches, a remaining dilated pupil and the resulting sensitivity to light.
What are the complications of an eyeball bruise?
A contusion of the eyeball is by no means to be taken lightly, as small damage to the eye, if left untreated, can later lead to serious impairment of vision.
First of all, it is therefore necessary for a doctor to examine the affected eye for possible fluid accumulation, bleeding and defects in the retina, damage to the lens of the eye, the iris and the eyeball itself.
Changes to the retina lead to impaired vision in the short and long term and are particularly dangerous if they are in the center of the retina, as this is where the sharpest vision is.
The resulting loss of vision may be permanent. The bruised eye can also cloud the lens (cataracts or cataracts) and increase intraocular pressure (which in turn favors the development of glaucoma).
Particularly strong blows to the eye area can also lead to broken bones, the so-called blow-out fractures. Here, the bone of the eye socket breaks, so that the eyeball can no longer be held in its original position and the eye muscles that move it can be pinched or torn off. The eye is then barely mobile or only to a limited extent and double images appear.
You might also be interested in: Chronic bone fracture - symptoms, therapy, prognosis



-und-lincosamine.jpg)