Shoulder blade pain
introduction
The shoulder blade (Scapula) together with the shoulder joint forms the connection between the upper arm and trunk. It is located on the side of the spine at the level of the chest and is only connected to the humerus (Humerus) articulated. Because the shoulder blade is surrounded by muscles (so-called rotator cuff), a fracture is very rare.
However, there are many other factors that can lead to shoulder blade pain.

causes
Appointment with a shoulder specialist

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is Carmen Heinz. I am a specialist in orthopedics and trauma surgery in the specialist team of .
The shoulder joint is one of the most complicated joints in the human body.
The treatment of the shoulder (rotator cuff, impingement syndrome, calcified shoulder (tendinosis calcarea, biceps tendon, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of shoulder diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any therapy is treatment with full recovery without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
You can find more information about myself at Carmen Heinz.
Muscle tension
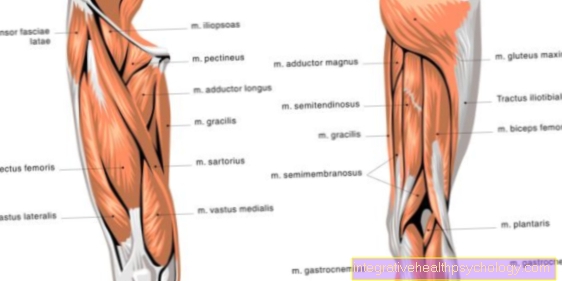
Pain in the shoulder blade can have several causes. Usually, the cause of the pain is not directly in the shoulder blade, but rather in the surrounding muscles. The muscles that surround the shoulder blade and attach to the upper arm are known as the rotator cuff. This includes the subscapularis muscle, which is located under the shoulder blade (Scapula), the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles, which are located on the back of the shoulder blade, and the teres minor muscle, which extends from the shoulder blade to the upper arm. If there is pain in the shoulder blade, it is possible that these muscles are tight or cramped.
The tension is often triggered by carrying heavy bags on one side or for too long. The posture while sitting and standing also affects the muscles of the entire shoulder.
If there is increased tension, you should do regular relaxation and strengthening exercises for the muscles of the shoulder. Furthermore, depending on the degree of tension, massages, heat packs and kinesio tapes can help to loosen the hardened muscles.
Incisura scapulae syndrome
There is a small notch on the upper edge of the shoulder blade (Incisura scapulae) through which a nerve (Suprascapular nerve) runs through. A band runs over the notch. However, it is possible that this ligament becomes ossified, creating a bony canal. This bone canal ensures the constriction of the nerves. The so-called incisura scapulae syndrome occurs, in which the innervated muscles (supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) are no longer properly supplied due to damage to the nerves. The affected patients suffer from pain in the shoulder blade area, especially when the shoulder blade is actively moving. Since active movements are avoided due to the pain, there may also be a decrease (atrophy) the size of the two muscles.
Read more on this topic at:
- Pinched nerve on shoulder
Inflammation of the muscles after overload
However, the rotator cuff muscles can cause pain not only from pinching nerves, but also when the muscle itself is inflamed. Muscle inflammation most often results from a pure overload of the muscles, which occurs after intensive training. Other reasons can also be everyday overexertion in the household, such as hauling crates of water. Most of the time, the pain disappears within a few days after rest and should not come back.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the shoulder blade
Scoliosis
Another cause of shoulder blade pain can be scoliosis. Scoliosis is a misalignment of the spine. This is usually curved in an S-shape instead of running straight through the back.
If there is such a misalignment of the spine in the thorax, this can lead to pain in the shoulder blade, as several muscles (for example the rhomboideus minor and major muscles) pull from the spine to the shoulder blade and attach there. If the spine is misaligned, the shoulder blade and the muscles attached to it are automatically put under incorrect strain. This can lead to cramps in the respective muscles, which then manifest themselves as pain in the shoulder blade area.
In particularly serious cases, the muscle can even become inflamed, which increases the pain.
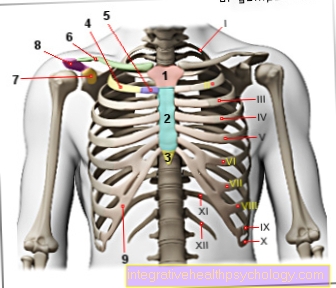
Figure shoulder blade pain

Shoulder blade pain
- Upper bone muscle -
Muscle supraspinatus
(second layer) - Deltoid - Deltoid muscle
- Subbone Muscle -
Muscle infraspinatus - Small round muscle - M. teres minor
- Large round muscle - M. teres major
- Suprascapular nerve
- Rhombus muscle -
Rhomboideus minor muscle
(second layer) - Notch - Incisura scapulae
- Shoulder blade - Scapula
- Rhomboid muscle -
Rhomboideus major muscle
(second layer) - Subscapular muscle -
Subscapularis muscle (second layer) - Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri - Suprascapular Artery -
Suprascapular artery - Tape on shoulder blade -
Transverse ligament
scapulae superius
(1st + 3rd + 4th + 11th = rotator cuff -
Muscle tendon cap)
Causes:
A - muscle inflammation /
Tension / cramping
B. - Incisura-Scapulae Syndrome
(Ossification of the ligament)
C. - Scoliosis
(Misalignment of the spine)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
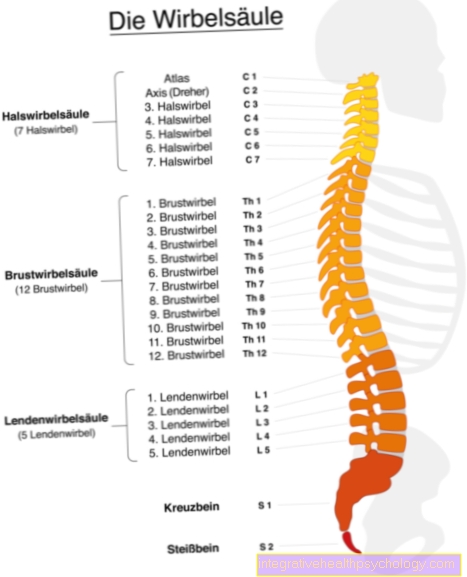
Vertebral blockage
Blocking a vertebra at shoulder blade level can also be the cause of pain in that area. In the X-ray image you cannot see any deformation of the entire spine, as would be the case with scoliosis, but pain in the shoulder blade can indicate a blockage of a single vertebra. The reason for this is that the so-called spinal nerve emerges at each individual vertebra, which sensitively innervates the skin in the individual trunk segments. If this nerve is pinched or damaged, pain and sensitivity disorders occur in the respective skin segment.
The following article may also be of interest to you: Pinched nerve on the shoulder / scapula - These are the symptoms.
disc prolapse
A herniated disc in the neck or a herniated disc in the thoracic spine in this area can lead to similar symptoms. If only one vertebra is affected, the pain is usually limited to a small, belt-shaped area. However, if several vertebrae are affected, the pain can extend over the entire shoulder blade.
Bursitis
In the area of the shoulder blade there are additional bursa, which normally allow the muscles to slide smoothly together. If there is an inflammation of the bursa (Bursitis), this leads to severe pain in the shoulder blade area, especially under stress.
It is often difficult for the affected patient to stretch their arm far away from the body, as the bursa is then narrowed even further.
Pain in the shoulder blade from coughing
If there is pain in the shoulder blade when coughing, a doctor should be consulted to clarify the cause. It can occasionally happen that this is a matter of strong tension, which is increased by the cough.
However, there are some lung conditions that can cause shoulder blade pain. Other symptoms often occur, such as recurring coughs or coughs with sputum. Therefore, a pulmonologist should be consulted to clarify the cause.
Painful breathing
Occasionally, there may be pain in the shoulder blade, triggered by breathing or exacerbated by breathing. There are various possible reasons for this.
If there are complications with the spine, for example due to age-related wear and tear or injuries, the so-called intercostal nerves can be irritated. These arise from the spinal cord at the level of the thoracic spine and run along the rib cage. By stretching while breathing, the irritated nerves send pain signals that can radiate into the shoulder blade.
The cause can also lie in the lungs themselves and should therefore be examined by a doctor.
Pain that occurs especially in the morning
If pain in the shoulder blade area occurs especially in the morning, an unhealthy sleeping position is often responsible.
A back-friendly mattress and pillow can help the muscles in the shoulder area relax overnight.
The morning pain can also be a sign of a rheumatic disease. Several joints are often affected. If, for example, there is additional pain in the wrist or knee joints, a doctor should be consulted for clarification.
Pain with numbness
Pain in the shoulder blade can also be accompanied by numbness. This often leads to tingling or abnormal temperature sensations. This is usually due to irritation of the nerves that supply the area around the shoulder blade.
This irritation can result from pinching or compression of the nerves, which are caused by tension in the muscles in the neck area. But there can also be problems with the spine. The pain and numbness often radiate beyond the shoulder blade.
Pain in the shoulder blade and costal arch
Occasionally, shoulder blade pain may occur along with costal pain. Often the tension in certain muscles is responsible for this.
The so-called serratus anterior is a muscle that originates in the ribs and attaches to the inside of the shoulder blade. Due to its location, it functions as a so-called auxiliary breathing muscle, as it can expand the chest while breathing and thus supports breathing. He is also subjected to heavy loads such as swimming and bench presses. If this muscle is overloaded, pain typically occurs in the shoulder blade and costal arch. The cause of this can be various intense stresses on the muscle, such as intensive coughing or extreme strength training with push-ups.
Long walking with crutches can also overstrain the serratus anterior muscle and lead to pain. These tensions can often be eased through massages and relaxation exercises.
The pain in the shoulder blade and costal arch can also be caused by irritation from nerves running there. If this pain persists for a long time, a doctor should be consulted.
Pain in the shoulder blade and back
Often pain occurs not only on the shoulder blade, but also on the back. The reason for this is usually either muscular tension or problems in the spine. Since the shoulder blade is in close connection with the spine and thus the entire back via bones and muscles, the pain in these areas is often mutually dependent.
An upright posture is essential for relieving the strain on the back and shoulder blades. Strengthening the muscles can also be helpful in reducing overload.
Pain in the shoulder blade and collarbone
The shoulder blade is connected to the collarbone by various ligaments. Together they form the shoulder girdle, which is very important for the function of the shoulder joint. Because of these connections, shoulder blade and collarbone pain is common when problems occur with the shoulder. This mainly occurs in the event of injuries, overloading from heavy bags or natural wear and tear in old age. But inflammation of the joints between the shoulder blade and the collarbone can also lead to pain and should be examined by a doctor.
Heart attack
In rare cases, a heart attack may manifest itself in the form of severe pain in the shoulder blade. The pain is localized either on the left shoulder blade or between the shoulder blades. Occasionally the pain also radiates to the left arm.
In the case of a heart attack, however, other symptoms usually also occur, such as a strong feeling of tightness in the chest and stress-dependent pain. Therefore, the mere occurrence of shoulder blade pain should not be taken directly to imply a heart attack.
fracture
In very rare cases and only under strong force, a fracture in the shoulder blade occurs. In most cases, however, other bones are also affected.
The cause here can be a serious fall on the shoulder, for example after a motorcycle accident.
Is shoulder blade pain an indicator of cancer?
It is extremely rare that the cause of shoulder blade pain is cancer or lung cancer. Other symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss and chronic cough also occur. If this persists for a period of several weeks, a doctor should be consulted.
Which doctor should I consult?
If there is pain in the shoulder blade, an attempt should first be made to relieve it by relieving the pressure on the shoulders. However, if there is no improvement even after a few weeks, a doctor should be consulted.
An orthopedic surgeon is responsible for this because it is usually a problem of the muscles or bones.
If necessary, in the event of acute injuries, such as after a fall or accident, the emergency room can be visited, where the treating doctor is a trauma surgeon.
diagnosis

First of all, an X-ray should always be taken in order to differentiate the pain in the shoulder blade more precisely. Here you can see, for example, a scoliosis or whether there were breaks in the area of the shoulder blade or the ribs below.
A CT image can also be helpful, especially if there is a muscular cause.
The doctor can detect any cramping just by palpation.
The nature of the pain
It is important to pay attention to the symptoms accompanying pain in the shoulder blade and to differentiate the pain. If the pain only occurs for a few days and disappears, the cause was probably a cramp or sore muscles.
If the pain always occurs during exertion or during certain movements, this may indicate a muscular cause or a bursitis.
If the pain persists, it could be due to scoliosis or a vertebral blockage.
therapy

Sufficient physiotherapy and possibly massages are usually sufficient to reduce the pain in the shoulder blade. However, this only applies as long as there is only a slight muscle cramp, for example due to a slight scoliosis.
If muscle inflammation occurs, usually only a pain-relieving syringe containing anti-inflammatory drugs will help.
Physiotherapy also does not help if the bursa becomes infected. Here you should rest your shoulder to avoid infection and possibly give glucocorticoids to reduce the inflammation in the bursa.
In the case of severe scoliosis, a broken shoulder blade, a broken rib or a herniated disc in the thoracic spine, usually only an operation will help.
In most cases, however, shoulder blade pain can be managed well with prescribed physical therapy exercises.
Taping the shoulder blade
For some time now, the technology of taping has enjoyed increasing enthusiasm in the field of sports medicine. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that it is versatile and easy to learn at the same time. There is also the possibility of applying tape bandages when there is pain in the shoulder blade area.
As in other parts of the body, it does not fulfill the function of completely immobilizing the joint and the muscle. Instead, it counteracts unwanted and excessive movements and thus represents a functional bandage. This is achieved during taping by transferring the forces acting on the joint to the skin, so that the joint is relieved. At the same time, there is a more conscious perception of body movements.
There are a number of online instructions for taping the shoulder region or the upper back between the shoulder blades. The tape dressing should by no means be understood as a panacea. It is merely a supportive measure and in no way replaces physiotherapeutic or medicinal treatment of the cause of the symptoms.
Localization of shoulder blade pain
Pain affecting the shoulder blade can be localized at different ends of the shoulder blade. This extends from the arms to the ribs and usually always has a different underlying cause.
Read about this too Pain between the shoulder blades
Pain in the left shoulder blade
Diseases of the internal organs are very rare, but cannot be ruled out. Lung diseases can also cause pain in the left shoulder blade area. An extremely rare cause of discomfort in the region of the left shoulder blade are circulatory disorders of the posterior heart muscles. The pain associated with this, however, is characterized by the fact that it occurs primarily during exercise and cannot be influenced by breathing or arm movement.
Right shoulder blade pain
Right-sided pain in the shoulder blade area is typical of a musculoskeletal cause. The pain increases when the right arm moves and often when breathing. Above all, postural tension in the muscles and blockages in the rib-vertebral joints are responsible for the development of pain. These are often associated with pinching nerves.
In rather rare cases, however, internal diseases can also be responsible for right shoulder pain. Here, for example, lung diseases or diseases of the liver and gall bladder are conceivable, which can radiate into the area below the shoulder blade, since there are connections between these areas via nerves.
Radiating pain in the arm
Complaints in the neck, shoulder and arm region with pain, tingling and numbness are often summarized under the term shoulder-arm syndrome. Here, neural pathways are impaired in various ways, which lead to the classic symptoms.
The most common reason for these latent disorders of the nerve function is one-sided overload and tension, especially in the neck area, but also the shoulder.The symptoms are also favored by underlying diseases of the body region or nerve-damaging diseases such as diabetes mellitus.
The treatment of shoulder-arm syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms. In almost all cases, painkillers form the basis from which further steps, such as physiotherapy, can be planned. Effective treatment should nonetheless target the underlying cause. This is the only way to ultimately achieve permanent relief from the symptoms.
Find out more about arm pain: Pain in the right arm or Left arm pain
Pain in the shoulder blade and ribs
A common cause of chest pain is what is known as intercostal neuralgia. Such pain syndromes in the intercostal area are referred to, which are usually caused by damage to nerves. As a result, they can generally occur anywhere on the chest, be it on the front of the chest or in the area of the shoulder blades.
Intercostal neuralgia is typically characterized by belt-shaped, pulling, and persistent pain. This can be increased by movements in the chest or shoulder and also by breathing movements. As part of the syndrome, sensory disturbances such as tingling or numbness can also occur.
The list of possible causes of intercostal neuralgia is long. The most common triggers of neuralgia include muscle hardening (myelosis) of the intercostal muscles or the subscapularis muscle in the case of pain in the shoulder blade area. Other possible triggers are lung diseases, the Herpes zoster (Shingles) or degenerative changes in the spine. The term intercostal neuralgia should therefore be understood more as a description of the symptoms than an actual diagnosis.
Treatment of the complaints is based on the cause, i.e. causally, if possible. However, since no precise cause can often be named, therapy is often difficult and is then symptomatic. Medicines with pain relieving and anti-inflammatory properties are mainly used here. First and foremost, these are drugs such as ibuprofen or diclofenac.
If the pain is severe, weak opioids and local anesthetics as well as muscle relaxants can be used. In addition, physical therapy and manual procedures are often useful.
Read more on the topic Rib pain
Pain in the neck
Pain in the shoulder blades and neck area is mostly due to Musculoskeletal problems, so the muscles and joints. An unnatural posture and incorrect stress in everyday life are very common here Tension and blockages of the rib-vertebral joints.
In the area between the shoulder blade and the neck, the trapezius muscle plays a particularly important role. In severe cases you can Muscle hardening (Myellosis) lead to nerve entrapment resulting in severe pain. Treatment is usually carried out through physiotherapeutic measures and the use of pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, which are also classically Ibuprofen and Diclofenac counting.