epidural
introduction
Pain is a big issue in all areas of medicine. In acute cases, pain can stress the circulation, worsen the subjective experience of an illness and can also become a long-term burden.
Sometimes you can no longer get a grip on pain with conventional medication in tablet form. You can then switch from so-called peripheral pain therapy to an invasive procedure close to the spinal cord, the so-called epidural anesthesia.
Read more on the topic: Conduction anesthesia

Definition and implementation
The Epi- or epidural anesthesia (PDA) is a procedure of analgesia, therefore Pain therapy, and has nothing to do with conventional anesthesia in the sense of (Full-) anesthesia to do.
With epidural anesthesia, a pain reliever or anesthetic is applied directly to the Spinal nerves and can transmit pain signals on the spot via the Spinal cord ans brain To block. So it doesn't have to be a detour via the Digestive tract be accepted, as with conventional tablets, but one makes oneself on nerve use the mechanism of pain transmission to specifically disrupt it (Effect via sodium channel blockade). For this purpose, substances such as Bupivacaine, is used. Medicines that act on the sodium channel often have the ending -cain in your name. Occasionally, too opiate used.
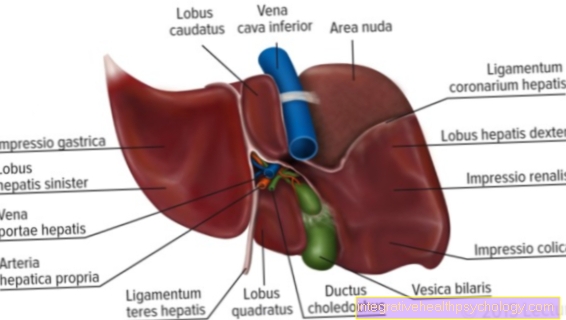
The epidural anesthesia is carried out by the anesthetist (Anesthetists), usually the patient is awake, sitting in a bent position or sometimes lying down. It is important that the Curved back is so that the distance between the thorns and the access to Spinal canal is facilitated. The spinous processes are the bone points that protrude in the middle of the back and make the course of the spine visible under the skin.
The skin The affected spinal column section is disinfected several times and covered with sterile covers. From now on it will sterile worked, that is, with sterile gloves, smocks and covers. In order to prepare the puncture, the site is first opened with a local narcotics injected under. After a short exposure time, the special puncture needle for epidural anesthesia is inserted at an upward angle.
The following layers are now pierced one after the other: the skin and the one below Subcutaneous fatty tissue, the ligament between the two thorns of the Spine, the outer sheet of the hard membrane of the spinal cord and now the tip of the needle is in the Epidural space, i.e. in the space between the inner and outer sheets of the hard skin of the spinal cord (Dura = Latin hard). The anesthetist feels the entry into the epidural space through a sudden loss of resistance of the needle. It should now be possible to inject sterile saline solution without any problems, because the epidural space is only filled by a loose network of connective tissue and small blood vessels.
The anesthetic can now either be fed directly through the needle unique injected or a fine hose be introduced. In both cases, the needle is withdrawn and the area is covered with a plaster. If long-lasting anesthesia is desired, the fine tube can be used continuously or in bursts Painkillers are pumped into the epidural space, one then speaks of a Peridural catheter.
Once injected into the epidural space, the pain reliever is evenly distributed in a certain segment and can now work. The pain medication must be dosed in such a way that the pain fibers are blocked, but the motor nerve fibers that are responsible for moving the muscles are not affected. So becomes a Pain-free with preserved mobility reached.
application
The epidural anesthesia or the epidural catheter can be used for all interventions in which a targeted elimination of pain in a specific body region is desired. Depending on the height of the surgical site, the pain catheter can be placed in different areas of the spine.
The best known is the use of epidural anesthesia during childbirth. In order to relieve the pain of childbirth, many women nowadays have an epidural anesthesia firmly planned. After the first contractions have started, the anesthetist can insert a pain catheter, but it must be ensured that the time until the effects start is at least 20-30 minutes. So if the patient decides to have epidural anesthesia for the pain during the birth process, it may be too late for that.
The case is clearer with caesarean sections. In order to enable the patient to be awake and conscious during the caesarean section, an epidural catheter is always placed beforehand in order to numb the skin in the abdominal region where the incision is being made and the pain sensors of the organs. The pain catheter is then placed in the area of the second to fourth lumbar vertebrae during a caesarean section and during normal birth.
Another area of application of the peridural catheter is the herniated disc. Alternatively, it can be used for patients who do not want surgery or who have too many risk factors (Age, previous illnesses etc.) exhibit. The catheter is then placed exactly in the area of the incident under CT control and has to remain in place for 5 days for drug treatment.
In the case of a herniated disc, in addition to painkillers, anti-inflammatory and osmotically effective substances can also be injected to decongest the nerve and even to shrink the herniated disc. In this way, the symptoms are relieved in the long term and the patient remains pain-free.
Furthermore, the peridural catheter can be used for virtually all procedures on the upper body, abdomen and legs. Even open heart surgery on an awake patient is possible with it (for this, the area from the seventh cervical vertebra to the third thoracic vertebra is anesthetized).
For operations on the upper abdomen, the area of the seventh to eighth thoracic vertebra is anesthetized, for the middle abdomen in the area of the tenth thoracic vertebra and for operations on the legs, e.g. Knee surgery, amputations or other pain in the area of the third lumbar vertebra.
advantages
The advantages are simply that No pain for the patient. Even after an operation, the pain can be switched off, so the patient is faster on his feet and a rehabilitation can be reached faster.
Gentle behavior or posture in the affected body part is avoided, which leads to a quicker recovery normal function can be achieved. For example, patients breathe on the after surgery lung normal faster and get enough oxygen if the pain has been numbed with a catheter.
disadvantage
Pain is used to perceive the processes in our body and is always a Warning sign. If this warning signal is turned off, complications can last longer after an operation go unnoticed or the patient turns up too soon too heavily loaded.
For epidural anesthesia during birth this also means that the contractions, which have their purpose in the natural birth process, are also eliminated. On the one hand, this is pleasant for the mother, but on the other hand it can lead to a prolonged birth to lead. The child stays longer in the birth canal, the birth becomes more stressful and the child reacts with it increasing stress level. This can be done until Birth arrest lead so that the child has to be picked up with the suction cup.
Complications
As with any medical procedure, the PDA Complications or side effects arise. Common side effects are Infections, allergy against the narcotic, itching and Bleeding. A bleeding or a bruise in the epidural space (peridural hematoma) can put pressure on that in the worst case scenario Spinal cord exercise and narrow this down.
This can temporarily to a Paraplegia lead and must then be treated surgically.
If the needle is pushed too far during the puncture, so that the hard inner lining of the spinal cord is also pierced, this can lead to Spinal cord injuries come through the needle.
With a PDA in Lumbar region can it to one Urinary retention come when the nerves supplying the urinary bladder are also affected. In order to be able to divert the accumulated urine, a Urinary catheter be created.
A warm feeling in the legs however, when introducing the anesthetic is normal.
Compared to spinal anesthesia
Spinal anesthesia means that the hard inner lining of the spinal cord is also deliberately pierced (comparable to CSF puncture). The anesthetic then does not reach the spinal nerves, but directly to the spinal cord. However, this has the consequence that the entire body below the puncture site is numb and paralyzed.
Spinal anesthesia can be used in patients for whom general anesthesia is not an option, such as in patients with malignant hyperthermia, problems with securing the airway or a generally increased risk of aspiration.
Spinal anesthesia is also used in emergency caesarean sections, where the onset of an epidural anesthesia would take too long.
You can find a lot more information under our topic: Spinal anesthesia