Dry mouth
introduction
Very many people suffer from dry mouth (dry mouth, Xerostomia).
It is believed that almost half of all over 60 year olds have this condition.
Most often, a dry mouth is an uncomfortable but harmless condition that can be traced back to being tense or not drinking enough fluids. However, sometimes it can also reflect a worse underlying illness.

Causes of Dry Mouth
The causes of dry mouth are numerous and most of them are often completely harmless.
Common causes of dry mouth can include:
- long talking
- low hydration
- increased loss of water (increased sweating, infections, medication)
- Sleeping with your mouth open (snoring, if you have a cold)
- Drinking alcohol
- Eating spicy foods
- Side effect of many drugs
- For chemo / radiation therapy in the head and neck area
- Autoimmune diseases (Sjören syndrome or Hashimoto's thyroiditis)
- Psychiatric illnesses (depression)
Medication as a cause of dry mouth
There are numerous medications that can cause dry mouth. Common remedies are:
-
Antihypertensive drugs, e.g. Beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, some diuretics, and calcium channel blockers
-
Pain relievers (e.g. opioids)
-
Parkinson's medication (e.g. dopamine agonists)
-
Sedatives and sleeping pills, i.e. some sedatives, hypnotics, and antispasmodics
-
Antihistamines
-
Anticholinergics
-
Antidepressants, neuroleptics, anti-epileptics
-
Antiemetics, i.e. drugs against nausea and vomiting
-
Chemotherapeutic agents, cytostatics
-
Drugs like cannabis, heroin, cocaine, ecstasy
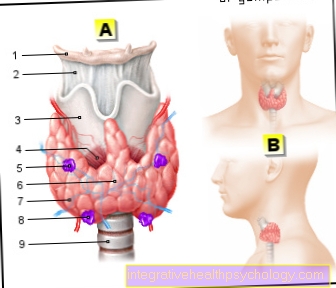
Thyroid disease as a cause of dry mouth
Thyroid diseases can occur at any age and affect many people. Hypothyroidism, known as hypothyroidism, is particularly common. The thyroid gland produces fewer hormones than the body needs. The causes of an underactive thyroid are wide-ranging. For example, it could be an autoimmune disease or an iodine deficiency. In fact, the most common cause of underactive thyroid is Hashimoto's thyroiditis. This is an autoimmune inflammation of the thyroid that leads to destruction of the organ and loss of function. The symptoms of hypothyroidism include numerous organs, as well as the skin and mucous membranes. If the thyroid doesn't produce enough hormones, those affected suffer from pale, cool and dry skin. At the same time, the mucous membranes also dry out, so that patients with an underactive thyroid often suffer from a dry mouth. Dry skin and a dry mouth are characteristic symptoms of an underactive thyroid. Hypothyroidism can be treated very well with drugs.
Read more on the subject below: Hypothyroidism
Diabetes as a cause of dry mouth
There are different forms of diabetes. These include diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus (diabetes).All types of diabetes can cause dry skin and mucous membranes as an accompanying or early symptom. This can show up in the form of a dry mouth.
In the case of diabetes mellitus, the diabetes mellitus, the blood sugar level increases. Blood sugar draws fluid from the body. The loss of fluid causes the skin and mucous membranes to dry out. In type 2 diabetes in particular, a dry mouth can be observed as an early indication of diabetes.
Diabetes insipidus is a form of diabetes that is accompanied by enormous urine output and severe thirst. This "water diabetes" can also cause dry skin and dry mouth in those affected.
Menopause as a cause of dry mouth
In addition to the characteristic symptoms such as hot flashes and mood swings, women can suffer from dry mouth, bad breath and dental problems during menopause. The reason for this lies in the changes in the hormonal balance. The hormone estrogen affects the salivary glands. As the level of estrogen falls during menopause, the activity of the salivary glands is reduced. Various mucous membranes become dry. In addition to vaginal dryness, women often experience dryness in the mouth.
Read more on the subject at: Menopause symptoms
Pregnancy as a cause of dry mouth
Typically, a dry mouth occurs in the early stages, i.e. in the first three months of pregnancy. This is the case even if the pregnant woman drinks more than usual. Humidifiers and repeated ventilation of the apartment can improve the situation.
If the dry mouth occurs during pregnancy rhinitis because the nose is blocked, only home remedies should be used to relieve the symptoms. Nasal spray contains substances that cause the nasal mucous membrane to swell permanently after prolonged use. The positive effect of a clear nose would be reversed after a short time. In addition, you should avoid medication as much as possible during pregnancy for the good of the child.
It is also often assumed that a dry mouth is related to gestational diabetes. However, this is not the case; it manifests itself in an increased feeling of thirst and sugar in the urine.
Depression as a cause of dry mouth
A dry mouth with a typical burning sensation occurs very often in depressed people. This is one of the first symptoms that become noticeable in this clinical picture. If this symptom occurs together with other symptoms of depression, you should seek advice and treatment from your doctor. Furthermore, the dry mouth can also be an expression of taking medication. Medicines for depression, psychosis and anxiety, in particular, can cause dry mouth. Some patients find this side effect very annoying, so another drug must be tried.
Read more on the subject at: Symptoms of depression
Causes of Dry Mouth at Night
If a dry mouth occurs, especially at night, this can be due to various causes. A stuffy nose, for example, caused by a cold or hay fever, which forces you to breathe through your mouth at night, is completely harmless. The oral mucous membranes dry out and you feel your mouth dry in the morning.
Sleep apnea (breathing pauses like snoring) or a crooked nasal septum may also be present. In smokers, the blood supply to the mucous membranes is reduced, especially in the mouth area, which means that less saliva is produced there.
Finally, attention must be drawn to the effects of drugs and alcohol. If you consume these remedies in the evening, your muscles relax and you unconsciously open your mouth at night. The mucous membranes dry out and you wake up in the morning with an uncomfortable feeling and taste.
therapy
Therapy for dry mouth always depends on the underlying cause.
Therapy recommendations can be:
- Sufficient fluid intake (water, unsweetened teas, juice spritzers) in the event of a lack of fluids
- Chew gum or suck candy
- Avoiding spicy foods
- Stop smoking
- Limit coffee / alcohol consumption
- Good oral hygiene
- Oral sprays / gels / rinses
- Therapy of the underlying diseases
Sprays for a dry mouth
Various sprays can help alleviate the symptoms of dry mouth. The Glandosane® spray, for example, is a liquid saliva substitute. It contains numerous mineral salts. If the mouth is dry, it is used to replace the body's own saliva. At the same time, the oral spray has a positive effect on tooth enamel and oral flora. It can be used several times a day.
The situation is similar with the Saseem® mouth spray, which replaces saliva and covers the oral cavity with a protective and nourishing film of moisture. It intensely moisturizes the oral mucosa and relieves the discomfort of dry mouth. Depending on your needs, you can put a corresponding number of puffs in your mouth.
For most oral sprays there are no restrictions on the period of use. The sprays can safely be used over a longer period of time as required. Another popular preparation is the Emofluor® oral moistening spray, which also counteracts unpleasant dry mouth. It ensures a moist environment in the oral cavity and protects the teeth from tooth decay.
Lozenges for a dry mouth
There are various lozenges that can be taken if you have a dry mouth. Lozenges stimulate the body's own saliva production, which moisturizes the oral mucous membranes. In order for lozenges to work as effectively as possible, it is recommended to drink at least two liters of liquid throughout the day and to suck on chewing gum or sugar-free candy in between to stimulate the flow of saliva as much as possible.
The Aquamed® lozenges are a possible preparation against dry mouth. The lozenges contain lysozyme, an endogenous enzyme, as well as xylitol and calcium lactate, i.e. active ingredients that promote tooth structure. Another example are Xerodent® lozenges. These stimulate the formation of saliva immediately and persistently in order to moisten the oral cavity. Ingredients are malic acid, which stimulates the production of saliva, fluoride, which protects the teeth against tooth decay and xylitol, which has a positive influence on the oral flora. The lozenges can be taken up to six times a day.
Home remedies for dry mouth
There are a few home remedies that are known to help with a dry mouth. Everyone has to find out for themselves what really helps them. Because as different as the means are, just as different is each body. Everyone reacts differently!
Above all, there is sufficient drinking. 1.5-2 liters should be drunk throughout the day. It also makes sense to have a glass of water or unsweetened tea on the bedside table at night. There are special types of tea that are particularly helpful, such as green tea. Sugar in tea should be avoided as it binds water again and thickens the saliva.
In winter there should be no dry heating air in the rooms. It is better to set up a humidifier. The smell of lemon stimulates the formation of saliva, similar to chewing gum or lollipops. You can therefore use the option of dripping some lemon oil on the pillow so that more saliva is formed at night. You should always have a piece of chewing gum with you when you are out and about to keep your mouth moisturized.
Finally, there are also some homeopathic remedies and Schüssler salts that are supposed to help against dryness.
Why do you get a dry mouth especially at night?
Typically, dry mouth is particularly bad at night, and people wake up with a sticky, dry mouth feeling and bad breath. The reason for this is that saliva production decreases significantly at night. At the same time, sleeping with your mouth open, i.e. breathing through the mouth, promotes an aggravation of dry mouth at night. In addition, during the day you tend to drink when you experience a dry mouth. This is not possible in sleep. The mucous membranes therefore lack fluid and moisture, especially at night and in the early morning.
Can dry mouth be a sign of pregnancy?
In fact, dry mouth can be a sign of pregnancy. Typical signs of pregnancy include the absence of a menstrual period, nausea, cravings, tight breasts, fatigue, frequent urination and an increased basal temperature. Dry mouth can occur during pregnancy, although women drink more fluids. The cause of dry mouth in the first few months of pregnancy is the pronounced fluctuations in hormones in women.
Read more on the subject at: Signs of pregnancy
Dry mouth and other symptoms
A dry mouth can be accompanied by characteristic symptoms. The main complaints are dried out mucous membranes, the oral mucosa is often stunted (atrophic), reddened and very sensitive to pain. As a result, the tongue can even stick to the mucous membranes. The lips are usually dry and cracked. Taste disorders, chewing and swallowing difficulties and pain when speaking can occur. A dry mouth can be accompanied by a burning tongue and bad breath.
Dry mouth and increased thirst
The body excretes more water due to increased blood sugar. This makes the oral cavity feel extremely dry. This loss of water causes the body to send out an increased feeling of thirst in order to rebalance the water balance.
If these symptoms persist despite drinking enough water, this can be a warning sign. One possible disease is diabetes, colloquially "diabetes". In addition, dry skin, tiredness, poorly healing wounds and itching often occur. Then you should quickly see your doctor and have your blood sugar levels checked. This disease is not to be trifled with because, without treatment, the chronically high blood sugar can cause serious physical damage.
There are also various drugs that can cause dry mouth and an increased urge to urinate. These include, for example, torasemide and citalopram®. If these drug side effects occur, the doctor can consider alternatives to reduce the undesirable effect.
Dry mouth and burning tongue
A burning tongue can be an accompanying symptom of a dry mouth. Burning tongue, also called glossodynia or burning-mouth syndrome, describes abnormal sensations in the tongue or mouth mucous membranes. The burning sensation often occurs on the tip of the tongue or on the side of the tongue. The discomforts often increase during the day, while the symptoms are relieved when eating. A burning tongue can be associated with taste disorders. There are several ways to treat the burning sensation of the tongue. The therapy depends on the cause of the symptoms.
Read more on the subject at: Burning at the tip of the tongue
Dry mouth and lips
The dry mouth can also dry out the lips. When the small salivary glands no longer properly moisten the mucous membrane, the lips burst from the dryness. They become very cracked and rough. This unpleasant symptom can be prevented with lip balm or special creams, but this does not treat the cause. You should apply these agents in good time, otherwise you have to wait a long time for these wounds to heal.
See here: Dry lips - these are the causes
Dry mouth and tongue
If the dry mouth occurs together with a dry tongue, this is usually noticed when the tongue sticks to the roof of the mouth. Often this occurs when one is excited, such as before an important lecture. But it can also indicate various diseases. If the body lacks fluid, a dry tongue indicates a "heat disorder". This includes fever or diarrhea, in which a lot of fluid is lost in the body.
Dry mouth even after drinking
If the mouth still appears dry despite sufficient fluid intake, the salivary glands may be diseased. You will then no longer produce enough saliva. This includes diseases such as mumps or inflammation of the salivary glands. However, worse diseases such as salivary gland tumors can also occur. These severely limit the function of the salivary glands. This means that less saliva is produced.
After the hormonal change in old age (menopause), an autoimmune disease called Sjogren's syndrome can occur, especially in women. It is associated with severe dry mouth, reddened mucous membranes, burning tongue and dry eyes.
Cancer patients with previous radiation therapy in the head and neck area in particular suffer greatly from the Xerostomia (Technical term for dry mouth). The salivary glands are then so affected that they can hardly produce any more saliva and those affected have a constantly dry mouth.
diagnosis
Of course, the diagnosis of “dry mouth” is ultimately made by the patient himself, as this is a subjective feeling.
In order to finally find out the cause of this, it can be useful to see a doctor. This is especially true if the dry mouth is accompanied by other complaints and is so pronounced that it severely restricts the person concerned in their everyday life or persists for a longer period of time for no apparent reason.
First of all, the doctor will conduct a thorough medical history survey. For this purpose, he will ask the patient about eating and drinking habits, other illnesses and medication, among other things.
Then, depending on what he suspects is the cause of the dry mouth, he can do a physical examination, take an X-ray, CT or MRI, or many other things. In order to objectify the findings, it is also possible to measure the saliva flow rate.
Saliva production
On average, a healthy person produces around 500 to 1500 milliliters of saliva per day; depending, among other things, on how much and what type of food he eats.
However, even without any food intake, a certain amount of saliva is produced, namely around 500 milliliters, which is known as basal secretion.
Various glands in the mouth are responsible for the production of saliva: there are three large salivary glands and a large number of small salivary glands. The large salivary glands include the parotid gland (Parotid gland), the submaxillary gland (Submandibular gland), and the sublingual gland (Sublingual gland).
Together, these are responsible for around 90% of the saliva formed, the majority of which is produced by the submaxillary gland, the rest is provided by the small salivary glands in the oral mucosa.
Function of saliva
Aside from the fact that saliva keeps the mouth moist (which enables us to speak, swallow and eat properly), it has other important functions:
Thanks to the enzymes it contains, the digestion of food can begin in the mouth, and saliva cleans the oral cavity from bacteria, viruses, fungi and tiny particles that get into the mouth. For all of these reasons, a sufficient amount of saliva is extremely important.
However, if the secretion of saliva is reduced or at least not sufficient for the current requirement, then the subjective feeling of a dry mouth occurs. However, since there is not only a lack of moisture, but also the enzyme protection in the mouth, the higher number of bacteria can also lead to bad breath and / or an increased susceptibility to infections or dental problems. Speaking and swallowing are also more difficult, which can lead to hoarseness in the further course.