Inflammation of the nail bed
Synonyms in a broader sense
- Onychia
- Oncychitis
- Onychia subungualis
- Onychia maligna
- Panaritium paraunguale
- Paronychia
- "Circulation"
English: Felon, Whitlow, Onychia
definition
The nail bed is the place on the finger or toe that is covered by the nail and from which the nail grows. Inflammation of the nail bed is a mostly bacterial infection of the skin at this point and can affect both fingernails and toenails. It manifests itself through the typical signs of inflammation, which include swelling, redness and pain. Often there is also an accumulation of pus in the affected areas.

General
Acute nail bed inflammation usually lasts about a week and resolves on its own, but in some cases it can spread and become chronic if left untreated or due to the presence of additional risk factors.
There are two types of nail bed inflammation, depending on whether it only affects the nail bed itself or the surrounding area. If the inflammation only affects the nail bed itself and pus accumulates under the nail, it is called panaritium subunguale (Panaritium is the general name for an infection of a Fingers or a toe). If the inflammation spreads quickly to the skin around the nail bed, the area around the nail bed is mainly affected and this is why it is also called "circulation" or in the medical panaritium paranguale.
frequency
The Inflammation of the nail bed provides the most common infection of the fingers Women are more often affected because they are more prone to injuries in the area of the nails from manicures or pedicures. Also, people have with Immune deficiencies, Circulatory disorders, Neurodermatitis and especially diabetes an increased risk of getting nail bed inflammation.
causes

The triggers of inflammation of the nail bed (Inflammation of the nail bed) are usually bacteria, mostly from the tribe of Staphylococci, less often too Streptococci, but viruses or fungi can also be responsible for nail bed infections. These penetrate into the deeper tissue through wounds in the cuticle, which are often so small that they go unnoticed themselves. The causes of injuries are very diverse. The skin below and around the edges of the nail can be wounded by, for example Too short cut nails, ingrown nails, Chewing finger nails, one torn cuticles, torn nails at the cornerslong-lasting pressure on the nail, corns under the nail or from a splinter. In the case of toenails, shoes that are too tight can lead to an injury. A bacterial infestation leads to a rapid, fungal attack to a rather slow development of the inflammation.
To the Risk factors counts among other things diabetes (diabetes). Diabetics are prone to infections, which softens the skin and enables bacteria to penetrate more easily. For the same reason, frequent contact with cleaning agents and / or water also promotes the development of a Inflammation of the nail bed.
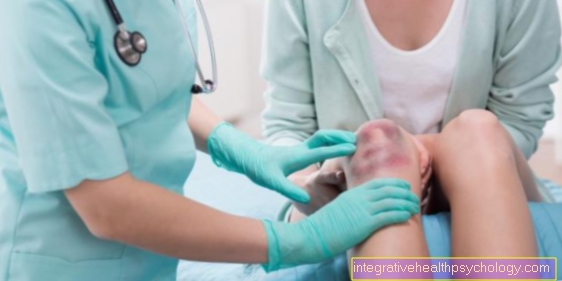
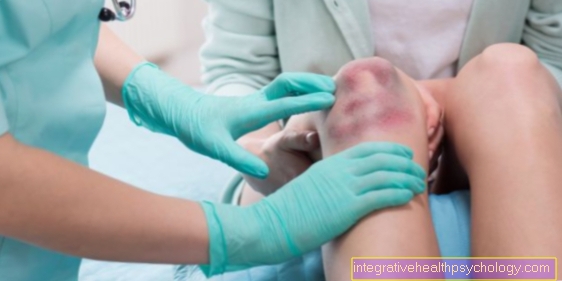
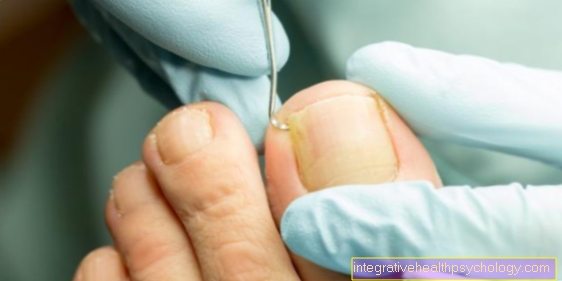
Illustration of an inflammation of the nail bed

Inflammation of the nail bed
(Finger and toe nails)
A - healthy nail
B - Panaritium subunguale
(Inflammation affects only
the nail bed)
C - Panaritium paranguale
(Inflammation affects this
Nail bed and the surrounding area)
- Nail fold - Matric sulcus
- Nail plate - Lamina unguis
- Cover fabric of the nail bed -
Hyponychium - "Moondchen" - Lunula
- Horny layer of the nail wall -
Eponychium - Nail root - Margo occultus
Nail bed inflammation symptoms:
a - pus
b - redness
c - swelling
d - skin around the nail bed
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Symptoms

The first sign of an acute inflammation of the nail bed is the reddening of the skin that borders the nail. This is followed by the development of the other typical signs of inflammation: The infected skin becomes hot and swells. The swelling causes severe pain, which is usually throbbing in nature, caused by the pulse of the small blood vessels in the affected area. Over time, a more or less pronounced accumulation of pus develops under the nail plate, which sometimes drains from the corners of the nail spontaneously or after pressure is applied (nail bed inflammation). It is not uncommon for the skin around the nail to itch, especially in the initial phase of the inflammation. Pain and / or swelling may severely limit the inflamed area's ability to act. In rare cases, inflammation of the nail bed also leads to the development of fever or swelling of the lymph nodes.
If the infection is not treated adequately, the nail can become deformed or even fall off completely.
The symptoms of chronic inflammation of the nail bed are slightly different from those of the acute form. Here you usually only find a reddish to bluish discoloration of the affected nail, pain is only very slight or completely absent, which often means that the inflammation is not noticed at all or is only noticed very late. Unlike acute inflammation, the chronic form usually affects multiple nails. This species is particularly common on the toenails of diabetics.
Read more about the topic here: Pain under the fingernail.
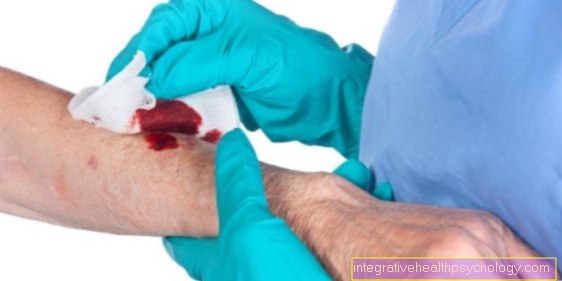
Pus as a symptom of nail bed inflammation
Pus arises from the death of the body's own inflammatory cells that migrate to infected areas. Pus-forming infections are usually caused by inflammation with bacteria, which are therefore also called “pyogenic” (pus-producing) bacteria. In the case of nail bed inflammation, these are usually so-called "Staphylococci“.
These are also found on healthy human skin and only cause problems when they break through the "skin" barrier. Pus occurs particularly frequently in a so-called "Panaritium subunguale" on. This is an inflammation of the cuticle under the nail, which is why the pus usually comes out at the edges of the nail.
Read more about this: Pus on the finger
Should one express the pus?
Often, especially when the pus is very close to the skin, the pus is transported to the surface by itself and is rejected there. However, if the pus is in deeper layers of the skin or, for example, under the nail, this is often not possible. In this case, a surgical opening may be necessary. Pus can and must usually be opened and drained, as otherwise the germs can "spread", for example in the bones. In addition, pus is often the cause of painful swelling. Since the nail bed and the nail fold are very sensitive, it can be pain relieving to drain the pus or to express it.
However, it is advisable to leave this procedure to the professionals, namely the surgeon or the family doctor!
"Wild meat"
A so-called “excessive granulation" designated. Due to tissue damage that has usually existed for a long time, there is an increased healing reaction. The injured or non-existent tissue is not only replaced, but a kind of overgrowth occurs. This is usually very well supplied with blood and therefore appears pink-reddish. The surface of the granulation tissue is roughly "grainy", as the name suggests (granular= grainy). With inflammation of the nail bed, and especially with ingrown nails, wild meat often forms as the body reacts to the irritation from the nail or the inflammation.
Blood poisoning
If the inflammation of the nail bed, as already described above, causes the infection to spread to deeper tissues, it may happen that the bacteria get into the bloodstream. This can trigger a systemic inflammation, which can be seen as blood poisoning or "sepsis" referred to as. Symptoms of blood poisoning are fever, fatigue, decreased blood pressure, increased pulse, paleness and increased sweating. Contrary to popular belief, there is no red line on the skin. Blood poisoning due to inflammation of the nail bed is extremely rare and mainly occurs in people with a weakened immune system.
Read our articles on this Blood poisoning and Symptoms of blood poisoning.
diagnosis
Usually the classic ones are enough for a doctor Symptoms of nail bed inflammationto make a safe diagnosis. In order to obtain precise information about the pathogen present, he can also use a smear from the affected area. If the suspicion of a chronic form of nail bed inflammation If present, the doctor should conduct a detailed medical history to identify underlying diseases such as a Diabetes mellitus to be able to rule out (nail bed inflammation treatment).
therapy
An acute inflammation of the nail bed, which is noticeable as slight reddening, swelling and throbbing pain in the toe area, can initially be treated with lukewarm foot or hand baths with curd soap or chamomile solutions.
They have a calming effect and support the natural healing process. Washing also loosens the horny layer and pus can be removed more easily. After the bath, the nails should be gently patted dry. In addition, the application of disinfecting ointments that contain antibacterial iodine, for example, helps, as they can help particularly with a bacterial cause of the nail bed inflammation and soothe the itching that occurs frequently. (E.g. Ilon® ointment)
The affected area should be immobilized by lying up, with cooling compresses or with the help of small splints. In the case of acute inflammation of the nail bed on the foot, shoes that are too tight should be avoided; instead, we recommend wearing shoes that offer enough space for the toe in order to avoid further irritation of the affected area.
Contact with cleaning agents and other chemicals should also be avoided (wear shoes and gloves, e.g. when cleaning with cleaning agents). If the pain is very severe, pain medication can help temporarily.
It is advisable not to lend a hand in the case of acute inflammation of the nail bed in the area of the nail bed, as self-therapy can make the situation even worse. If the inflammation lasts for several days, a doctor should definitely be consulted.
If the nail bed inflammation has not subsided after the first treatment (e.g. with baths and ointments), if swelling, overheating or pus occurs, or if the symptoms increase, a doctor should be consulted. However, if the inflammation has progressed to the point of fever, chills, swelling of the lymph nodes, and a general feeling of illness, antibiotic treatment may also be needed. The active ingredient group of penicillins comes into consideration for this, as they are particularly effective against staphylococci, the bacteria that most frequently cause nail bed inflammation.
If an ingrown nail is the cause of inflammation of the nail bed, the nail can be surgically reduced in size by a doctor. In some cases, the nail plate must also be completely removed.
Before choosing surgical therapy for an inflammation of the nail bed caused by an ingrown nail, a number of other measures can be tried out. For example, a brace can be inserted between the nail and the skin, cotton wool can be placed or the side wall of the nail can be pulled away by a plastering belt.
If nail bed inflammation is treated late or not at all, growth disorders of the nail can occur or the nail can be rejected.
Read more on the topic: Treatment of inflammation of the nail bed
When do you need an antibiotic?
An inflammation of the nail bed is usually acute and disappears by itself after about a week. The infection takes place in the superficial part of the skin.
In rare cases, the inflammation can progress into deeper layers. There is a risk of reaching over onto the bones or blood vessels. So if nail bed inflammation does not subside by itself after a few days or even gets worse, a visit to the doctor is inevitable. The doctor decides whether antibiotics, a surgical opening or both are necessary. As a rule, antibiotics from the group of penicillins are prescribed.
Treatment with ointments
The treatment one Inflammation of the nail bed is mainly based on the complaints that Expression of the inflammation and the result of the medical examination. A distinction must be made whether the inflammation is caused by bacteria, Yeasts or Viruses was triggered.
Depending on which one Pathogens the Inflammation of the nail bed triggered, there are also different ones Anoint and drug into consideration. Basically work in the case of nail bed inflammation anti-inflammatory baths and Anoint calming and can even aid the natural healing process.
For this come special disinfecting solutions or ointments that contain iodine or others antibacterial contain active substances. Especially when bacteria were the cause of the nail bed inflammation, these ingredients can help Healing process to accelerate. In order to find out the most suitable ointments and measures in the individual case, it makes sense to talk to the attending physician.
Under certain circumstances it can have a negative effect on the course of the disease if you experiment with ointments on your own. It is particularly important not to manipulate in the area of the nail bed inflammation and to try to use the unsuitable tool Drain pus allow.
In the case of a more advanced, more severe inflammation, the use of ointments containing antibiotics become necessary. If there is any spread of inflammation with swollen lymph nodes and fever comes, so can additionally a antibiotic be prescribed in tablet form.
If the nail bed inflammation is none bacterial cause but for example one infection With Yeasts, so are Anoint with a Anti-fungal agents effective. Also certain Viruses can cause inflammation of the nail bed. An infection with Herpes viruses can be treated well with an ointment, the so-called Virus statics contains, i.e. ingredients that fight the virus (e.g. acyclovir).
It should be noted that with slight inflammation of the nail bed applying a ointment as well as protecting the affected nail (for example by wearing appropriate footwear) are usually sufficient to prevent the inflammation to heal. In more severe cases, a small operation may be necessary where the nail may have to be removed so that the Drain pus can. Then a disinfecting ointment bandage is applied so that the wound can heal well.
At chronic inflammation of the nail bed it may be useful to certain Irritants to avoid. Some ingredients in ointments or (hand) creams can also be responsible for the recurrent inflammation of the nail bed and should be avoided. People who come into contact with a lot of aggressive substances should regularly apply sufficient fatty ointments to their hands to prevent inflammation of the nail bed.
Treatment with a pull ointment
In the case of inflammation of the nail bed, the use of pulling or pulling ointment can be helpful. Pull ointment is used in medicine for inflammatory skin diseases, abscesses, boils, acne, as well as splinters and nail bed inflammation. The ointment has an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, blood circulation-promoting, pain-relieving effect and softens the top layers of the skin so that foreign bodies and pus can be more easily transported to the outside. The latter is also the reason why pull ointment is often used for inflammation of the rodent bed. The existing pus, for example under the nail, creates a painful pressure, which can be alleviated by removing the pus.
Read more on the subject at: Pull ointment
Treatment with Betaisodona®
Betaisodona® is a trade name used in Germany for “Povidone-Iod”. Povidone-iodine is an iodine-containing disinfectant that is widely used in medicine. Iodine damages the shell of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and bacterial spores and thereby kills them. In addition to Betaisodona®, numerous other disinfectants containing iodine are used in medicine.
However, Betaisodona® has the advantage that it is particularly suitable for use on sensitive areas such as mucous membranes and wounds.
Betaisodona® is applied in a mostly 10% dilution over a large area over the area to be disinfected. Betaisodona® can also be used for inflammation of the nail bed, especially if the cuticle is infected or soiled.
Disadvantages are itching, rashes and frequent allergic reactions. In the case of diseases of the thyroid gland, products containing iodine should under no circumstances be used, as these can have a very strong influence on the metabolism of the thyroid gland.
Which doctor do I have to contact?

A slight inflammation of the nail bed occurs not infrequently and usually heals after a few days when the nail is relieved and possibly with supporting, antiseptic baths or Anoint is treated. It can be a good idea to show a doctor if you have a badly inflamed nail bed Self-measures taken as it may worsen the inflammation. As a rule, the first step is to contact the Family doctorwho treats nail bed inflammation.
Depending on how pronounced the inflammation the family doctor can make a referral to one Dermatologist (Dermatologist) or one Surgeons exhibit. Inflammation of the nail bed occurs more frequently chronic underlying diseases like diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) on.
In this case, the attending physician should provide the Underlying disease seek out. The family doctor usually recognizes an inflammation of the nail bed when examining the affected area. Nevertheless, the doctor will first take the medical history (anamnesis) of how the injury occurred in order to be able to draw conclusions about the possible pathogen or to be able to give advice on preventing recurrent nail bed inflammation (e.g. wearing suitable shoes).
In some cases it can be useful for the doctor to take a smear of the inflamed tissue to remove the Identify pathogens. At an advanced stage, the doctor may recommend a X-ray (or possibly Magnetic resonance tomography / nuclear spin) of the hand or foot as necessary to clarify whether the inflammation is already in deeper tissue, bone or Bone marrow has advanced.
Homeopathy for nail bed inflammation
Inflammation of the nail bed is a common condition. Small injuries in the area of the nail, which can become infected, quickly occur. In many cases, an inflammation of the nail bed is recognized very early by pain or reddening of the tissue.
At such an early stage of nail bed inflammation, homeopathic remedies can often be used successfully. In order to make the right choice of homeopathy, a distinction is made between the symptoms that are in the foreground. Homeopaths generally recommend Tarantula cubensis in a potency of D12 for nail bed inflammation, of which five globules are taken three times a day.
If the affected nail is reddened and warmed up, Belladonna D12 can be taken against the inflammation. Until the symptoms decrease, five globules should be taken every two hours. If the nail bed inflammation has progressed to the point that pus has formed, the homeopathic Hepar Feel D10 (five globules six times a day) can be used to support the healing process.
The teaching of homeopathy also recommends Silicea D12 if the nail has already been damaged and is deformed or brittle (five globules twice a day). Basically, homeopathic remedies should only be taken in conjunction with sparing the affected nail. Adequate disinfection of the area and an anti-inflammatory ointment containing iodine can prevent bacteria from entering.
If the symptoms of nail bed inflammation do not improve despite homeopathy, a doctor should be consulted. Since the inflammation can spread and possibly cause complications, in more advanced cases of nail bed inflammation often only antibiotics or an opening of the pus bladder will help to get the inflammation under control.
Tea tree oil
Tea tree oil is extracted from the leaves of the tea tree that grows in Australia and has been used in medicine for over a hundred years. It has an "antiseptic", i.e. disinfecting, effect and primarily fights bacteria and fungi. If the nail bed becomes inflamed, it is often added to a warm water bath. In addition to the antiseptic effect, psychological effects, such as an increase in drive, are also described. Sometimes the use of tea tree oil can lead to a contact allergy, which is why particular caution is required when using it for the first time.
Read more on the subject at: Tea tree oil.
Risk of contagion
Inflammation of the nail bed is almost always caused by bacteria. However, these are mostly bacteria that occur in the human skin flora and / or in the oral cavity anyway. The pathogen must get into an open wound in order to cause infection. Infection is therefore not possible or only with great difficulty. In rare cases, when an inflammation of the nail bed is caused, for example, by a skin fungus, it can lead to an "infection" or better said to a "transmission".
Duration
The duration of nail bed inflammation depends on many different factors and is therefore difficult to predict. Most of the time, the inflammation will subside on its own within a week. The most important factors are how severe the inflammation is and how early treatment was given. An early application of warm baths, ointment and disinfectants (e.g. Betaisodona®) can improve the process. Healing also depends on the person's immune system and can therefore vary widely. Another factor is the cause of the inflammation. Usually these are small stab wounds or cuts.
An ingrown nail is often the cause, especially with inflammation of the toenail beds. This can make the inflammation chronic, which significantly increases the duration. In this case, the footwear is often to blame and a change can provide permanent relief.
Read more on the subject at: Ingrown toenail.
Inflammation of the nail bed on the toe
An inflammation of the nail bed toe (Panaritium) can be very painful. It is an inflammatory disease of the Tissue under the Toenail.
The nail bed on the toenails is right Well protected from the surrounding structures. Still, it is possible through that minor injuries in the cuticle or in the nail wall pathogens such as bacteria or Mushrooms penetrate the nail bed and lead to nail bed inflammation.
On the toenail, the cause of this is often that the nail grows wrong and pushes itself into the skin. To tight footwear can then additionally promote the development of the nail bed inflammation, since it leads to a deformation of the toenail.
When the toenail grows into the nail bed as a result, it forms one Entry gate for infections. Inflammation of the nail bed on the toe can be both acute as well as chronic occur. Chronic nail bed inflammation usually manifests itself in damage multiple nailsthat are more or less painful. Care should always be taken when doing this Foci form. In this case, a doctor should be consulted immediately, as in the worst case the inflammation can spread to the bone can expand.
Prevent nail bed inflammation on the foot
In addition to the Foot care also a careful cutting the toenail, the lateral nail area should not be injured. Also, the sides shouldn't be too aslant or to deep get cut. Nails that are cut too short offer the nail bed less protection and increase the risk of developing nail bed inflammation.
The toenails should regularly and straight cut and the skin of the feet should be cared for, for example with the help of nourishing creams or foot baths.
It is important that the Cuticle is not injured when cutting. nail polish and nail polish remover can additionally irritate the nail and the surrounding tissue and cause nail bed inflammation. So if you suffer from nail bed inflammation frequently, you shouldn't use nail polish.
Especially at Growing children Care should always be taken to ensure that they wear suitable, comfortable shoes that allow enough space for the toenails.
Because even Bruises on the toes can lead to minor injuries in the Pathogens can penetrate. For pathogens that can lead to nail bed inflammation, there is one humid environment an advantage, so care should be taken to keep the feet dry.
You should also have something suitable for every occasion protective Wear shoes so that minor injuries in the area of the nail bed cannot occur (e.g. sturdy shoes when gardening).
Misalignment of the toes or the foot can lead to the development of nail bed inflammation, for example by creating pressure points. Here, orthopedic insoles can be prescribed to correct the misalignment and reduce the risk of nail bed inflammation.
Inflammation of the nail bed on the toe in chronic diseases

Chronic illnesses like that diabetes-Illness (Diabetes) increase the susceptibility to inflammation of the nail bed. Inflammation of the nail bed on the toe is particularly dangerous for diabetics as it can lead to serious complications and is often chronic. As it is due to the diabetes disease too Sensory disturbances nail bed inflammation can occur easily undetected stay.
Because they too Wound healing is often slowed down due to diabetes, the nail bed inflammation can lead to complications, including tissue death. At worst, this sometimes means the affected toe amputated must be taken to prevent the infection from progressing.
A well-adjusted one Blood sugar level and careful foot care, especially of the toenails, are very important for diabetics.
But not only diabetics, but also people who Circulatory disorders or one immunodeficiency Suffer (leukemia, HIV-Infection, Tumor disease), have an increased risk of complicated inflammation of the nail bed on the foot.
Any sign of acute inflammation should be taken seriously and a doctor should be consulted. In general, the following applies to chronically ill people: the better they are Underlying disease the better complications due to delayed wound healing and chronic courses can be avoided.
Inflammation of the nail bed on the finger
A acute inflammation of the nail bed on the finger shows through swelling, Redness and Pain on the affected fingernail. The affected skin area often feels hot and it typically becomes a throbbing pain perceived. This is caused by increased pressure on the small blood vessels through the inflamed tissue, causing the Pulse rate 'palpable" becomes.
To the lateral edges and under the nail plate of the finger forms after a while pusthat sometimes comes out due to pressure on the nail. A severe inflammation of the fingernail can also cause it to swell Lymph nodes under the armpits and in the crook of the elbows or too fever come.
In most cases, nail bed inflammation occurs on the finger due to mistakes in the care of the fingernails. Sharp nail polish removers, nails that are too short and rough cutting of the cuticle when shortening nails are typical things that promote the development of nail bed inflammation. For this reason, it is important to trim your fingernails regularly, but not too deeply into the lateral nail wall. Moisturizing hand creams can reduce the risk of skin cracking and should be applied regularly to the skin around the fingernail. When doing housework or gardening, gloves should be worn to protect the fingers from chemicals and injuries, both for prevention and in the event of an existing inflammation of the nail bed on the finger.
Inflammation of the nail bed on the thumb
A Inflammation of the nail bed can appear on all fingernails or toenails, including thumb. This is often shown Tissue reddened and a severe swelling occurs. There is pulsating pain as the process progresses, one Feeling hot, Pus blisters, Sensitivity to pressure and knocking and the thumb is often restricted in its mobility.
One distinguishes between superficial and deep forms of the Inflammation of the nail bed. If the disease occurs on the thumb, the peculiarity of a so-called V phlegmon come. Since the anatomical structures in the area of the fingernails Drainage of pus outwardly difficult, a phlegmon causes the inflammation to spread into surrounding soft tissue structures, as well as in Joints, bone and Tendon sheaths. The V-phlegmon denotes the Inflammation of the tendon sheaths from thumb and Little finger (the infection is V-shaped). Because of the risk of a Spread of inflammation Inflammation of the nail bed on the thumb (as well as on all other toenails and fingernails) must always be treated as quickly as possible.
Purulent inflammation of the nail bed
In acute inflammation of the nail bed, pathogens penetrate the tissue through small wounds, causing reddening and swelling. After a while it can lead to the formation of pus come, which is very painful.
Pus is usually caused by a Infection with bacteria triggered and is a Immune response of the body to the inflammatory stimulus. Due to the anatomical structures in the area of the fingernails and toenails, the pus cannot get out easily flow away. Therefore, the infection will spread to surrounding soft tissue structures, as in bone and Tendon sheaths even favored with a purulent inflammation of the nail bed.
Therefore, the purulent nail bed inflammation must be possible quickly be treated. In some cases, a purulent inflammation of the nail bed is a minor one surgical intervention in local anesthesia or under general anesthetic necessary. So that the pus can drain away, the pus focus must be cut open sometimes has to be opening created by the nail or the nail removed. The resulting wound must then be cleaned and re-bandaged daily, preferably under close medical supervision.
Before the surgical procedure, a X-ray Provide information on how far the purulent infection has penetrated into adjacent tissue or even to the bone.
Allowing the pus to drain is therefore necessary to prevent a possible Blood poisoning to avoid and a scattering prevent infection in the body. In addition, the pus-filled swelling of the skin is very much painful and the opening of the pus bladder is often felt to be beneficial because of the Tenderness immediately improves and the symptoms subside.
As a medical layperson one should refrain from any manipulation of a pus focus and not self-employed try to prick or express the nail bed inflammation. This could be dangerous Spread of the germs lead to deeper tissue layers and further complications, in the worst case it can lead to blood poisoning (sepsis) come. If the pus drains by itself, the open wound may only be used for hygienic reasons Gloves, Disinfectants and sterile dressings be treated. In addition, hands should be washed thoroughly after each dressing change and body orifices and other people should be protected from the pus to prevent the spread of germs (Phlegmon) to prevent.
Inflammation of the nail bed in babies

At Infants, Babies and Toddlers Inflammation of the nail bed occurs relatively often. Small injuries in the area of the nails arise when To grab and Play fast, and it is often not easy to cut the little fingernails and toenails. Especially those Toenails should so straight cut as possible to prevent nail bed inflammation or to prevent toenail ingrowth in the baby.
It comes to one acute inflammation of the nail bed, the baby often screams more often, it drops a nail on the affected nail severe redness, swelling and possibly one Pus formation on. Babies do not yet have as well-developed immune systems as adults, which is why one Inflammation of the nail bed spread faster in the body and to fever, chills or increased fatigue can come.
For this reason, it is important to identify and treat nail bed inflammation in a baby early. It makes sense to see a doctor, especially if it is a more advanced form of nail bed inflammation. In this case there may be a Opening of the pus focus with following disinfection necessary. The application of Anoint and solutions, the disinfectant and antibacterial work, may relieve the baby's discomfort. However, only preparations that are approved for babies should be used.