Physical examination
introduction

A physical exam is part of every medical exam. The physical examination performed differs from the doctor by which it is performed. This difference is due, on the one hand, to the symptoms of the patient and, on the other hand, to which specialty the examining doctor belongs to. A complete physical examination takes a relatively long time, so that the examination is often symptom-oriented.
General, superficial examination
At the very beginning of an investigation, the Blood pressure measured by the patient. At a general physical examination the doctor first looks at the patient (inspection). The doctor first pays attention to changes in the Rib cage (thorax). These changes can Scars from surgery like one Bypass surgery his or her changes in the area of the bony structures such as a Funnel breast be. He also judges the color of the skin (Skin color).
Usually the doctor also looks at the hands and not only assesses them here Warmth of the handsbut also the shape of the Fingertips and Nails. These can be long lasting limited supply of oxygen the form of something called Drumstick fingers and Watch glass nails take in. To further assess an oxygen deficiency, the doctor will also examine the Color of lips and tongue. At a Blue color These parts of the body are called central or peripheral, depending on the cause cyanosis. When further inspecting the face, the doctor pays attention to the shape of the Pupils and the white eye skin (Sclera). A Yellowing of the sclera is an indication of a Jaundice (Jaundice).
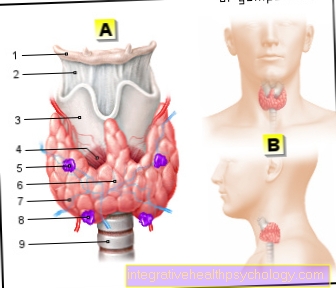
When doing another physical exam, many doctors begin examining the Lymph nodes. Most doctors begin by examining the Lymph nodes in the Neck and throat area. To do this, they feel along the muscles and once below the Lower jaw. Many investigators take this opportunity to look directly at the thyroid with at. For this purpose, the patient is usually asked to swallow once while the doctor palpates the thyroid gland. Then the lymph nodes are once above and once below the Collarbone (Clavicle) keyed. Then the lymph nodes in the armpit are examined. To do this, the patient sitting on the couch is asked to cross his arms behind his head so that the doctor can feel the lymph nodes in the anterior and posterior axillary folds. To examine the lymph nodes deep in the armpit, the doctor forms an abutment by pulling the patient's arm down.
Examination of the thorax
When you sit down, the lung examined. To do this, the examining doctor first places his hands on the sides of the Rib cage and examines the way the movement of the chest (Thoracic excursion). Then the doctor puts his hand on the burst basket and taps it with his other hand (percussion). So you can Pounding sound of the lungs examine and draw conclusions about the ventilation pull. In addition, the Lung borders to be determined. Then the examiner hears the lungs with a stethoscope from (Auscultation). Not only is the back bugged, but also the Lungs tips, just behind the collarbone and also from the front. The opportunity can also be used on the windpipe (Trachea) to listen.
After examining the lungs, the patient is allowed to lie down. It should be ensured that the upper body is raised at a 45 ° angle. So can Fill status of the neck veins (Jugular veins) be assessed. Another statement about the regular filling of the Veins makes the so-called Hepato-Jugular Reflux Test. To do this, the doctor presses deep under the right one Costal archwhere the liver is located.
Then that begins Listening to the heart with the stethoscope. It starts in third intercostal space on the left (3. ICR left) on Inheritance pointwhere all Flap tones listen loudly. To between the first and the second Heart sound to be able to differentiate, the Pulse for example on wrist groped. After that, the individual heart valves bugged. The Aortic valves will be in second intercostal space right (2.ICR right), the Pulmonary valve will be in second intercostal space on the left (2. ICR left), the Mitral valve will be in fifth intercostal space Left (5. ICR left) and the Tricuspid valve will be in the fourth Intercostal space right (4. ICR right) bugged. For a more detailed investigation, the Carotid artery (Carotid artery) heard. Transmission noises could possibly be heard here. For particularly close listening, you can ask the patient to bend forward so that you can hear the Sounds of the aortic valve can hear even better. To the exact Listening to the mitral valve the patient should turn on their left side so the doctor can reassess the mitral valve on the left side. The mitral valve lies between left atrium and the left ventricle and is in the Relaxation phase of the heart open. The aortic valve lies between left chamber and aorta and is during the Tension phase of the heart open. Like the mitral valve, the tricuspid valve is open during the relaxation phase and lies between the right atrium and the right ventricle. The Pulmonary valve lies between the right chamber and the Pulmonary artery and is also open during the tension phase.
Examination of the abdomen
When the doctor has finished examining the chest, he turns to him abdomen to. An inspection is also started. During this, the examiner looks for scars that may indicate operations the vein drawing and if necessary on one tight abdominal wall. Then the Intestines bugged with the stethoscope, paying particular attention to the Bowel noises is respected.
Then the abdomen is palpated (Palpation). When scanning is on Resistances, Defense tensions and Signs of pain the patient respected. The localization of the pain and the immune system is indicative of the disease. For example free air in the abdomen to exclude, the doctor places his fingers on the patient's stomach and then taps his fingers with his free hand, assessing the sound quality of the abdomen. This investigation will too percussion called.
The examination of the intestine is followed by the examination of the internal organs in the abdomen. First be the liver borders determined below the right costal arch. To do this, the patient is asked to breathe in deeply while the doctor places his hands under the costal arch to feel the edge of the liver. Another possibility is the so-called scratch auscultation liver. The stethoscope is placed on the Sword extension (Xiphoid) placed between the costal arches, while at the same time walking along with the fingernail at liver level.
The examination of the spleen and Gallbladder on. This examination is only noticeable if the organs are painful or palpable. For this examination, the doctor forms an abutment with his hand while he feels for the spleen with the other.
Similarly, the Kidneys examined. This examination is also suspicious if the kidneys are painful. In addition, the kidneys are examined for painful knocking. To do this, the doctor taps both kidneys briefly. A positive result can be an indication of a Pyelonephritis (Pelvic inflammation) be.
Depending on the patient's complaints, the examinations based on a Appendicitis (appendicitis) point out, investigated. The doctor asks the patient to lie on his back. The patient is then asked to raise the right leg against resistance. In case of pain this is so called Psoastest positive. In addition, the doctor will assess the painfulness of the McBourneypointswhich is halfway between the navel and the front upper tip of the right hipbone. Furthermore, the Lanzpunkt checked, which is on the connecting line between the two front upper tips of the hip bone after a third on the right side.
Examination of the extremities
When examining the extremities will be on Blood circulation, Motor skills and sensitivity examined.
For the study of the Blood circulation in the legs the pulses are sent to the Feet measured behind the ankle and on the back of the foot, side by side. In addition, the pulses in the Hollow of the knee and in the groin groped. When examining the feet, the doctor also paid attention to them Skin color and the temperature. The feet may be cold, but not differently warm or differently cold. When examining the blood flow in the arms, the pulses are usually measured side by side. The pulses are here in the armpit and on the Wrists measured. Again, the pulses on both sides should be the same, as a difference in the pulses is an indication of one Occlusion of the arteries you are a reference to the peripheral arterial disease (PAOD) can be. This finding is especially common in patients who have had a long history Nicotine consumption is known to be very important as smoking is the emergence of a PAOD massively favored.
The Motor skills of the extremities is also examined in side-by-side comparison. For gross motor skills, the focus is on measuring force, while for smaller joints such as the fingers, the focus is on examining fine motor skills.
When examining the Gross motor skills the patient is usually asked to give his Joints to stretch or bend a resistance. When examining the Fine motor skills the patient is asked to move his fingers in different movement patterns.
The Sensing the extremities can be examined for example with a vibrating tuning fork. This is held on the patient's ankles while the patient is asked to tell the doctor whether or not they can feel the vibration. The sensors are also always examined in a side-by-side comparison.