Contact allergy
definition
A contact allergy is an allergy of the so-called late type. After previous asymptomatic contact with the substance that triggers the allergy, repeated contact leads to a symptomatic reaction. Both genetic and non-genetic factors exist that favor the occurrence of a contact allergy. The most common contact allergens are nickel and cosmetics. Contact allergy of the immediate type is rarer than the late-type contact allergy. The first contact with the allergen leads to a symptomatic reaction. Common allergens for such an immediate contact allergy are plant and animal products.

causes
A contact allergy is based on a disturbed immune reaction to a triggering allergen. In the so-called late-type allergy, after a sensitization phase in which no symptoms occur, symptomatic eczema occurs on renewed contact with the allergen. In the sensitization phase, the allergen encounters skin cells that react by releasing various immune substances such as interleukin-1 and TNF-alpha. In a complex reaction of the immune system, so-called memory cells are created that remember the allergen, e.g. nickel. When they come into contact with nickel again, these memory cells react with an inflammatory reaction, which is reflected in the typical symptoms of a contact allergy, namely swelling, reddening, itching and blistering.
The situation is different with a contact allergy of the immediate type. There, an eczema reaction occurs after the first contact with the antigen, for example a pollen. This is what so-called mast cells are responsible for, which bind IgE antibodies to their surface. The total number of these IgE antibodies is typically increased in people with such a contact allergy.
You can find more about nickel allergy on our website Nickel allergy
Contact allergy to detergents
Detergents are one of the typical triggers of a contact allergy. Various ingredients of the detergent can lead to the typical skin changes and agonizing itching. A common cause are softeners contained in the detergent. Apart from softeners, however, fragrances are also often the cause of an allergic reaction to a detergent.
One easy way to find out if the detergent reaction has occurred is to change the detergent. It is preferable to use a detergent without fragrances and softeners. Special detergents adapted to allergy sufferers are particularly recommended in this context.Targeted allergy diagnostics by the dermatologist ultimately provide precise information about the cause of the contact allergy.
Read more about this under Detergent allergy
Contact allergy to nickel
Nickel is probably the most common contact allergen. Nowadays, nickel has therefore been largely banned from the production of costume jewelry, belts and metal buttons. However, nickel is rarely found as a component of clothing, for example in zippers, or pieces of jewelry. A nickel allergy is usually clearly visible on the skin that has come into contact with the metal. These are, for example, the ears (wearing earrings), the stomach and hips (zippers and belt buckles) or the cleavage and wrists (wearing chains and bracelets).
More on this topic on our pages: Symptoms of a nickel allergy
Contact allergy to plants
Just like fragrances and other allergens, plants are also typical triggers of a contact allergy. They can cause both late-type allergies and immediate-type aeroallergic allergies. Arnica, mugwort or chamomile are classic triggers of a late-type contact allergy. Chamomile in particular, which is very popular as a home remedy, is a common cause of contact allergies. Therefore, chamomile compresses on the eyes in particular should be avoided. People with a tendency to atopy (allergic tendency) in particular are more likely to develop contact allergies of the immediate type, which are caused by aeroallergens. These are especially asthmatics or people with neurodermatitis. Here too, herbal components, especially pollen, play an important role in the development of the allergy.
Contact allergy to tomatoes
As a rule, tomatoes do not lead to the development of contact allergies. However, the consumption of tomatoes can lead to a deterioration of the complexion of the skin in patients with neurodermatitis. The reason for this is not, as is often assumed, a direct allergenic effect of the tomato, but the acidity of the juice. Onions and vinegar also have a negative effect on the skin of some neurodermatitis sufferers. Avoiding acidic foods often improves the skin.
You can find more on this topic on our website Tomato allergy
Contact allergy to latex
The latex allergy is usually an allergy of the immediate type. After first contact with the allergen, reactions occur that can range up to anaphylactic shock. Contact allergies can also arise from direct skin contact with objects containing latex. People who work in the healthcare sector are particularly at risk, as a lot of latex is processed there. Latex is found in gloves, plasters, ventilation bags and urine bags, among other things. Objects that contain latex can also be found in everyday life. Examples of this are household gloves, seals on doors and windows or rubber pads. In addition to medical treatment, it is recommended to avoid objects with latex for life so as not to provoke a dangerous, allergic reaction.
You can find more about this on our website Latex allergy
Contact allergy to disinfectants
Disinfectants are mainly used in health care, but also in many people's everyday lives. Components of the disinfectant, especially preservatives, can lead to a contact allergy. However, a contact allergy to disinfectants is rather rare. Frequent disinfection of the hands is more likely to lead to eczema that is not allergic. The disinfectant has a strong drying effect. It is therefore very important to regularly apply cream after using disinfectants.
Contact allergy to wool wax
Wool wax can also be a possible cause of a contact allergy. An allergic reaction to wool wax or wool wax alcohol is rare, but possible. Wool wax is contained in various cosmetic products such as lipsticks, shaving soaps, shampoos and soaps. Wool wax and wool wax alcohol can also be found in industrial fats and household products.
Sensitization in the patch test is found quite often, but is not very specific. A use test should therefore always be carried out. This means that after such a positive test result, one tries out whether an allergic reaction occurs when using products containing wool wax.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of a contact allergy includes various common tests of allergy diagnostics.
The most important test for diagnosing late-type contact allergy is the patch test. In this test, potential allergens are very strongly diluted into petroleum jelly and worked into the back of the person affected. The standard test series of such a patch test comprises 29 substances, such as wool wax, propolis or fragrances, which are often involved in the development of a contact allergy. The skin reaction is read off after 48 and 72 hours. Redness and vesicles as well as papules (small protrusions) are rated as positive reactions. Such a reaction can be used to determine whether a substance is a possible trigger for the contact allergy.
Contact allergies are less common allergic reactions of the immediate type. In order to determine such an allergy, special blood values, namely the total IgE and the RAST laboratory, are determined. These values are typically elevated in people who are prone to allergic diseases. In addition, the atopy patch test is carried out. This test is very similar to the patch test, only so-called aeroallergens are tested here. These are allergens such as pollen and animal hair, which reach the skin via the air and cause an allergic reaction there. The so-called prick test is also often used, in which allergens are applied to the forearm.
You can find more on this topic on our website Allergy test
Concomitant symptoms
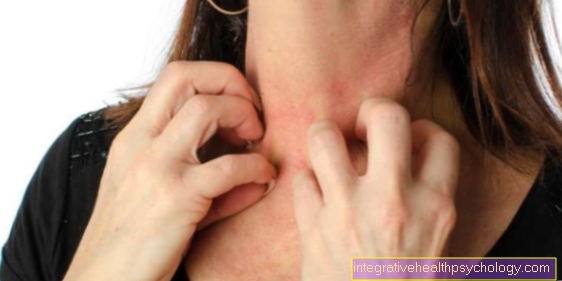
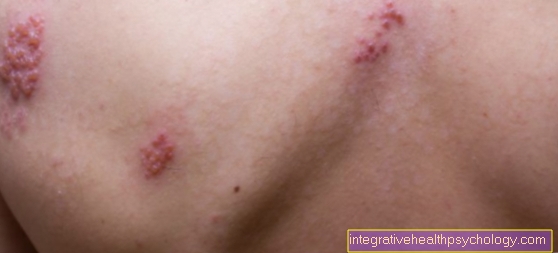
The symptoms of a contact allergy are limited to the skin. In the acute stage of eczema, redness, swelling and itching of the affected skin area are typical. Weeping eczema and blistering are also not uncommon. Chronic eczema develops if the skin has repeated contact with the allergen over a long period of time. This is characterized by very dry skin, a coarsened complexion (lichenification) and painful cracks.
Symptoms such as asthma attacks, watery and itchy eyes or even shortness of breath, which are typical with other allergies, do not occur with contact allergies. An exception is the combination of a contact allergy with a pre-existing allergic disease, such as asthma. In this case, the contact allergy can also lead to general symptoms such as shortness of breath or dizziness and circulatory failure. However, this is very unusual.
therapy
A very important measure in the treatment of a contact allergy is to avoid the triggering allergen, for example nickel. Contact allergies usually do not disappear over the course of a lifetime, so the only consistent way is to cut off contact with the allergen.
If contact eczema has already developed, different measures are used depending on the symptoms. Acute oozing skin should be treated with moist compresses. In this case, greasy ointments are not recommended. They may lead to further irritation. If the skin is itchy or inflamed, local cortisone preparations can be applied. However, cortisone should only be used on small areas of skin and for a short period of time, as it leads to thinning (atrophy) of the skin. A distinction is made between preparations with a high water content, such as creams and lotions, from ointment bases that are more fatty. Creams and lotions are mainly used on acute eczema as they moisturize the skin.
In the case of chronic eczema, which is more characterized by dry, flaky and cracked skin, fatty ointment bases are particularly suitable for treating contact allergies. If there is no improvement, ointments with immune-modulating agents such as tacrolimus can also be used. This active ingredient reduces the activity of the immune system and thus leads to the healing of eczema. Chronic contact eczema is occasionally treated with UV therapy.
Home remedies
If you have a contact allergy, you should refrain from using home remedies. These can increase skin irritation or possibly promote the occurrence of further contact allergies. It is therefore advisable not to treat the irritated skin yourself with home remedies or ointments, but to consult a dermatologist directly. This is the best way for the doctor to assess the condition of the eczema and determine the contact allergy based on its appearance. Home remedies or the use of ointments can almost falsify the complexion and make diagnosis more difficult.
homeopathy
Unfortunately, a contact allergy cannot be treated with homeopathic remedies. When contact allergies develop, complex processes take place in the immune system that cannot be influenced by homeopathic remedies. Incidentally, there are no other drugs available to cure a contact allergy. The allergy as such persists. Only avoiding the allergen prevents eczema from occurring. Medicines that dampen the allergic reaction, such as antihistamines, are mainly used in the case of immediate-type allergies and prevent the symptoms. However, they also do not make the allergy go away.
Duration
A contact allergy usually subsides within several days if the triggering allergen is avoided. Consistent medical treatment with cortisone ointments and moist compresses will accelerate healing. '
However, if the allergen is not avoided, contact allergies can lead to persistent eczema that lasts for weeks or even months. A contact allergy usually does not disappear in the course of a lifetime, so the triggering allergen should be consistently avoided.
course
In the case of a contact allergy, there is an acute reaction of the skin. This acute contact eczema is characterized by reddening, itching and the formation of small blisters or papules. The eczema may ooze and continue to be itchy. If there is no contact with the allergen, the symptoms resolve on their own within a few days and weeks.
However, if the allergen remains in continuous contact with the skin, chronic contact eczema develops. This is mainly characterized by dry skin and a coarse skin pattern. The latter is also known as lichenification. Cracks in the skin and flaking are also possible with chronic contact eczema. The contact allergy as such usually lasts for a lifetime. However, by avoiding the allergen, the course can be influenced very favorably so that freedom from symptoms can be achieved. Chronic eczema occurs only very rarely.
Contact allergies by location
By the hand
The hand comes into contact with many materials and substances in everyday life. It is therefore not surprising that eczema and skin problems frequently affect her. Contact allergies can also show up on the hands and lead to a real restriction in everyday life. Itching, weeping eczema and redness are the typical symptoms of a contact allergy on the hands. Possible triggers are chemicals, metals or plants. Occupational groups such as hairdressers, chemical workers, construction workers or bakers, who are in constant contact with allergens, usually suffer more from such hand eczema. The most effective treatment is avoiding the allergen. Consistent wearing of gloves is recommended, especially in the case of mandatory occupational exposure, in order to prevent chronic contact dermatitis.
In the face
The face is not an all too rare location for contact allergies. In particular, cosmetics, care products or fragrances are typical triggers of a contact allergy. It is characterized by reddening, itching and small blisters or papules on the skin of the face. Jewelry can also be a possible trigger. Earrings that repeatedly touch the cheeks, for example, are also a possible, albeit less common, cause of a facial contact allergy. The face is a specialty in the treatment of contact eczema. Ointments containing cortisone must not be used here, or only for a very short period of time and in a very low dose. For treatment, therefore, preparations with substances such as tacrolimus are used, which somewhat dampen the excessive reaction of the immune system.
More on this topic on our website Eczema on the face
In the genital area
A contact allergy can also develop in the intimate area. If this is the case, there are several possible triggers. An intolerance to textiles, panty liners or care products is very likely. The triggering allergen must have direct contact with the genital area in order to cause the eczema. A contact allergy should not be confused here with infectious eczema.
A common cause of eczema in this area is scabies, also called itch mite infestation. It should also be considered as a possible cause of the eczema. An examination by the dermatologist can provide information about the underlying cause and rule out an acute infection.
More about this on our website Eczema in the genital area
On the eye and on the eyelid
Contact allergies to the eyes or eyelids are often caused by chamomile poultices. The popular home remedy is often used as a decongestant, for example for tired eyes. Chamomile, however, is a very strong allergen that can quickly lead to contact allergies, especially in the eyes. Therefore, chamomile compresses should not be used to treat the eyes. Make-up, eye creams, and other care products are also possible triggers for contact dermatitis on the eyes. If you have suspicious symptoms, it is advisable to first see an ophthalmologist so that a serious cause, such as an eye infection, can be ruled out. The dermatologist then takes over the treatment of the contact allergy.
More about this on our website Eczema on the eye and eczema on the eyelid
On the scalp
Shampoos, dyes, oxidizing agents and textiles can cause scalp contact allergies. These are often not seen - unless they spread to the forehead and the surrounding skin - but the agonizing itchiness is felt all the more. Contact allergies of the scalp are treated in the same way as other contact allergies. If you have repeated eczema, you should take care of your scalp hair. Coloring the hair and aggressive bleaching should be avoided.
More about this on our website Eczema on the scalp
Allergy types
Allergies are divided into different types (types I-IV) depending on their mechanism of origin. The contact allergy is usually a so-called type IV allergy. This type of allergy is also known as the late type. The first time you come into contact with the allergen, such as chamomile, there are no symptoms. However, the immune system reacts to the allergen without the person concerned noticing it and releases various messenger substances. Ultimately, so-called memory cells are created that literally memorize the allergen and react when there is renewed contact. This then leads to an allergic reaction on the skin. The first symptom-free contact with the allergen is also known as sensitization.
Less commonly, contact allergies are type I allergies, also known as immediate type. The first contact with the allergen leads to an allergic reaction. Typical allergies of type 1 are, for example, house dust or pollen allergies. In the case of contact allergies, so-called aeroallergens are the main triggers of this type 1 contact allergy. Aeroallergens are substances that come into contact with the skin via the air, such as pollen or other plant components. Typically, in such a case, the uncovered skin is affected by a flat rash.
Nettle
On contact with the skin, nettles lead to itchy wheals, which are often misinterpreted as allergies. This is not an allergy, but a kind of toxic reaction of the skin to the stinging hairs of the stinging hairs. However, the nettle can also lead to allergies caused by its pollen count. As an airborne allergen, pollen can lead to a contact allergy.This is particularly the case with people with atopy, who suffer from asthma or neurodermatitis, for example. However, direct contact of the nettle with the skin does not cause a contact allergy.
Can I get a tattoo if I have a contact allergy?
In principle, there is no reason to decide against a tattoo if there is a contact allergy. The contact allergy initially has nothing to do with the tattoo. However, it should be noted that a tattoo itself can be the cause of a contact allergy. Black tattoos have a lower risk of causing an allergy than colorful tattoo inks. This is due to the different ingredients in the paint. In general, however, it is not possible to speak of a tattoo ban even with regard to this risk. Whether you want to get a tattoo and are prepared to take any risks is ultimately an individual decision.