Lower abdominal pain
General
Lower abdominal pain can have numerous causes. The diagnosis is all the more difficult. For this reason, in addition to the exact nature of the pain, the location and the accompanying symptoms, the timing of the pain is of great importance.

causes
Changes in the body can cause pain, especially at the beginning of a pregnancy. These arise from Elongations of the various bands of the uterus (uterus), which adapts to the new situation. In addition, the Pregnancy hormones (ß- HCG) not yet sufficiently present and the uterus tends to Contractionswhich can cause abdominal pain.
In later stages of pregnancy you can also Kicks or an unfavorable one position cause pain in the child. But also Exercise contractions are normal in the last trimester and only serve the uterus to prepare for childbirth. However, these contractions have no effect on the cervix and do not serve to induce childbirth. For this reason, these must be differentiated from birth-related contractions that initiate the birth and one Premature birth can evoke.
Symptoms
A simple Pulling in the stomach, similar to during the MenstruationHaving no bleeding is usually harmless and merely a sign of changes in the uterus. Nevertheless, this too should be confirmed by a doctor to one Abortion to avoid. If the amount of pregnancy hormone is too low, it can cause the uterus to contract and possibly lead to a miscarriage.
If pain occurs later in pregnancy, it is usually necessary between child movements, labor pains and premature labor can be distinguished. Kicks the child against the abdominal wall or an unfavorable position of the child can be very painful, especially if the space in the abdomen is significantly reduced. However, by changing the mother's position or animating the child to reposition, the pain usually stops. This type of pain is also different from contractions, as the pain does not occur regularly and lasts much shorter or can be ended by repositioning.
Practice contractions are particularly common in the third part of pregnancy and are used to prepare the uterus for delivery. However, they are not relevant to birth and do not lead to an opening of the cervix. Just like real labor pains, it is about contractions, which are accompanied by a hardening of the abdomen. They differ from birth-related contractions because they only last a maximum of 45 seconds and do not occur more than 3 times an hour. A CTG be put on by the gynecologist or in the hospital. This shows both the labor activity and the heart activity of the child
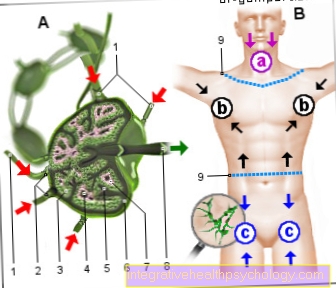
Localization of the pelvic pain
Lower abdominal pain on the left
Pain in the left lower abdomen is common in adult patients and can be a sign of intestinal diverticulosis. These are benign bulges in the intestinal wall which often arise in the context of chronic constipation and a weakened intestinal wall.
The reason for this is probably the increased pressure in the intestine caused by chronic constipation, and the weakened intestinal wall at the same time. For this reason, older patients are often affected. The pain can also be felt as a burning sensation in the abdomen.
Read more on the topic: Abdominal pain and constipation
In most cases, these diverticula have no symptoms at all. However, the diverticula can become inflamed and cause severe pain in the left lower abdomen. These often occur suddenly and severely affect the patient.
In many cases, the pain is also accompanied by fever and general symptoms such as tiredness, exhaustion and headache and body aches. If there is only inflammation of the diverticula without evidence of a breakthrough into the free abdominal cavity, there is no indication for an operation.
This article may also help you: Abscess in the intestine
The pain can be treated with pain relievers and antispasmodic drugs. Also be Antibiotics used to treat inflammation. The ingestion of food should initially be avoided in order to protect and calm the intestines. The patients are then temporarily fed via the vein. The pain should subside within a few days.
If the inflammation has led to a breakthrough in the free abdominal cavity, this must be treated surgically immediately. Only in this way can a life threatening Peritonitis be prevented.
As part of the operation, the S-shaped part of the Colon (Sigma) removed, and the rest of the colon connected to the rectum. There is no need to create an artificial anus. This therapy is also recurrent in the case Inflammation of the diverticula preferred to prevent imminent breakthrough of the diverticulum.
An ectopic pregnancy can also lead to pain in the left lower abdomen in women of childbearing potential. These are associated with symptoms similar to those of a ruptured diverticulum. The pain is acute and very severe. They are also often accompanied by fever, a very weak general condition and possibly vaginal bleeding.
Since this is also an inflammatory cause with a breakthrough into the free abdominal cavity and the great danger of a Peritonitis the ectopic pregnancy must be operated on immediately.
Also a pinched one Inguinal hernia is accompanied by severe, sudden pain. The hernia in the hernial sac in the groin area can also often be felt. Signs of inflammation such as fever are absent in many cases. Since the Inguinal hernia can lead to an entrapment of the bowel, it must also be treated as quickly as possible. In some cases, the hernia can be reduced manually. Surgical closure of the inguinal hernia should then be carried out promptly.
If the hernia cannot be freed from its entrapment, an operation must also be carried out immediately to prevent the affected part of the intestine from dying off. Also one Testicular torsion can lead to sudden severe pain as it is a twisting of the spermatic cord with the supplying vessels and nerves. In most cases, testicular torsion can also be treated manually.
Ureteral stones If too big to pass through the ureter, they can cause colic-like pain in the lower abdomen. In most cases, pain reliever and anticonvulsant therapy is sufficient and the stone is transported into the bladder by itself and then excreted. If this is not the case, the stone must be dissolved by ultrasound-guided waves or stone-dissolving medication. In exceptional cases, surgical removal of the stone is necessary.
Lower abdominal pain on the right

Right-sided lower abdominal pain, like the left side, can occur due to an ectopic pregnancy, a pinched inguinal hernia, a ureteral stone, or a cervical torsion. Again, the pain can be felt more like a burning sensation.
Read more on the topic: Burning in the abdomen
On the other hand, appendicitis is specific for right lower abdominal pain, as it is found in the right lower abdomen. Appendicitis pain often begins in the mid-abdomen around the navel and then slowly migrates to the lower right abdomen. The reason for this is the progressive inflammation of the appendix with increasingly precisely localizable pain. The pain is often accompanied by a slight fever, nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
The pain is more of a dull, persistent character and increases in intensity. When the appendix breaks through, the pain may initially subside. With increasing inflammation of the peritoneum, however, the pain in the lower abdomen becomes significantly stronger and can ultimately affect the entire abdomen. Since such peritonitis can be life-threatening, it is important to recognize appendicitis early and, if necessary, to operate.
Appendicitis is often detectable by an ultrasound examination and the increased inflammation parameters in the blood. As long as the inflammation is confined to the appendix, the operation can often be performed laparoscopically. All you need to do is make three small incisions to insert the camera into the abdomen. The remaining scars are very small and hardly visible in the long run.
Since appendectomy is a routine procedure, complications are very rare and the risks are low.
In addition to appendicitis, the appendages (adnexa) in women can also become inflamed. In women, the appendages denote the fallopian tubes (tuba uterina) and ovaries (ovaries). Adnexitis can occur unilaterally or bilaterally and therefore, strictly speaking, also on the left side. However, for reasons unknown, right-sided adnexitis appears to be more common. An acute inflammation of the appendages is accompanied by sudden severe pain in the area of the right lower abdomen.
If the inflammation is not treated correctly and does not heal completely, scarring and adhesions in the area of the fallopian tubes or ovaries can occur, causing symptoms to persist for years.
The causative agents of adnexitis are diverse. However, chlamydia can be detected in 40% of cases. The pain often occurs laterally after menstruation or during ovulation. If the cervix or uterus are affected in addition to the appendages, discharge and spotting may also occur.
In the case of severe infections, vomiting, fever and nausea can also occur. If the inflammation leads to rupture of the fallopian tube or ovaries, an acute abdomen such as appendicitis can also occur.
A gynecological examination with palpation of the uterus should be performed diagnostically. This test causes pain if there is inflammation. The speculum examination also reveals the inflammation of the uterus through severe reddening and edema. A microbiological smear should be taken as part of this examination. Abscesses, swellings or secretions in the area of the fallopian tube and ovary can be shown in the ultrasound. If the diagnosis cannot be established, a laparoscopic examination must also be performed in this case.
In addition, increased inflammation parameters can be detected in the blood count. As a rule, the adnexitis is treated with antibiotics after the microbiological smear has been taken.
Since in most cases chlamydia are responsible for the inflammation, tetracyclines or fluoroquinolones are used for at least 10 days. If the therapy does not work, the antibiosis should be switched to cephalosporins and metronidazole. If this therapy cannot produce the desired results either, treatment should be based on the microbiological result and resistogram. If abscesses have developed, they are usually treated as an inpatient and relieved surgically. Pain medication such as ibuprofen can be used for severe pain.
Lower abdominal pain in the middle
Lower abdominal pain in the middle abdomen occurs in most cases due to unspecific Colon discomfort. First and foremost, this includes constipation (Constipation). This can occur due to insufficient fluid intake or poor nutrition. In the case of simple constipation, severe, spasmodic and cramp-like pain in the lower abdomen occurs.
Enemas or short-term use of laxative drugs can clear the constipation. As a prophylactic, one should eat a balanced, high-fiber diet and drink enough fluids. To diagnose the other causes of constipation, further examinations are often required, such as one Colonoscopy, a Ultrasonic or one Computed Tomography necessary.
In addition to the non-specific constipation, which can occur in the entire abdomen, the inflammation of the pancreas as a specific pain in the middle abdomen, which radiates in a belt-shaped manner around the abdomen. The pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and possibly an acute intestinal obstruction (ileus).
The Inflammation of the pancreas can occur both acutely and chronically and is usually the result of heavy or long-term alcohol abuse. The diagnosis is based on the medical history (anamnesis), physical examination, a Ultrasonic and various laboratory tests. The acute pancreatitis needs to be treated in the hospital. The patients are not allowed to eat anything until the symptoms and laboratory values have improved significantly. This is used to immobilize the pancreas. During this time, the patient receives a lot of fluids, as well as electrolytes, nutrients and vitamins via the vein. Painkillers are used to relieve the symptoms. When the symptoms have subsided, a slow diet is built up.
Therapy of chronic Inflammation of the pancreas is often much more complicated, as the cause is often unclear or no longer treatable. In some cases, both forms may require surgery.
Another cause of mid-abdominal discomfort can be a Umbilical hernia be.There is a prolapse of intestinal loops in the area of the umbilicus through the obliterated umbilical annulus. This represents part of the umbilical cord in the prenatal period and closes after the birth. This part of the umbilical cord can be a predilection point for an umbilical hernia and then contains parts of the peritoneum and possibly parts of the intestine. If only parts of the peritoneum are contained in the hernial sac, or if the sac is very small, there are often no symptoms. However, if the fracture gap is large enough or if parts of the intestine are trapped, localized pain occurs in the umbilical area. The navel is often swollen and possibly reddened as a sign of a bulging bowel under the skin.
Predisposing to such an umbilical hernia are overweight (obesity), intense physical exertion and a significant increase in pressure in the abdomen (for example, a pregnancy). In addition, women are more likely to have an umbilical hernia.
If the umbilical hernia is accompanied by significant symptoms, it is treated surgically. Here the hernial sac is removed and the hernial gap is closed with a double seam. In some cases, a mesh can be sewn in to hold the abdominal wall in place.
This can be another life-threatening cause of mid-abdominal discomfort Abdominal aortic aneurysm be. This is a bulging of the vessel wall of the abdominal aorta. Such an aneurysm is often normal at first. In some cases, patients feel dull abdominal pain and back pain, which can also radiate to the legs. However, the actual symptoms only appear when the bulge ruptures. At this moment there is a strong, stabbing and devastating pain in the middle abdomen. Due to the massive loss of blood, life-threatening shock symptoms then occur. Because of this very acute and life-threatening situation, an operation has to be performed within a very short time.
The diagnosis is made through an orienting ultrasound examination and the immediate opening of the abdomen to stop the bleeding.
Also one Cystitis can manifest itself in lower abdominal pain. Usually come first burning sensation when urinating and a constant feeling of need to urinate.
Will the Cystitis If left untreated, abdominal pain in the middle lower abdomen and fever can also occur. The diagnosis can often be made using a urine test and clinical symptoms. A cystitis should be treated with plenty of fluids and possibly drug therapy with antibiotics.
therapy
Most causes of abdominal pain do not require any form of therapy. In particular, contractions at the beginning of a pregnancy cannot be treated well, as this is an adaptation of the body to the new circumstances. Early labor, on the other hand, must be taken very seriously and, under certain circumstances, treated as an inpatient. Most of the time, the affected mothers have to follow a strict one for the rest of the pregnancy bed rest adhere to and be medicated with contraceptive drugs treated. If the cervix opened too early, this can be done with a so-called Cerclage tentatively closed again to an ascending order infection of the child and to avoid a premature birth.
Type of pelvic pain
Lower abdominal pain after eating

Pain in the lower abdomen after eating is often an indication of various food intolerances. If children or infants complain of abdominal pain after eating, there can be several causes.
First and foremost, older children must have a food intolerance, especially the Lactose intolerance be thought. This is an intolerance to lactose, which is caused by a lactase deficiency. This enzyme is normally used to break down milk sugar into galactose and glucose. If there is an enzyme deficiency, osmotically effective amounts of lactose enter the large intestine and bind water there. Then the symptom arises first diarrhea (Diarrhea). In addition, the water leads to an overall higher filling level of the intestine and thus to it stomach pain. As the process progresses, the lactase is broken down by the bacteria in the intestine, creating gases and Flatulence arise.
Diagnostically, an attempt to omit foods containing lactose can be undertaken. In many cases this leads to a spontaneous cessation of the symptoms. If the diagnosis cannot be made with certainty in this way, an H2 breath test can be carried out.
The best therapy for confirmed and symptomatic lactose intolerance is to avoid or reduce the amount of lactose consumed daily. Lactase tablets, which contain the enzyme, can help before traveling or when you plan to take milk sugar.
In addition to lactose intolerance, other foods such as fish, nuts, shellfish or chicken eggs can also lead to gastrointestinal complaints, in particular pain, diarrhea and flatulence. In the differential diagnosis, especially in babies with abdominal pain and flatulence, 3-month colic should be considered. These lead to persistent crying attacks in the infants after meals, the peak of which is around 6 weeks old. Usually the symptoms subside at the end of the third month of life. An exact cause for this is not yet known. It is assumed that drinking too much, swallowing a lot of air during the meal (aerophagia) and increased gas formation in the intestine leads to painful peristalsis (bowel movement) and flatulence. Therapy is not required here. Symptomatic warming blankets on the stomach or a circular stomach massage in the direction of the intestinal outlet (clockwise) can help.
Celiac disease does not cause symptoms until the children start eating cereals. In this case, abdominal pain and diarrhea can also occur, often accompanied by ill-humor in the child and failure to thrive. The reason for this is a sensitivity of the small intestinal mucosa to gluten. Since the intolerance leads to atrophy of the small intestinal mucosa, it is important to make the diagnosis as early as possible. By following a strict lifelong diet, the symptoms quickly recede and the intestinal mucosa can regenerate. In some patients, celiac disease can be asymptomatic for years and only becomes noticeable in these cases in adulthood. The symptoms largely correspond to the symptoms in childhood. However, failure to thrive and ill humor do not occur.
Lower abdominal pain in men
Some causes, among other possible diseases, can be specifically responsible for pelvic pain in men. Particularly noteworthy are diseases of the male genital organs. Urological diseases such as testicular torsion can lead to severe pain in the lower abdomen. The testicle rotates on its own axis until there is a lack of blood supply to the testicle. Both a genetic predisposition and accidents with testicular involvement can lead to the occurrence of the torsion.
Sexually transmitted infections can also be responsible for the symptoms. If there is chronic inflammation, enlargement or a tumor of the prostate, this can also be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
In the end, it should always be remembered that the symptoms of men can also be a hernia. These occur more frequently in men than in women and can lead to severe pain in the lower abdomen, especially if parts of the intestine are pinched off in the hernial sac.
In some cases, back pain can radiate into the area of the lower abdomen due to nerve irritation. This option should be considered, especially if you have back pain at the same time.
Sometimes the pelvic pain also comes from a certain section of the intestine or a loop of intestine. The causes are varied and can also occur in women. Read on below: Pain in a loop of intestine
Lower abdominal pain during pregnancy
Lower abdominal pain in the pregnancy can have numerous causes. All other causes, regardless of the pregnancy, can also be responsible for abdominal pain during pregnancy. During pregnancy, most of the symptoms are caused by simple adaptation processes of the body to the new situation.
Due to the strong changes in the entire body that occur during pregnancy, the muscles and ligaments are stressed. In addition, as the uterus grows, it increasingly takes up space in the abdomen, causing discomfort and Stomach cramps may occur.
The abdominal pain often has a pulling character in the lower abdomen and is similar Menstrual cramps. Bleeding, fever or other symptoms do not occur. The therapy consists of relaxing measures, reducing stress and applying heat. In addition to the harmless causes due to the adaptation processes in the body, the cause can also have other origins. If the pain occurs with bleeding at the beginning of the pregnancy, a doctor should be consulted as in some cases the symptoms with a Abortion accompanied. This diagnosis can often be made easily with the help of an ultrasound.
Abdominal pain in pregnancy are a frequent Symptom which often causes great concern.
However, in most cases this is unfounded, as slight abdominal pain in the Lower abdomen are not uncommon. The causes of the pain are very different and, despite everything, require clarification by a doctor.
Summary Bulking Pain During Pregnancy
Abdominal pain during pregnancy is a common and often harmless symptom as a sign of the body's adjustment to the new situation. Depending on the week of pregnancy, the causes of abdominal pain can be numerous and some are completely harmless. However, in order to avoid a serious risk to mother or child, a medical consultation is usually a good idea. By simple methods using Ultrasonic, CTG and laboratory the doctor can easily determine whether the pain is in need of therapy or not.
Summary of pelvic pain
Lower abdominal pain are a non-specific symptom with numerous diagnoses. For this reason, the precise history of the nature and duration of the pain is essential to make the correct diagnosis. In which area of the lower abdomen the pain occurs is also an important indication of the cause.
While the Appendicitis causing pain in the right lower abdomen is the Diverticulitis found in most cases in the left lower abdomen. The urinary bladder is located in the middle lower abdomen, so Cystitis cause pain in this area. Due to the variety of causes, more extensive diagnostics using imaging methods and a blood test are always necessary. Abdominal pain can also occur during pregnancy or after eating. Since in these cases other causes can be the reason for the pain, pregnancy or a history of food consumption should also be reported. The pain in pregnancy can be accompanied by simple adjustment processes, but also dangerous inflammatory diseases that require rapid diagnosis and therapy.
After eating, especially children develop pain and should then be examined carefully, as children often suffer from failure to thrive and development deficits when they are suffering from a food allergy. But even in adult patients, the pain after eating should be diagnosed urgently, as the symptoms are often excruciating and serious illnesses can also be the cause.