Burning in the intestines
definition
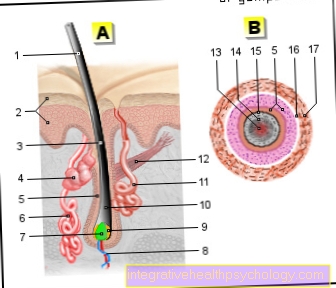
The intestine encompasses the entire digestive tract between the stomach and anus and is an approx. 6 meter long tube that is located in the entire abdominal area and is arranged there in loops. Burning in the bowel describes a non-specific symptom that can indicate many underlying diseases. The most important factor in determining the exact symptoms is the exact location of the burning sensation in the abdomen. An inflammation of a section of the intestine is in the foreground when determining the cause. This can range from very harmless causes to severe chronic or acute illnesses. Important warning signals when there is a burning sensation in the intestine are frequent occurrence and accompanying symptoms such as weakness and decreased performance.

causes
When determining the causes, the intestinal inflammation is in the foreground. Probably the most common cause of a burning sensation in the intestine is the simple gastrointestinal flu, which can take on various dimensions and symptoms depending on the pathogen and seasonally fluctuating. However, behind this disease are not the typical flu pathogens, but viruses such as the "noro virus" and bacteria such as "salmonella". These pathogens can be ingested through smear infections, through the air, spoiled food or droplets and spread throughout the body. The triggers vary seasonally, as there are bacteria and viruses typical of summer and winter. The burning sensation in the abdomen affects large parts of the intestine and occurs diffusely in the abdomen, often combined with diarrhea and vomiting.
Another very common cause of a burning sensation in the abdomen is appendicitis. On the other hand, it can be clearly demarcated locally in the right lower abdomen. The pain can be strongly provoked by external pressure. Appendicitis can also be accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting. If drug therapy does not improve after a few days, the inflamed appendix may have to be surgically removed. If the inflamed appendix ruptures beforehand, life-threatening complications can develop.
Find out more about the topic here: Signs of appendicitis
Inflammatory changes in the upper gastrointestinal tract can also lead to a burning sensation in the intestines. In the gallbladder, which is also part of the upper digestive tract, small gallstones can cause inflammation, which can cause severe, burning pain. The flow of bile is particularly stimulated by foods rich in fat or alcohol. If you are constipated by gallstones, you may experience typical colicky pain, especially shortly after eating. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa can also develop in the upper digestive tract, which is felt with burning pain. This leads to an overproduction of stomach acid, and heartburn can also occur at the same time. The so-called "reflux disease" can also be behind it and cause long-term acid-related burning pain in the upper abdomen. In many cases, "Helicobacter pylori" bacteria cause such burning inflammations of the gastric mucosa. Very many people carry this bacterium in their stomach without experiencing symptoms.
On the other hand, more rarely, but with an increasing tendency, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases can be responsible for a burning sensation in the intestine. The causes of these diseases are largely unknown. The most important representatives of these diseases are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Different sections of the intestine become inflamed, similar to autoimmune diseases.The inflammation can be very serious and painful and complex.
Find out more about the topic here:
- Symptoms of Crohn's Disease
- Inflammation of the small intestine
- Inflammation of the rectum
diagnosis
The diagnosis begins with an exact inquiry about the symptoms and accompanying circumstances as well as a subsequent physical examination. In order to differentiate between the various inflammations and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the exact symptoms and accompanying symptoms, as well as the location of the pain and the exact time of occurrence, for example at night or after eating, are decisive.
If there is a suspected diagnosis, the relevant section of the intestine can be examined more closely with the help of an ultrasound scan. Inflammation, blockages, stone formation and many other changes can already be recognized here. In order to take a closer look at inflammatory processes or changes in the intestinal structure, CT and MRI examinations can also be performed. Symptoms suspected of being in the stomach or colon can also be examined more closely with the help of an endoscopic examination. A tube with a camera is inserted into the body via the mouth or via the anus, with which the condition within these intestinal areas can be diagnosed. Small interventions such as taking tissue samples or removing small polyps can also be carried out directly in endoscopy.
Concomitant symptoms
The accompanying symptoms can provide crucial clues to the suspected diagnosis. In many cases, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting can be present. With a pathogen-related inflammation, fever, body aches, headaches and other typical flu symptoms often occur. Loss of appetite and weight loss can also be typical. On the other hand, blood in the vomit and stool are less common. They speak for ulcer-like changes, tumor diseases or advanced inflammation. Chronic inflammatory bowel disease, on the other hand, can be associated with general symptoms such as inflammation of the skin, eyes, blood vessels and kidneys. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa, on the other hand, often manifests itself as fullness and heartburn.
Also read: Intestinal bleeding
diarrhea
Diarrhea is one of the most common symptoms of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. In the later sections of the small intestine and large intestine in particular, much of the fluid within the intestine is absorbed into the body. If the intestinal mucosa is inflamed, these absorption mechanisms are quickly disturbed, which leads to the excretion of valuable water. In the case of long-term infections, it is imperative to pay attention to the water balance and the feeling of thirst, as the body loses control over it and the body can quickly lose water and become dehydrated.
Here you can find out more about the following topics:
- Causes of diarrhea
- Home remedies for diarrhea
Flatulence
Flatulence occurs when there is too much air in the bowel. This can occur on the one hand due to excessive air intake through the mouth and on the other hand due to the formation of gases during digestion. Inflammation of the intestines can be the cause of increased gas production. In most cases, however, flatulence is caused by a poor diet with a lack of water and electrolytes. Severe constipation with flatulence can sometimes lead to severe pain in the abdomen.
Find out more about: Causes of flatulence
treatment
As a rule, conventional gastrointestinal flu subsides on its own within a few days. The pathogen-related infections can be accompanied by severe symptoms, but often heal within a week. During this time, attention must be paid to the body's water balance and, if necessary, therapeutic pain medication can be used to make the healing phase more bearable. The body often cannot cure stubborn bacterial infections on its own. Therefore, antibiotics can be used that target the bacteria. Antibiotics can also fight potentially causative bacteria in the case of gastric mucosal inflammation. In the case of inflammation caused by acid, acid blockers must be prescribed medication. However, these are only used when changes in eating and living habits have not been successful.
Inflammation of the appendix and gallbladder can first be treated with medication. In many cases, however, the inflammation cannot be treated, which is why the organ must be surgically removed. Even with the rarer diverticulitis, the inflammation can progress to such an extent that the section of the intestine must be surgically removed.
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases are similar in their development to autoimmune diseases. Treatment with immunosuppressive drugs such as cortisone also helps with these diseases in the acute episode.
Home remedies
Gastrointestinal flu can be treated well with home remedies. In most cases it takes the body around a week to fight the disease. During this time, in addition to diarrhea and vomiting, burning and stabbing pain in the intestine can occur, which can be alleviated with home remedies.
The diarrhea can be treated with pectins, activated charcoal and swelling agents. These substances bind the toxins in the mucous membrane in the intestine and can reduce the symptoms. In addition, chamomile, ginger, fennel and nettle teas are popular home remedies, as the herbs have a soothing effect on the stomach and intestinal mucosa and the liquid actively counteracts dehydration. The herbs are still said to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects, so that they also actively support the body in fighting the pathogens.
Duration
The duration depends on the cause of the burning sensation in the intestines. Gastrointestinal flu caused by bacteria or the Noro virus, for example, usually heals within a few days. In most cases an improvement of the symptoms can be expected after about 3 days. Stubborn infections will also improve within a week of starting treatment.
In the case of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, on the other hand, it is often lifelong chronic diseases that progress in phases with asymptomatic phases. With the right treatment, these diseases can also be largely controlled. However, a complete cure is not to be expected in these diseases.
Burning locations
Burning in the left bowel
The exact location of the burning sensation in the intestine enables the best conclusions to be drawn about potentially affected intestinal sections or possibly involved abdominal organs. The left abdomen contains the descending large intestine and the so-called "sigmoid", i.e. the last sections of the large intestine before the transition into the rectum. A lot of inflammation of the colon takes place in this area. The most important diseases that are often found on the left side are diverticulitis and ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis begins in the rectum and gradually affects the large intestine in higher and higher sections. At the beginning, slimy-bloody diarrhea is typical.
This article might also interest you: Symptoms of ulcerative colitis
Burning in the bowel on the right
In addition to parts of the stomach and important parts of the small intestine, the gall bladder, biliary tract and appendix are located on the right side. The gallbladder and appendix can both cause acute and burning pain in the right abdomen when inflamed. Often these are feverish, extremely painful illnesses that subside after a few days. Gastrointestinal infections in this area often subside after a few days. In the case of chronic pain that has persisted for weeks, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease must also be considered in this area.
Read more about the topic here: Pain in the bowel
Burning in the middle of the intestine
A burning sensation in the intestine, which can be located exactly in the middle, indicates a disease of the stomach. This is often caused by an inflammation of the stomach lining, a "gastritis". In most cases the cause is the bacterium "Helicobacter pylori", which is harmless and symptom-free in the majority of people, but rarely leads to painful inflammation. In rarer cases, the gastric mucosal inflammation is also caused by chemical stimuli. Behind this is the aggressive stomach acid, the amount of which in the stomach can be massively influenced by diet and lifestyle habits such as smoking. Without therapy, painful ulcers and other complications in the stomach can develop.
The item stomach pain might interest you too!
Burning sensation in the anus
Inflammation of the bowel can also develop in the anus and rectum. These are often particularly painful because the anus is exposed to external stimuli and considerable pressure during bowel movements. The cause of the inflammation at the anus can be infections. Typical pathogens of the sexually transmitted diseases that are transmitted in anal intercourse are often behind it. Important infectious diseases of the anus are gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia and herpes. However, in rare cases, symptoms of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can also occur at the anus. Annoying symptoms in this area are permanent itching and constant urge to defecate.
You can find more information on the topic here: Burning of the anus and Burning sensation after defecation