Sternum fracture
introduction
The breastbone, also known as the sternum, is the bone that forms the connection between the left and right ribs in the upper body. It consists of three parts:
- Manubrium,
- Corpus Sterni, as well as from the
- Xiphoid process.
The sternum is a very stable bone and breaks very rarely, because it needs a strong impact on this bone before it breaks. This usually happens in car accidents in which the driver is not buckled up and their upper body hits the steering wheel.

Symptoms
A broken sternum often causes severe pain in the sternum.
The pain from a broken sternum can occur at rest, with certain movements, and can get worse with breathing. The pain when breathing often leads to shortness of breath, which can be treated with pain reliever medication.
The area of the broken sternum is also very painful to pressure. Often there are also:
- Redness,
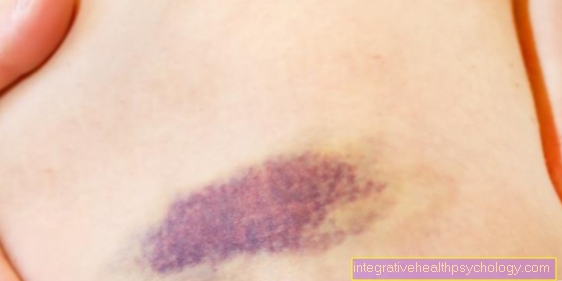
- Swelling and bruising (bruising).
If the heart and lungs are also damaged, this can lead to shortness of breath and cardiac arrhythmia.
Sternum pain
Since the sternum fracture is usually caused by a very strong force, it is usually very painful. On the one hand, there is a pressure-sensitive bruise in the area of the sternum. On the other hand, there is breath-dependent pain, as the sternum moves with every breath and is therefore irritated. In addition, when the sternum breaks, surrounding organs, nerves or bones are often injured, which also causes pain in the ribs.
It is also important that even severe chest pain is not evidence of a fracture of the sternum; a bruise of the sternum can also be very painful.
In case of doubt, only an X-ray or CT scan can help to prove a break.
Another type of pain that can occur when the sternum breaks is called neuropathic pain. This is pain caused by injury or irritation to a nerve itself. Since a large number of nerves run in the area of the sternum and ribs, neuropathic pain is not uncommon for sternum fractures. The pain is then more burning than stabbing and not necessarily dependent on the breath. In addition, they usually do not appear immediately after the injury, but only after days to weeks. Unfortunately, nerve pain is difficult to manage and does not respond well to standard pain medication. Therefore, it makes sense to consult a doctor with the additional designation "pain therapy" in the case of long-term nerve pain.
There are also other diseases that are associated with severe chest pain, in particular heart attack and pulmonary embolism, neither of which is related to violence and the pain of a heart attack is usually not breath-dependent.
In the further course, especially when lifting heavy objects and also e.g. Expect pain when sitting down. It takes up to six months for a broken sternum to heal completely, during which time pain occurs when exercising. This can also be understood as an indication that the break has not yet healed and should be protected further.
Read more on the topic: Sternum pain and Pain in the sternum
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
causes
A broken sternum often occurs in a car accident. The heavy impact on the steering wheel and the pull through the seat belt are responsible for the trauma. A car accident causes severe violence to the possibly osteoporotic bone tissue.
In addition, chest compressions during resuscitation can also lead to a fracture of the sternum. In such a procedure, strong force is exerted on the chest so that the impulses reach the heart.
Older people naturally suffer from decreased bone density. In the widespread disease of osteoporosis, the bony structures, such as the sternum, are prone to fractures when violent.
diagnosis
It always starts with the anamnesis, i.e. the patient interview. The doctor asks questions about how the sternum fracture occurred in order to find clues about other injuries. Then the patient is palpated, and a broken bone can often be felt manually.
If there is pressure pain over the breastbone, it can also be a bruise. If nothing conspicuous is felt, it may still be advisable to use imaging in addition:
- Ultrasonic,
- X-ray or a
- CT.
If there is actually a fracture of the breastbone (sternum fracture), further injuries must be looked for. The lungs and heart are below or near the sternum and must therefore always be examined.
Usually these organs are first listened to, the heart can be examined well using EKG and ultrasound, while the lungs are clearly visible on CT. If these organs are injured, this manifests itself very quickly in, for example, shortness of breath and pain.
Vertebral fractures and rib fractures are also common in a broken sternum and should be examined.
therapy
Fortunately, although the sternum fracture is very painful, it rarely requires an operation. This is only necessary if parts of the broken sternum shift or breathing is severely impaired by the broken bone and drug therapy is insufficient. An operation is performed under general anesthesia by opening the skin over the breastbone and stabilizing the breastbone with plates and screws.
However, since the sternum cannot be cast or splinted like a broken arm, the fracture cannot practically be immobilized. It is therefore important to combat breathing-related pain in particular. Different pain relievers are conceivable here, for example ibuprofen, Novalgin or also opiates, i.e. pain relievers that fall under the Narcotics Act.
The freedom from pain is also important for the patient because a relieving posture, which can lead to back pain, should be avoided at all costs. In addition, especially in older people, there is a risk that people no longer breathe deeply enough to ventilate the entire lungs. This can then be the basis of pneumonia, which can be very difficult in old age. In this case, painkillers are not just "feel-good drugs" for the patient. The aim of pain relievers is to enable normal breathing without pain and to enable easy activities early with tolerable pain.
Breathing therapy can also be carried out together with pain therapy, whereby the patient is instructed to breathe normally despite the fracture. Breathing therapy is particularly important for old people and patients who have been injured several times and are therefore temporarily bedridden, as well as for people with respiratory diseases that existed before the injury. The aim of everyone is to prevent pneumonia. This is mainly caused by secretion in the lower lung areas. Physiotherapy can also be prescribed, but is not always necessary.
Another important part of the treatment is protecting the fracture. Especially in the first two months after the injury there is an absolute ban on sports! Even after two months the bone has not healed completely, but cycling or something similar can slowly be started. Weight training or climbing should rest for about six months after the injury. Overall, those affected should listen to their bodies. If pain occurs during exercise, you should stop the exercise. Excessive ambition is out of place here.
The treatment of the accompanying injuries that occurred during the fracture is also important. In about half of the sternum fractures, there are other relevant injuries (for example of the heart or lungs). Because the heart is just behind the breastbone, heart contusions occasionally occur (Cardiac contusion) which can lead to cardiac arrhythmias. Therefore, it is common practice to monitor patients with a broken sternum in the hospital for at least one night.
Operation of a broken sternum
An uncomplicated fracture of the sternum usually does not require an operation. On the other hand, surgery should be performed, especially in the case of displaced (displaced) fractures or an impression fracture (part of the sternum is dented).
Occasionally, even with initially uncomplicated fractures, a so-called false joint (pseudarthrosis) occurs due to incorrect healing. Then the fracture gap is permanently mobile, which allows the breastbone to move unnaturally. This can also make an operation necessary. Even severe, persistent pain can justify an operation.
During the operation, when the bone is displaced, the bone is first brought into its original position; the surgeon speaks of a reduction. Then the break is fixed. This can essentially be achieved by two methods:
- If the break is longitudinal and there are only two fragments, the surgeon can fix the fragments together with wire. To do this, several opposite holes are drilled into the bone in the left and right fragments and then, similar to a shoelace, the holes are tied together with a wire. One speaks of a cerclage.
- If there are several fragments, the break can also be fixed with a plate. The individual fragments are screwed together with a metal plate and screws. This method has the advantage that several small fractions are connected to one another in such a way that they no longer move. The disadvantage is that a rather large foreign body is built in. It may be necessary to remove the plate after months or years.
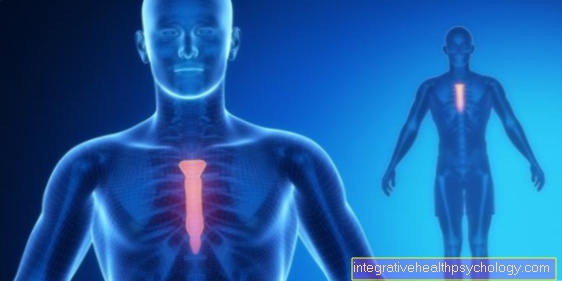
Illustration of the sternum

I - III sternum -
I-III sternum
I - sternum handle -
Manubrium sterni
II - sternum body -
Corpus sterni
III - sword process -
Xiphoid process
- Incision for that
Collarbone -
Incisura clavicularis - Sternum angle -
Angulus sterni - Fiber cartilage -
Symphysis xiphosternalis - Collarbone sternum
Joint -
Sternoclavicular joint - Collarbone - Clavicle
- Ribs - Costa
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
forecast
Breasts of the breastbone usually heal within a few weeks without complications. In rare cases, pseudoarthrosis can develop.
Duration
A sternum fracture (sternum fracture) occurs only very rarely, especially when the sternum has been subjected to enormous mechanical stress, for example in a car accident in which the driver was thrown with his chest on the handlebars or in a riding accident. The problem with a sternum fracture is that the sternum can neither be cast in nor splinted. Accordingly, the patient must be very careful not to put too much strain on the sternum under any circumstances. If the breastbone is severely broken, an operation may be necessary in which a plate or splint is inserted into the breastbone (sternum) to stabilize it.
The duration of a sternum fracture always depends on various parameters, above all the age of the patient, the severity of the fracture and the patient's health. The older a patient is, the worse and slower a fracture grows together. Even patients who are very overweight will in all likelihood have to struggle with a broken sternum for a longer period of time, since the sternum is automatically more stressed in women with a large bust than in slim patients.
In fit, young patients it is said that the duration of a sternum fracture is around 2 months. Only then has the bones grown together again enough to take part in small loads such as jogging or cycling (important: no weightlifting or heavy loads) without complications and pain. The time until complete pain relief and until the patient can load the sternum completely normally again is around six months for young patients. Before doing this, it is very important that the sternum is always stressed as little as possible during the entire duration of the sternum fracture, otherwise faulty bone growth can occur and, in the worst case, the duration will only be extended.
If an operation had to be performed on the sternum fracture, the duration of the sternum fracture is extended indirectly, since the plate or splint in the sternum usually has to be surgically removed again as soon as the bone has completely grown back together. Depending on the bone growth, this can take up to a year. Without surgery, however, the fracture of the sternum should have healed very well after six months and no longer cause any problems for the patient.
cure
A broken sternum is not a “classic” break compared to a broken arm, as a plaster cast or other support aids are not used. In order to heal a broken sternum, one must rely on other aids.
In most cases, a fracture of the sternum is not operated on; an operation is only useful in particularly severe cases, for example if the sternum has shifted. Usually, however, one tries to treat the broken sternum with a lot of rest and little stress. This healing of the sternum fracture is usually very successful as long as the patient follows the doctor's instructions. It is especially important to treat the symptoms. Healing of the sternum fracture is usually unproblematic, but the symptoms must be combated with painkillers. On the one hand, the painkillers help with shortness of breath, because despite the pain that actually occurs when breathing, you can breathe more and more easily, on the other hand, the painkillers help to keep the pain that has arisen due to the fracture under control.
However, pure pain therapy is not enough to achieve a complete healing of a broken sternum. Respiratory therapy must also be carried out with the patient so that the patient inhales deeply and evenly despite the pain or discomfort, otherwise the symptoms cannot be completely cured. In addition, professional physiotherapy should be carried out, which on the one hand strengthens the back muscles to counteract a bad posture and on the other hand supports the healing of the sternum fracture.
In order to promote the healing of the sternum fracture, it is also important not to overload yourself. Lifting heavy objects is absolutely counterproductive and should be avoided. Sports that place particular stress on the sternum, such as strength training, should be avoided until the sternum has healed completely. This can take longer than 6 months. It is also important not to interfere with healing with cockiness. The surrounding tissue and the bones need at least 6-8 weeks to grow back together properly. In addition, it cannot be said that the bone fracture has healed again after 8 weeks for everyone.Older people in particular have poorer bone growth and therefore it often takes longer for a sternum fracture to heal completely.
It is also important in healing to monitor the healing process. False joints can develop as the sternum grows together (Pseudoarthoses). The ribs are usually connected to the sternum, but a fractured sternum may cause an extra joint to form, which will affect healing. It is therefore important to have an x-ray taken again and again while the sternum fracture is healing in order to avoid any problems. If one of the complications mentioned above should arise, only an operation will help to avoid permanent damage. During the operation, metal plates are usually inserted into the breastbone to stabilize it and promote healing. These plates can be removed months or years later if necessary, but they can remain in the sternum as long as they do not cause pain.
Usually, however, the real problem is not the fracture of the sternum itself, but rather the side complications. A broken sternum is almost always associated with shortness of breath and can even lead to heart problems. In order to achieve complete healing, it is therefore important not only to look at the fracture itself, but also at the other complaints. One can only speak of a complete cure if the shortness of breath has been adequately treated, i.e. if breathing exercises have been done and the pain medication is dosed high enough that the patient can breathe in without problems.
In addition, an EKG should be done to check the functionality of the heart and to rule out any damage. Overall, in an otherwise healthy patient, healing should have taken place after about 8 weeks and no further complications should occur. Nevertheless, it is important to note that an already broken sternum will always be more susceptible and that, even if it heals well without complications, excessive stress on the sternum should be avoided in order to avoid a new break. However, if you stick to the grace period and do not put too much strain on the breastbone, complete healing is very likely.
How long will you be on sick leave with a broken sternum?
In the case of an uncomplicated sternum fracture, the person concerned is usually on sick leave for at least two weeks. The pain usually lasts much longer.
If there is a complicated sternum fracture with injured neighboring structures, such as a rib injury, the sick leave can last significantly longer.
If the job consists of heavy physical activity, the sick leave can be significantly longer.
Exercise after a broken sternum
A break can occur not only in car accidents or blows to the sternum, but also during sports. However, this must result in an enormous amount of violence. Theoretically, this is possible in almost every sport, for example when riding a bicycle if the rider falls off his bike or in football, when the opponent hits the elbow very hard on the sternum. Riders are also prone to a broken sternum, as it can break easily, especially after a fall, but also with a horse that kicks off with its hooves. Martial arts or strength training can also lead to a broken sternum. A fracture does not always have to occur, however, the sternum is often only bruised.
However, if the sternum breaks, no plaster cast or splint to stabilize the sternum will help. It is therefore extremely important to put as little strain on the breastbone as possible. Which kind of sport you are allowed to do again from when depends very much on the age of the patient and the severity of the fracture. The older a patient is, the worse the fracture heals back together. It can take up to six months for the fracture to heal sufficiently that sports that do not put strain on the sternum (cycling on an elliptical cross trainer or jogging) can be performed again without pain.
In young patients who have normal bone growth, the fracture should be healed enough after 6-8 weeks to allow slow rehabilitation training again. However, until the fracture has completely healed and sports such as soccer, handball, strength training, horse riding and the like can be practiced again, it takes at least 3 months.
The Duisburg handball player Flemming, for example, took over 3 months to be fully operational again after he broke his sternum. It is important to keep this deadline in any case. Loose training is often possible again after 6 weeks. However, if the patient overcomes it, the fracture cannot heal properly. There is a risk that the sternum grows together incorrectly or that incorrect joints (Pseudoarthroses) form. If the sternum grows incorrectly or if pseudoarthroses develop, usually only an operation can help. During this operation, the front of the rib cage must be opened and the sternum partially assembled using plates. After such an operation, it can take even longer until the sternum is properly resilient again, especially since the plate bothers many patients and they can have it removed again after several months.
A major cause of the slow healing of a sternum fracture is breathing. The sternum is above the lungs and heart. If there is increased breathing due to heavy exertion, this irritates the breastbone very much and it comes to severe pain. In severe cases, the break can tear even further. Breathing always stresses the fracture in the breastbone, even at rest. Many patients still complain of pain in the sternum even years after their sternum fracture and can therefore not do any sports at all. Often, however, it is easy for the patient to accept it again after a few weeks (about 6 weeks minimum) loose running units to start. What is important here is a building-up training course. Care should be taken to begin with easy running sessions. Sports that put too much strain on the arms and thus also the thoracic muscles should definitely be avoided. These sports include, for example, dumbbell training in the gym, gymnastics on the horizontal bar and gymnastics in general, basketball and handball training, volleyball training and horse riding. All of these sports should be practiced after 3 months at the earliest, otherwise there is a risk of unnecessary complications.
As long as you stick to the therapy plan and with you Physiotherapists slowly resumes training, a broken sternum should heal properly like any other fracture. However, since the fracture is very stressed due to breathing, it is possible that even after 3 months there has not yet been a complete healing. In this case, it can take even longer (sometimes up to six months or longer) before the old sports training can be resumed with the old workload.
When can you do sports again after a broken sternum?
If you break your breastbone, you should avoid sport and vigorous physical activity for at least eight weeks.
During this time you shouldn't lift heavily and take care of yourself physically. If you start exercising again afterwards, you should start training again slowly.
Sternum fracture in children
A broken sternum (sternum fracture) is extremely rare and only occurs in one very severe bruise on the upper body. This can be in different sports, for example in Martial artsin which the patient receives a violent blow to the sternum. A broken sternum is extremely rare in children. For one are Child bonesthat are still growing, a lot softer and more flexible as the bone the adults. This is also the reason why children generally do not break a fracture as quickly while older people suffer bone fractures much more quickly. However, in a car accident, the child may experience a hard impact on the sternum or a hard hit on the sternum while playing. In such cases, a sternum fracture is possible even in children, but mostly the adjacent ones break Ribs first.
In children, too, attempts are made to avoid the operation of the sternum; an operation is only necessary in very severe cases. Since under the breastbone the two Lungs, the heart and in the case of the child often also the Thymus the fracture of the sternum can cause constrictions or injuries. It is therefore very important to have the child under medical supervision over a longer period of time after a broken sternum. In addition, the child should Painkiller Don't get around because of the permanent pain one Relieving posture ingestion, which can then lead to incorrect contraction of the sternum. In general, a child's sternum fracture is not very different from an adult's. In the child, however, such a break is much less likely. Since children are still growing, one is adequate Aftercare and sufficient physical therapy but essential!
Compensation for pain and suffering after a broken sternum
A fracture of the sternum occurs when the sternum is subjected to enormous stress and is associated with absolute restraint and recurring pain for the patient concerned for 2 months. In the worst case, the joints can develop incorrectly and the broken sternum must then be repaired. If, in a car accident, a broken breastbone occurs because driver A, driver B drove into the car and he broke his breastbone as a result of the impact, driver B can demand compensation for pain and suffering from driver A after a precise diagnosis has been made. The amount of compensation for pain and suffering in the event of a broken sternum depends on various factors. If there is only a fracture of the sternum without injuring other structures (ribs, lungs, heart, collarbone ...) and if this fracture can be treated without surgery, the compensation for pain and suffering amounts to around € 1,000-2,000. However, if there are other injuries besides the broken collarbone, the amount of compensation for a broken breastbone increases very quickly. For example, if, in addition to the sternum fracture, there is a rupture of the small intestine, lung problems and also chest bruises, the sum of the compensation for pain and suffering can amount to € 12,500. The reason for this is a longer inpatient admission and, in addition, the multiple organ stress. It is more common that in addition to a broken sternum, ribs and the collarbone (clavicle) are broken. Since the lungs almost always suffer damage in this case, compensation for pain and suffering of € 9,000 can be expected. It is important, however, that the amount of compensation for pain and suffering always depends on the severity of the accident, the organs involved, the length of the inpatient admission and the psychological damage. Therefore, the sums of compensation for pain and suffering in the event of a broken sternum can vary from patient to patient.