Chronic pelvic inflammation
Synonyms
Medical: pyelonephritis
Upper UTI (urinary tract infection), pyonephrosis, urosepsis
definition
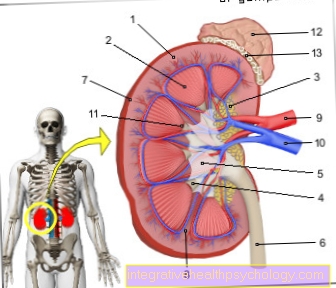
Inflammation of the renal pelvis (pyelonephritis) is an interstitial (i.e. between the actual kidney tissue), bacterial, tissue-destroying (destructive) inflammation of the kidney and the renal pelvis system. Kidney inflammation can occur on one or both sides.

causes
Chronic pelvic inflammation can be caused by an inadequately treated urinary tract infection (UTI) (risk factors may be present). The original germs only serve as an impetus, since the chronic inflammation is sustained without germs.
Risk factors
- Metabolic diseases with immunodeficiency (e.g. Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus)
- Anatomical urinary flow obstruction (constriction of the bladder, urethral valve)
- Urinary flow obstruction (kidney stone, enlarged Prostate (Prostatic hyperplasia), Tumor, pregnancy)
- Lying Urinary catheter
- Urine reflux from the bladder in the ureter (vesico-ureteral Reflux)
You can find further information under our topic: Kidney malformations
Symptoms
Frequently is there almost no noticeable symptoms. General symptoms such as headache, loss of appetite, tiredness, slight increase in temperature (subfebrile temperatures) etc. can occur. The acute episode can lead to fever and pain in the kidney bed.
diagnosis
Diagnosis is difficult because specific symptoms are often absent. Often the following is noticed during routine examinations because of the symptoms mentioned above:
- White blood cells (leukocyturia) and bacteria (bacteriuria)
- in the urine
- increased inflammation values (ESR, CRP)
- abnormal blood count (renal anemia = anemia)
- incipient kidney weakness (Renal failure / Non-failure)
- High blood pressure (artrial hypertension)
To exclude risk factors, ultrasound, x-ray and urogram should serve. In the X-ray a plump of the renal pelvis calyx system and scarred retractions are noticeable. The function of the kidney should be checked for restrictions.
therapy
In acute episodes should Antibiotics are used. Under certain circumstances, long-term therapy may be necessary to prevent recurring infections (recurrences). If risk factors are present, these should be eliminated (possibly also through an operation).
Therapy can also be carried out homeopathic medicines get supported. We have created a completely separate topic for this.
Read more about this under our topic: Homeopathy for pelvic inflammation
forecast
If the chronic inflammation of the renal pelvis is recognized in time, the inflammation can heal. If this is not the case, kidney function declines sharply in the final phase of the disease.
The result is so-called shrink kidneys with high blood pressure, kidney weakness (kidney failure) and urine poisoning (uremia) (see below).











.jpg)