Delta-shaped muscle
Synonyms
Latin: Deltoid muscle
English: deltoid muscle
Synergists: M. pectoralis major, M. biceps brachii, M. latissiums dorsi, M. triceps brachii
Antagonists: M. latissimus dorsi, M. triceps brachii, M. pectoralis major, M. biceps brachii
definition
The delta-shaped muscle is an upper arm muscle, the shape of which is reminiscent of an upside-down Greek delta and therefore gets its name. According to its origin, it is composed of three parts, one part from the outer clavicle, another part from the shoulder blade and a third part from the shoulder blade bone. As a triangular muscle, it surrounds the shoulder joint from the front, back, top and side. It is also known as the deltoid muscle and its different parts are involved in different arm movements.
Due to its location directly under the skin, the trisection can be easily recognized in slim and defined people. It is the largest muscle in the shoulder muscles.
The deltoid muscle is specifically trained in weight training.
Due to its tension, the deltoid muscle can move the arm in all directions of movement; its most important function is to raise the arm laterally, especially when it is spread over 90 °.
course
Approach: Humerus (Deltoid tuberosity - roughening of the humerus)
Origin:
Pars claviculares: lateral third of the collarbone
Pars acromiales: Acromion - the bony process of the shoulder blade
Pars spinales: originates on the spina scapulae - bony elevation of the shoulder blade
Innervation: Axillary nerve of the brachial plexus (segments C5-6)
function
The function of the Delta-shaped muscle varies depending on the activity of the different muscle parts. It allows the arm to move in all directions. The deltoid muscle (Musculus deltoideus) is by the vom Shoulder roof outgoing middle section to the main lifter of the arm.
Pars clavicularis - Clavicle portion:
- Highlight (Anteversion) of the arm
- Incentive (Adduction) from the arm
- Internal rotation from the arm
Pars acromialis - Shoulder roof proportion:
- Abspreitzung (Abduction) from the arm
Pars spinalis - Shoulder blade portion
- Splay (Abduction) from the arm
- External rotation from the arm
- Lifting back (Retroversion) from the arm
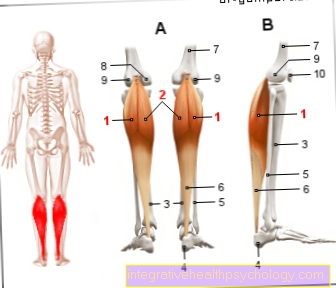
Figure deltoid

Deltoid
(Deltoid muscle)
- Deltoid -
(1a. + 1b. + 1c.)
Deltoid muscle
1a. Posterior deltoid
(Bone part) -
Pars spinalis
1b. Middle deltoid
(Shoulder height part) -
Pars acromialis
1c. Anterior deltoid
(Clavicle part) -
Pars clavicularis - Scapula bone -
Spina scapulae - Shoulder blade - Scapula
- Collarbone - Clavicle
- Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Common illnesses
The delta-shaped muscle is essentially involved in shoulder mobility. The shoulder joint is a predominantly muscular joint.
The so-called rotator cuff, a muscle group consisting of four muscles, plays a decisive role in the stability of the shoulder joint.
But even with degenerative changes in the tendons of the delta-shaped muscle, shoulder mobility and stability are restricted.
Paralysis of the axillary nerve often results in atrophy of the deltoid muscle.
In addition, the delta-shaped muscle plays a major role in various neurological diseases, e.g. the neuralgic shoulder amyotrophy.