Diagnosis of polyneuropathy
How is the diagnosis of polyneuropathy made
Anamnesis is particularly important when diagnosing polyneuropathy (Questioning the patient) and examining the patient. The anamnesis includes familial nervous disorders, alcohol, drug and medication addiction and possible contact with toxic agents in the workplace (Exposure) he asks. Mostly pain and symmetrical sensory disorders of the feet and hands, i.a. sensitive irritation symptoms such as the "burning feet“, That is, burning soles of the feet, as well as vertigo and nocturnal muscle cramps.
Read more on this topic at: Burning feet and burning feet syndrome.

The examination begins with an examination of sensitivity, which is evident in all qualities, e.g. Sense of touch or vibration may be impaired. The reflexes are usually reduced or even extinguished in the lower extremities. Of the Achilles tendon reflex, also a self-reflex, is missing even before sensory disturbances are detectable. The detection of glove or stocking-shaped sensitivity disorders with a reduced sense of vibration in the lower legs and lack of reflexes almost always leads to the diagnosis of polyneuropathy. The coordination is also examined. Pronounced ataxia is a.o. observed with poisoning with mercury and with diabetic and alcoholic polyneuropathy ("Pseudotabes diabetica or alcoholica"). Asymmetrical multiplex-type distribution patterns are common at Diabetes mellitus, Lead polyneuropathy and polyneuropathies after tick bites (Lyme disease), syphilis - and leprosy.
Also often at Diabetes mellitus are a mononeuropathy and the involvement of Cranial nerves. Mental susceptibility can be observed especially in alcoholism, porphyria and thallium poisoning. The anamnesis and the clinical examination are supplemented with laboratory tests to clarify the cause of the polyneuropathy.
In particular:
- the blood count
- the electrolyte
- Blood sugar-
- Liver and kidney values
- vitamin B12
and - Folic acid
examined in the blood.
A distinction is made between polyneuropathies with predominantly damage to the medullary sheath of the nerve fiber (demyelination), which results in a significantly reduced nerve conduction velocity with normal strength of the impulse, and polyneuropathy with predominant damage to the nerve process (axon degeneration), which is a normal NLG with less strength of the impulse brings itself. In electroneurography (ENG) the nerve conduction velocity is measured, which depending on the cause of the polyneuropathy can be normal, moderately or severely reduced. With electromyography (EMG), spontaneous impulses can be measured in predominantly axon degeneration, which do not occur in a healthy nerve. In addition to ENG and EMG, a sural biopsy can be performed to clarify an axonal or demyelinating form. Tissue is taken from the sural nerve, a nerve that lies superficially under the skin of the lower leg, and examined. In addition, in numerous polyneuropathies such as diabetic polyneuropathy, an increase in the protein concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid (liquor cerebrospinalis) can be determined.
Differential diagnosis
Sensory disturbances and pain in polyneuropathies are often confused with arterial circulatory disorders.
Diagnostic guidelines
To a Polyneuropathy Doctors often make a diagnosis after certain tests.
Various examinations can point to a polyneuropathy or, depending on the result, rule it out, and another disease is responsible for the symptoms.
Since various forms and manifestations of polyneuropathy are known, the examinations can also provide information about this. The focus of the diagnosis is a detailed anamnesis of the complaints.
This is followed by the clinical findings, which provide conclusions about the extent of the symptoms and thus make an important contribution to the classification.Signs of acute or chronic, symmetrical or asymmetrical polyneuropathy can be clarified here. (please refer: Symptoms of polyneuropathy)
Next, the damage to the nerves is considered. Do this electrophysiological studies how the measurement of the nerve conduction velocity is carried out. They provide information about the type of damage to the peripheral nerves.
An inner (axonal) and an outer (demyelinating) Differentiated damage patterns.
It can also be used to check whether the nerve is still transmitting excitations or whether muscle parts are no longer being reached and therefore no longer being innovated. Blood tests and CSF examinations are carried out to look for possible causes. Different values can provide an indication of a basic illness or acute inflammation.
The laboratory offers the possibility to take many factors into account and can also be expanded. Since polyneuropathies also have genetic factors, a genetic examination should also be carried out if, especially if polyneuropathies are already known in the family. Finally, a sure diagnosis provides one Nerve biopsy. It is especially carried out if there is a suspicion that it is a treatable polyneuropathy. (please refer: Polyneuropathy therapy)
Laboratory for a polyneuropathy
By means of laboratory tests the cause of the polyneuropathies is sought in particular.
The laboratory chemical examination therefore includes the basic diagnostics and those with suspicion of a certain disease.
The basic diagnosis includes parameters such as the sedimentation rate and the CRP. Both values are used to clarify an inflammation. Furthermore, the individual electrolytes are like Calcium and magnesium checked as well as the typical values for checking liver and kidney function.
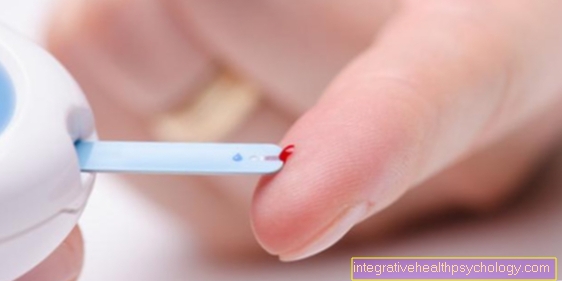
Since a polyneuropathy is also caused by the Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus), evidence of the presence of diabetes is also sought in the blood.
Fasting blood sugar is usually checked, a daily blood sugar profile is created and a glucose tolerance test is carried out. He gives in the blood HbA1C Worth first indications of a sugar disorder. This is a non-enzymatic saccharification of hemoglobin in the blood when the sugar content is particularly high.
In order to rule out or to discover further diseases, various Vitamins, Antibodies and immunoglobulins tested. Alcohol abuse can also be the cause of the polyneuropathies, which is why the blood transaminases are also checked, which are usually greatly increased with frequent and excessive consumption of alcohol.
MRI as a diagnostic tool for polyneuropathy
Since polyneuropathy involves changes in peripheral nerves, which usually have very small and fine structures, we diagnose a Magnetic resonance imaging difficult or is rather not possible.
The MRI is a very good imaging examination, which can also show soft tissue structures and their changes very well, but this is not possible in the case of nerve courses and changes.
In addition, there is the fact that an MRI examination is very expensive and is therefore rarely used for the early detection of polyneuropathies. In rare cases, the examination is carried out and then serves to rule out other possible diseases that may be causing the symptoms.