The fluids of the body
definition

Body fluids are generally understood to mean water, which is located in different sections and parts of the human body and, depending on the section, is provided with substances dissolved in it, such as waste products or electrolytes.
A distinction is made between body fluids that circulate in different body systems, such as blood or bile, from those that are located within different body cavities, such as the aqueous humor of the eye or gastric acid. The latter fluids are also subject to a certain circulation through consumption and regeneration.
If you look at the distribution of body fluids one step lower at the cellular level, you can differentiate between fluids that are located within cells (intracellular), which form organs and body structures, from fluid outside the cells (extracellular). This is not a fixed system and, depending on the current situation and needs, is subject to fluctuations, i.e. water can always flow out of and into the cell. This process is technically known as diffusion. These systems are regulated by certain hormones, among other things. In the sections below, the most important body fluids with their most important functions are briefly presented.
Quantity, distribution, loss, absorption
Generally there is the about 55-65% of the human body is made up of waterwhich, as already stated, is distributed throughout the body. However, there are slight differences in this percentage, which for example decreases in the course of life. As a result, children have a higher proportion than adults. Women have 5-10% less body water than men. 2/3 of the body water is located within the cells, 1/3 is accordingly outside of these before.
The human Body loses Every day on average 2.5 liters of water by sweat and Excretions like urine and stool. As a rule of thumb, that can help the body 30 ml of water per kilogram of body weight per day should be replenished through drinking. At excessive sweating However, this need is increased in the context of sport or high temperatures.For one hour of physical activity, this increases by half a liter.
If there is not enough fluid in the body, one speaks of one Dehydration, if there is too much fluid from one Hyperhydration.
function
The functions differ depending on the body fluid. In general, however, they serve this Transport of nutrients to organs, as well as the Removal of partially toxic metabolic products from these.
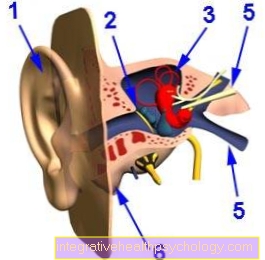
blood
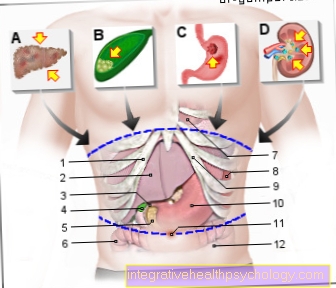
Probably one of the most well-known body fluids flows within Blood vessels, the Veins and Arteries through our body and supplies it with vital things Nutrients and oxygen. In addition, the blood serves that Removal potentially harmful degradation products that arise in the organs during metabolism.
The engine this cycle is that heart. In the lung the enrichment of the blood takes place with oxygen.
You can do that blood as a mixture of solid and liquid components to introduce. The firm Components include the red blood cells, the Transport oxygen, the white blood cellsthat for the Immune and pathogen defense are indispensable to our body, as well as the Plateletswhich, for example, close a cut as quickly as possible by clumping the blood and thus counteract excessive blood loss.
The liquid part of blood is also called plasma designated. This is too over 90% water. The remaining 10% are made up of substances dissolved in it, such as Proteins, hormones, nutrients, breakdown products and electrolytes together.
Lymph fluid
The lymph is also a body fluid and is used for Removal of excessive tissue fluid from the fabric bed back to the venous system of the blood and thus prevents water retention in the body. The lymph is transported via so-called Lymphaticsin which on certain parts of the body Lymph nodes are switched on. In the lymph nodes the Filtered lymph and for possible foreign substances, such as Germs or tumor cells checked. If these are present, those contained in the lymph nodes react Immune cells with a Activation of the immune system and fight the intruder. Thus, the lymph with associated lymph nodes also has an important role in the Defense against infection and foreign bodies.
Another important function of the lymph is Transport of proteins and fats from the digestive tract into the body veins, from which it is washed into the liver and further processing can take place there. The proteins and fats are transported in the lymph in the form of compact globules, which are called Chylomicrons are designated. Especially after a high-fat meal, the lymph from the digestive tract can therefore take on a whitish to yellowish color.
Stomach acid
Stomach acid is, as can be deduced from the name, is an acid (more precisely hydrochloric acid) With extremely low pHwhich the Digestion of ingested food and serves as the first defense against pathogens ingested with food. Alternatively, the word "Gastric juice“Used.
The consistency is slimy, because in addition to the acid also mucus to the protection the lining of the stomach before self-digestion and a protein-breaking enzyme by the name of pepsin is formed by different stomach cells. The gastric juice also contains a Transport molecule, the so-called intrinsic factor, which is for the inclusion of Vitamin B12 in the Small intestine is essential. Among other things, vitamin B12 has an important function in blood formation. The mere sight or smell of food leads to gastric juice being released. Another secretion occurs after and during the ingestion of food by stretching the stomach.
saliva
saliva is one of the Salivary glands Body fluid produced, which is used to pre-digest the food ingested and to moisten it. The Humidification leads to Slipperiness of the chyme and facilitates the passage of the esophagus. Those contained in saliva Break down enzymes mainly contained in food multi-chain sugar molecules, like for example Strength and thus facilitate further digestion. Furthermore, antibodies that get into the oral cavity with the saliva prevent infection by neutralizing possible pathogens.
bile
The Bile is a body fluid that formed in the liver is released into the small intestine through the bile ducts. The Gallbladder serves the storage and rapid mobilization of bile, is not absolutely necessary for survival. In the small intestine the greenish body fluid serves the Digestion and absorption of fats. For this reason, bile is released especially during and after eating.
Furthermore, are in the bile Metabolic products dissolved, which are excreted with the stool after it is released. This includes, among other things Bilirubinwhich in the breakdown of the red blood pigment arises and gives the chair its brownish color. The body also gets rid of absorbed heavy metals through excretion with the help of bile. The acids contained in the bile also kill bacteria and protect the body from infection.
Digestive enzymes pancreas
The pancreas not only has the well-known function of Production of the hormone insulinwhich controls blood sugar levels.
In addition to insulin, be also numerous digestive aids, so-called enzymes, which play a key role in the utilization of proteins, carbohydrates and fats. These enzymes are common with the bile released into the small intestine and only activated there. This mechanism protects the pancreas from digesting itself.
urine
In the paired kidneys, our blood is filtered and purified of toxic metabolic products and other pollutants. The result of this filtering process is urine. Above all, metabolic products are eliminated from the protein metabolic pathway, including urea. The composition of the urine can vary depending on the situation and needs of a person, since the kidneys are not only responsible for filtering harmful substances in the blood, but also play an important role in regulating the water balance. For example, if you drank very little, the kidneys are able to excrete less water, which makes the urine appear more concentrated and dark yellow. Conversely, if a lot of fluids have been consumed, the urine will appear light yellow. You can find more information about this at: Urine color - what's behind it?
Through various regulation and control mechanisms, the kidneys are able to influence the composition of the urine in such a way that toxic substances are removed from the body and the person is not over- or underwatered. Healthy people pass around 2 liters of urine a day. Various diseases can be associated with excessive or reduced urine excretion. People with diabetes are noticeable, for example, by going to the toilet very frequently, while in men, urine output can be impeded as a result of an enlarged prostate.
Sweat
The Sweat is through sweat glands in the skin produced and released to the surface of the skin through small channels. It's about a watery secretionthat next to 99% water also Electrolytes and Fragrances contains. The latter are individual for each person.
The sweat evaporates on the skin, whereby heat is withdrawn from the environment, which in turn causes the body cools down. One of its main functions is thus the Thermoregulation.
Fresh sweat doesn't smell. The unpleasant one odor comes only in Result of bacterial decomposition of sweat components caused by skin bacteria.
Breast milk
Breast milk becomes natural in the mammary glands during and after a pregnancy produced. She serves the Feeding the child.
Breast milk has one whitish-yellowish color and includes besides Proteins and Lactose (lactose) numerous Vitamins, minerals, antibodies and Antibodieswhich protect the child from infection. The composition changes following the birth. The first breast milkmaking the woman is called Colostrum refers to and mainly includes those already mentioned above Antibodies. They are particularly important in the first days and weeks of a child's life, as their own antibody production must first be started. Frequent mooring by the child will as a result of sucking and the accompanying Stimulation of the mammary glands promotes milk production.
It is generally known that breastfed Children less often at Infections get sick and in the course of their lives less chronic diseases, how Allergies and asthma develop, which is why breast milk is also viewed as the best food for the child and that Breastfeeding recommended.