The gluten sensitivity
What is gluten sensitivity?
Gluten is a protein that is found in many different types of grain. Examples of foods that contain gluten are bread, pasta, and pizza. They can be easily consumed by most people. But part of the population suffers from gluten sensitivity, which is also known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS).
In contrast to gluten intolerance, the sensitivity does not lead to chronic inflammation of the intestine, but only provokes a hypersensitivity reaction. Affected people usually suffer from gastrointestinal complaints. However, fatigue and headaches can also be caused by the consumption of foods containing gluten.
The reasons
Gluten sensitivity is based on an intolerance to gluten. Gluten is a protein found in various types of grain, such as in wheat and spelled. The consumption of foods containing gluten has increased significantly in the last century. In this context, it has been observed that an increasing number of people suffer from gluten sensitivity. However, the exact mechanism that causes this disease is not known. However, it is known that no antibodies are formed that would destroy the intestinal mucosa. An autoimmune disease, such as celiac disease, is therefore excluded.
You also know that there is no allergy. In allergic reactions, the immune system produces antibodies of the IgE class. In patients who suffer from gluten sensitivity, these antibodies are undetectable, so one can conclude that another mechanism is behind it.
There may be a correlation with the increased consumption of foods containing gluten, as foods such as wheat have been genetically modified. Digestion can be impaired and the symptoms of gluten sensitivity can develop. However, this is currently the subject of research, so that no reliable information can yet be made.
Also read the article: Celiac disease.
The symptoms
The symptoms of gluten sensitivity are very variable. Gastrointestinal complaints are the most common. These can manifest themselves in the form of nausea, abdominal pain, gas, constipation and diarrhea. The constipation and diarrhea can alternate and resemble an irritable bowel. The diarrhea can in turn lead to an iron and vitamin deficiency, which can manifest itself in different ways - for example through anemia (so-called anemia).
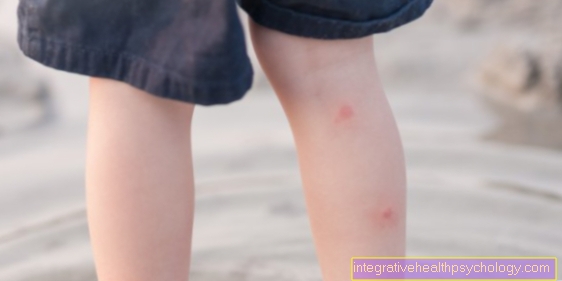
In addition, symptoms such as headache, concentration disorders and chronic fatigue can occur. Muscle and joint pain have also been observed in connection with gluten sensitivity. Some patients report sensory disorders in their hands and feet. Gluten sensitivity also seems to cause skin problems. Patients' skin is reddened and often itchy. In some cases, eczema can also develop. Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease that manifests itself in the form of blisters and crusts.
Psychiatric complaints such as mood swings, depression and anxiety disorders were also observed.
If gluten sensitivity is suspected, it is advisable to avoid foods containing gluten for a month. After a month you should see the improvement of some complaints. This makes it easier to judge which symptoms are caused by the sensitivity and which symptoms are caused by something else. If the symptoms persist despite the diet, a doctor should be consulted. There may be another medical condition behind these symptoms.
This article might also interest you: The gluten intolerance.
The diagnosis
The diagnosis of gluten sensitivity is usually a diagnosis of exclusion. This means that other diseases must first be ruled out before a gluten sensitivity diagnosis can be made.
The most important differential diagnosis here is gluten intolerance, also known as celiac disease. For this, blood can be taken, which is then examined for specific antibodies. An endoscopy (colonoscopy) can also be performed, in which the intestinal mucosa is examined more closely. The most important difference between gluten intolerance and gluten sensitivity is the destruction of the intestinal mucosa. In the case of sensitivity, the intestinal mucosa is inconspicuous in endoscopy, since in this case no chronic inflammatory reaction is triggered. A wheat allergy should then be ruled out.
If the diagnosis did not reveal any abnormal findings, a gluten-free diet should be followed. If the symptoms are alleviated, a diagnosis of gluten sensitivity can be made.
The treatment
Gluten sensitivity can be successfully treated with a gluten-free diet. Affected patients are not allowed to consume foods containing gluten, such as wheat, rye, barley, green spelled, spelled, kamut, emmer and einkorn. It must also be taken into account that gluten-containing additives may be present in ready meals. For example, some instant soups and sauces contain gluten. Gluten can also be found in sausage products or in snack foods. For this reason it is particularly important to check the ingredients and make sure that they do not contain gluten. In addition to solid food, drinks such as beer and malt beer are no longer allowed to be drunk.
Foods that can be eaten are: rice, corn, potatoes, soybeans, buckwheat, millet, quinoa, amaranth and manioc. Unprocessed foods such as fruits and vegetables are also safe.
Since the diagnosis of gluten sensitivity usually means a change and most patients are at a loss, it is advisable to seek nutritional advice. With the help of nutritional advice, a nutrition plan can be drawn up that ensures a healthy and balanced diet.
Also read the article: The diet in celiac disease.
The duration and forecast
If you do not eat foods containing gluten, the prognosis is very good. Most of the patients are so symptom-free.
Since gluten sensitivity lasts a lifetime, the diet must also be adhered to for a lifetime. Avoiding gluten-containing foods is currently the only therapeutic option, so there is no getting around it.
The course of the disease
The course of the disease is variable and depends on the extent of the disease. Some patients experience only mild gastrointestinal discomfort, while other patients experience rashes, headaches and fatigue.
Avoiding foods containing gluten leads to an improvement in the symptoms. However, mild symptoms subside faster than severe symptoms. A patient who only suffers from mild gastrointestinal complaints can be symptom-free six weeks after starting the diet. Another patient may take a few months to reach this state. However, it can be said that the symptoms subside slightly one month after starting the diet.
How contagious is that?
Gluten sensitivity is not a contagious disease. It is more of a hypersensitivity reaction of the body to gluten. So you can't get infected with this disease.
However, gluten sensitivity may be inherited. However, the disease is still largely not understood, so that no precise information can be given about it.