Cramps during pregnancy
introduction

Due to the increasing physical strain on the pregnant woman in the course of pregnancy, cramps in the legs and also in the abdomen occur frequently and are rarely seen as a serious problem by those affected.
Through the Weight gain and the Size growth of child and uterus, the leg, abdominal and back muscles can be quickly and easily overloaded, so that they tense up reactively. Most often, cramps occur in the second and third trimester of pregnancy because this is where the burden on pregnant women is greatest. About 14% of all pregnant women suffer from it during pregnancy Calf cramps.
Abdominal cramps during pregnancy
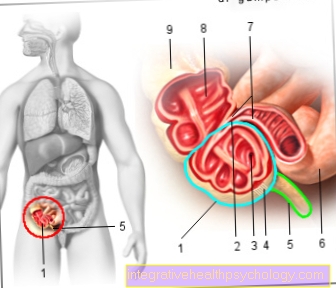
cramps and the occasional Sensation of pain in the area of the abdomen - both in the Abdomen, as well as in the upper abdomen - are normal to a certain extent during pregnancy and usually not worrying.
Especially with advanced Stage of development of the child in the womb, the increase in size of the unborn child and the uterus leads to increasing loads on the internal organs, the abdominal and back muscles, the ligamentous apparatus of the pelvis and the surrounding vascular and nerve tracts. So can Pressure on the displaced intestinal loops lead to cramping abdominal pain.
A permanent overload of the trunk muscles as part of overexertion, a poor blood circulation (through compressed vessels) or one disturbed stimulus transmission cause cramps in the abdominal muscles (through nerve compression).
In addition, there can always be causes that have nothing to do with the pregnancy: one Appendicitis, Kidney or Bladder stones, one Cystitis or Gallbladder disease can occur parallel to an existing pregnancy and lead to pain and cramping in the abdomen. Should the Stomach cramps however, after a few minutes do not stop by itself or other symptoms such as Bleeding, nausea/Vomit or fever in addition, these should be clarified urgently by the treating gynecologist. Especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, longer and more frequent episodes of cramps in the abdomen accompanied by bleeding in connection with an impending Miscarriage or pregnancy outside of uterus (Ectopic pregnancy, e.g. Ectopic pregnancy) stand.
Read more here Pregnancy Complications - What Are The Signs?
In contrast, atypical abdominal cramps in the last trimester of pregnancy can indicate a possible impending premature birth. The perceived Abdominal cramps are in this case by the contraction of the uterine muscles or by Labor pains which - albeit too early - are intended to drive the child out. In addition, you can Fibroids (benign muscle tumors of the uterus) that existed before pregnancy, depending on their size and location, can lead to cramps in the uterus or even premature labor.
Cramps in the legs
A common ailment in the second half of pregnancy is the frequent occurrence of cramps in the legs - especially in the calves or thighs.
The most common reason for this is a disturbed water and electrolyte balance, which can easily shift in pregnant women: increased sweating and an increased urge to urinate (due to the increased pressure of the child on the bladder), compared to non-pregnant women Loss of fluids and minerals through the skin and urine.
The minerals magnesium and calcium, which are responsible for regulated muscle function and muscle relaxation, are decisive for the development of (calf) cramps. If there is a deficiency, muscle spasms can occur. Nevertheless, cramps in the legs can occur even in spite of normal magnesium and calcium levels in the blood.
Read more on the topic: You can recognize a magnesium deficiency by these symptoms
Another cause can be physical overexertion and increased stress at the end of a pregnancy, which can lead to overloading of the leg / calf muscles.
In addition, circulatory disorders in the legs can lead to cramping, as this means that the (calf) muscles cannot be adequately supplied with blood or fluids and electrolytes. Such circulatory disorders or such reduced blood flow to the leg muscles can result from sitting and lying down more often in the second half of pregnancy (lack of exercise is therefore a risk factor for calf cramps).
Somewhat less often, but still a possible cause of cramps in the legs, can also be a pinched nerve, which can be compressed by the greatly enlarged uterus and the extra weight of the child and the signal transmission from nerve to muscle can be disrupted .
Excessive levels of phosphorus in the blood (caused by a poor diet during pregnancy) can also lead to leg cramps. Unfavorable sleeping positions (often lying on your back and permanently hyperextended feet) can possibly lead to nocturnal calf cramps.
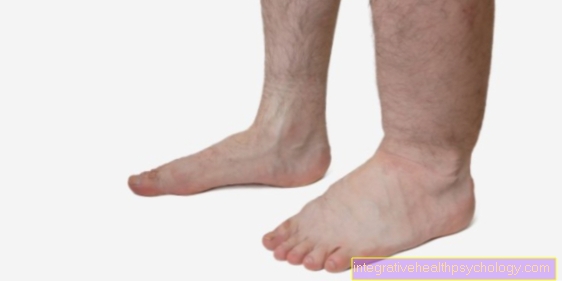
It is important that in the event of long-term cramps and swelling and constant pain in one leg (swelling in both lower legs usually indicates water retention and is usually harmless during pregnancy), a doctor is consulted immediately in order to rule out a possible thrombosis.
Read more on the subject at: Leg cramps during pregnancy
Diagnosis
Since it is mostly about harmless pregnancy ailments occasional, slight abdominal and leg cramps, which are not accompanied by any further symptoms and which get worse over time, should not be clarified with any major diagnosis. However, should the doctor or patient have doubts due to the severity and frequency, various examination methods are available.
In the case of leg cramps that occur frequently, the attending physician will not only have a detailed discussion but also one physical examination perform in which the Blood circulation and the Nerve reaction getting tested.
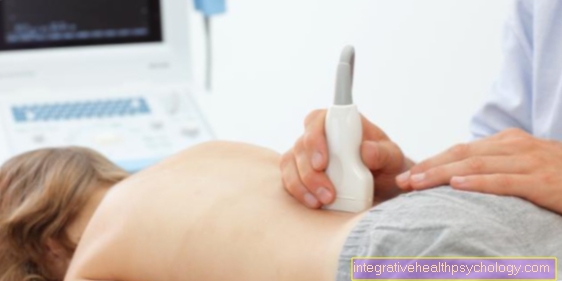
In addition, a Blood test of the Electrolyte status be assessed (it is also possible to determine the muscle enzymes and Thyroid hormones). In some cases, the Electromyography (EMG) and the Electroneurography (ENG), in which the muscle and nerve activity in the extremities can be measured specifically and more precisely. Ultrasound diagnostics of the vessels in the legs can also provide better information about the blood flow situation.
For cramps in the upper or lower abdomen that deviate from harmless pregnancy symptoms, different examinations can also be carried out - depending on the stage of pregnancy - in order to rule out a possible miscarriage or extrauterine pregnancy in the first trimester of pregnancy, a Ultrasonic of the abdomen. This can confirm the intactness and correct fit of the pregnancy and other causes, such as appendicitis, ureter colic or gallbladder disease, can be excluded. In addition, a blood test based on the determination of Inflammation parameters the clarification of inflammatory processes as the cause of the abdominal cramps. As a rule, the ultrasound and blood tests are always accompanied by a detailed gynecological and physical examination.
If the abdominal cramps occur more frequently in the last trimester of pregnancy, the diagnosis is always made towards the possibility of one early birth respected. As a rule, this includes the vaginal examination, the ultrasound examination of the child in the womb and the vascular situation of the uterus, child and placenta, as well as cardiotocography. The latter is a method of recording the Heart sounds of the child and the labor activity, so that it can be determined whether the cramping symptoms in the abdomen are through premature labor to be triggered.
therapy
Against Cramps in the legswhich occur mainly at night in pregnant women, only helps in acute cases with already existing cramps Move: If there are cramps in the calf, foot or thigh at night, getting out of bed quickly, stepping carefully and walking around so that the Muscles automatically used and especially stretched and the spasm can be contained.
Also light ones Massages and a targeted counter-stretching the affected parts of the body can relieve cramps by increasing the blood flow. The placement of acts in the same way Hot water bottles or Heating pad and cold-warm alternating showers.
Furthermore, an attempt can be made to compensate for a possibly existing magnesium and / or calcium deficiency with a healthy, balanced diet and thus reduce the cramp potential.
If this is not possible through targeted nutrition, dietary supplements may have to be used during pregnancy.
Also read: Cramps despite magnesium
To prevent leg cramps during pregnancy, you should take care to put your legs up as often as possible. In the case of harmless abdominal cramps that are not accompanied by other symptoms, warm baths usually also help Hot water bottles and drinking soothing teas (fennel, caraway, chamomile tea). However, if the abdominal cramps last longer and are accompanied by secondary symptoms, a gynecologist should be consulted as soon as possible.
You might also be interested in: Painkillers in Pregnancy