Knee osteoarthritis
Synonyms
- Osteoarthritis of the knee
- Arthrosis deformans
- Osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Cartilage damage in the knee
Medical: Gonarthrosis
English: knee arthritis
definition
Under the Knee osteoarthritis (Gonarthrosis) are all wear-related (degenerative) diseases of the Knee joint to understand who through a increasing destruction of the articular cartilage with the involvement of the joint structures such as bones, joint capsules and muscles close to the joint.

Forms of knee osteoarthritis
Three bones form together with a complex Capsule- and Tape apparatus (Collateral and cruciate ligaments) the framework of the Knee joint.
These are:
- the thigh (Thigh rolls or femoral condyles)
- of the Tibial head (Tibial plateau)
- the kneecap (patella).
If you would like to find out more about the therapy options for cartilage damage in the knee or behind the kneecap, we recommend our topics:
- Cartilage damage in the knee
and - Cartilage damage behind the kneecap

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
The picture below shows that the bones are in close contact. This means that the contact surfaces are also painless and undisturbed agility of the knee joint can take place, the bones on the respective contact surfaces are very smooth, whitish Cartilage layer overdrawn. Only through them is pain-free and undisturbed mobility of the knee joint possible.
In the case of knee osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) there is a Knee joint wear in front. Signs of wear and tear can occur in isolation or preferably affect the inner or outer part of the knee joint.
The detailed definition of knee osteoarthritis shows which part of the knee joint is mainly affected:
- medial knee osteoarthritis: mainly affected inner proportion of
- lateral knee osteoarthritis: mainly affected outer Proportion of the knee joint
- Retropatellar osteoarthritis: mainly affected Kneecap articular surface
- Pangonarthrosis: everyone is affected three Joint parts
- Osteoarthritis of the thigh roll (Femoral condyle)
- Osteoarthritis of the Tibial head / Shin Plateus (Tibial plateau)
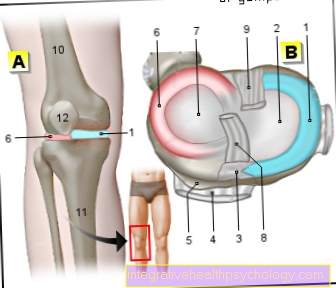
Illustrations of the knee joint

- Thigh muscles (Quadriceps femoris muscle)
- Thighbones (Femur)
- Thigh tendon (Quadriceps tendon)
- Kneecap (patella)
- Kneecap tendon (Patellar tendon)
- Kneecap tendon attachment (Tibial tuberosity)
- Shinbone (tibia)
- Fibula

A - Right knee joint from the left
B - Right knee joint from the front
C - Right knee joint from behind
- Kneecap - patella
- Femur - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
- Fibula - Fibula
- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Kneecap ligament -
Ligamentum patellae - Outer band -
Ligament collaterale fibulare - Inner band -
Ligament collateral tibial - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Ligament cruciatum posterius - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Ligament cruciatum anterius
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
frequency
Knee osteoarthritis is a common disease in adults with a high prevalence (depending on the study, 27-90%) among people over 60 years. Due to this fact, it is of great social medical importance. Knee osteoarthritis affects both the ability to work and the personal quality of life.
Gender distribution
The female gender is clear more often affected by knee osteoarthritis.
causes

Causes for the development of knee arthrosis / gonarthrosis:
- Axis deviations (knock-knees or bow-legs)
- Injuries to the knee joint, e.g. Fracture with joint involvement
- Systemic diseases, e.g. B. Hemophilia
- Rheumatoid arthritis (rheumatism, chronic polyarthritis)
- Inflammation of the knee joint caused by bacteria (bacterial arthritis)
- misplaced kneecap
- muscular imbalances caused by, e.g. Paralysis
- Osteochondrosis dissecans
- Osteonecrosis (e.g. M. Ahlbäck)
- Metabolic diseases, e.g. gout
Important influencing factors that favor osteoarthritis of the knee:
- Obesity
- Improper loading
- endocrine factors (e.g. hormones, increased occurrence of osteoarthritis after menopause)
- Cruciate ligament tear
You may also be interested in this topic: Chronic knee pain
Symptoms

After lying or sitting for a long time, those affected often complain of a feeling of stiffness in the knee joint, combined with a Starting pain.
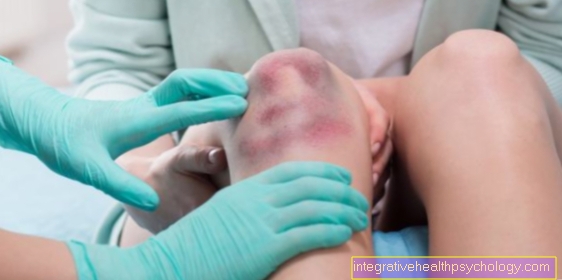
The knee joint tends to Swelling and Effusion, whereby the pain increases even with less stress.
Bursts of stimulationthat appear rarely at first become more noticeable. In addition, the knee joint needs a longer time to return to an irritation-free state.
The Exercise sensitivity increases more. Climbing and descending stairs becomes painful faster. The knee joint appears unsafe to the patient, and the symptoms of irritation increase.
In the further course of the disease, increasing pain forces you to stop, for example when walking. This significantly reduces the walking distance. Due to the pain-related rest, the muscles of the thigh shrink. Attentive observers have the impression that the stability of the knee joint decreases, especially on uneven ground.
This ultimately leads to the fact that the joint mobility continues to decrease and severe discomfort occurs even when the patient is resting (e.g. while sleeping). There can also be changes in the axis of the knee joint, in the sense of bow legs (= Varus - gonarthrosis or varus gonarthrosis) or knock knees (= Valgus gonarthrosis or valgus gonarthrosis) come.
Knee osteoarthritis can cause fluid to accumulate in the bones due to damage to the joint cartilage. This is mostly reflected in the clinical picture of a bone edema on the knee. Read our article on this: Bone edema of the knee
diagnosis
1. Clinical diagnostics
Inspection (consideration):
- Assessment of the leg axis: muscular atrophy, Leg length difference,
- Gait pattern, Knee swelling, Skin changes
Palpation (touch):
- overheat
- Effusion, swelling, dancing patella
- Crepitation, d. H. noticeable rubbing behind the kneecap
- Kneecap mobility
- Displacement pain of the patella (Zohlen - sign)
- Tension pain in the patellar facets (tenderness on the right and left of the kneecap)
- Pressure pain at the joint space
Function test and pain test:
- Assessment of range of motion and pain in motion, ligament stability
- Meniscus mark - for the detection of damage in the area of the inner meniscus or the outer meniscus
2. Apparative diagnostics
Necessary technical examination:
X-ray of the knee joint in 2 planes
Apparative investigations useful in individual cases:
- X-ray functional images and special projections for planning surgery and assessing special forms of arthritis
- Sonography (ultrasound): assessment of the knee joint effusion, Baker's cyst
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee: meniscus damage, cruciate ligament damage, osteonecrosis
- Computed tomography: fracture with a cartilage step?
- Skeleton Scintigraphy: Inflammation?
- Clinical-chemical laboratory for differential diagnosis = blood test: signs of inflammation?
- Puncture with synovial analysis: rheumatism, gout, bacteria?
Medical history / anamnesis
Which facts play a role in the Medical history survey an important role?
- Localization, functional impairment, duration, intensity, daily rhythm, radiation of the pain
- Resilience
- limp
- agility
- Entrapment, blockage, feeling of instability
- Pain-free walking distance
- Tendency to swell, complaints when going downstairs / downhill
- Walking aids
- previous accidents
- previous patellar dislocation (dislocation of the kneecap)
- Previous knee joint diseases
- Previous conservative or surgical treatment
MRI of the knee
The Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a very good diagnostic method for determining the extent of knee arthrosis.
This is particularly the case in the MRI Soft tissue, so especially the Cartilage damage in the knee, shows very well, but the bone can also be assessed. Since osteoarthritis has many sequelae, the MRI can be used very well to assess the course and can reveal consequential damage to the joint apparatus.
The MRI enables a high resolution representation of the cartilaginous joint parts - the Menisci. These are often affected and worn out in the context of knee arthrosis. The extent can be clearly seen on MRI images.
Also accompanying injuries to the menisci, such as Meniscus tears, can be detected by MRI of the knee. In knee osteoarthritis there are also irregular bony attachments in the joint area, the so-called osteophytes. These can also be detected using MRI in the early stages.
A Inflammation of the joint lining (Synovitis/Synovitis) can also be seen in the MRI of the knee joint. A thickened and signal-reinforced joint mucosa is evident. Joint effusion often forms, leading to swelling of the knee.
However, the MRI can also detect other pathological changes in the knee joint area, especially the cartilage damage. Is the adequate one Blood circulation of the bone is no longer guaranteed, it can lead to so-called Osteonecrosis come. The bone dies in this area and can cause severe pain. MRI is the diagnostic method of choice in order to detect such changes at an early stage.
Therapy for osteoarthritis
Exercises
To stabilization the knee joint muscles and coordination skills as well as for discharge of the affected joint, targeted exercises can make a big contribution. Ask your physiotherapist about individual, suitable exercises. In principle, exercise units should be chosen not painful and correspond to the possible range of motion of the knee osteoarthritis.
Before starting the exercise, warm up for about 5-10 minutes and then carry out the exercises calmly controlled by. A short stretching phase is recommended after every workout to prevent muscle and ligament shortening. In order to achieve optimal training success, you should do the exercises two to three times complete.
Two simple examples can be:
- bridge: Lie on your back and stand up both legs. Now lift your pelvis until only your shoulders are in contact with the floor. Hold this position for 30 seconds and then carefully lower your buttocks. As a variation, one leg can alternately be released from the floor and stretched.
- Dangling legs: Sit carefully on a table top so that your legs are hanging freely in the air. Then move your legs alternately forwards and backwards.
Medical therapy

In the foreground of the drug therapy of knee osteoarthritis is the Fight pain. At the beginning of therapy, drugs such as Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Voltaren® (Diclofenac) or Novaminsulfone (Novalgin®). These drugs have a good pain reliever effect, but they can help permanent ingestion can damage the stomach, kidneys and liver. To prevent gastric mucosal inflammation or gastric bleeding, a supportive drug therapy should therefore be used, especially if it is taken for a long time Gastric acid blockers (Proton pump inhibitors, Pantoprazole) can be used.
With advanced knee osteoarthritis and accompanying severe pain, stronger pain medication may have to be used. Funds from the group of Opioids, such as. Tramadol or tilidine.
In the long term, drug therapy for knee osteoarthritis is only one option Symptom control and does not remove the trigger. Long-term and regular use of pain relievers, especially ibuprofen etc., should be due to the many Side effects be avoided!
Physiotherapy / manual therapy
Physiotherapy and manual therapy are an important component in the therapy of knee osteoarthritis. Targeted physiotherapy exercises strengthen the muscular support system, stabilize the knee ligaments and promote the Coordination skills of the patient.
During physiotherapy, those affected are gradually introduced to the exercises or devices and ideally learned how to do them at home. Especially with knee osteoarthritis, e.g. the Aqua aerobics excellent because the joint is relieved.
Many patients also suffer from Lymph drainage disorders in the affected joint - the knee swells and becomes thick. In manual therapy, special Massage and wrapping techniques Provide relief and drain the lymph.
surgery

In the case of osteoarthritis of the knee, an operation should only be carried out in those patients in whom all conservative therapeutic measures have been tried over a reasonable period of time and have not been able to bring about any improvement in symptoms.
In principle, there are three different surgical interventions that can be considered:
- Arthroscopy (Jointoscopy, it can be open or closed), if necessary in combination with a removal of damaged menisci (meniscus tear), cartilage fragments or the joint mucosa, cartilage smoothing, a so-called bioprosthesis (Abrasion chondroplasty) or a microfracture.
- An operation (osteotomy) to correct the knock knees or bow legs.
- The implantation of an artificial knee joint, i.e. a knee prosthesis. Which technique is chosen depends on various factors, especially age, general condition, individual suffering and pain and the stage of the disease.
During the conversion operation, the physiological axes in the knee joints are restored in order to prevent the false and excessive stresses in the joint caused by the knock knees or bow legs and thereby prevent the osteoarthritis from progressing.
In the Arthroscopy cartilage parts are removed that have become detached in the course of osteoarthritis and lead to the symptoms. Also, the damaged Strengthened cartilage layer. This measure is usually only carried out in patients in whom the osteoarthritis is still in a relatively early stage and a layer of cartilage, albeit a thin, layer is still present. The advantage of this operation is that it enables the affected person to relieve pain on the knee relatively immediately after the operation.
But if the osteoarthritis continues advanced the cartilage layer has been completely lost at least in parts and there is exposed bone in the joint. Such "Bone holes“Can be refilled with tissue made from fiber cartilage.
In the Microfracturing tiny holes are made in the bone and then covered with blood that contains stem cells. These form over time new cartilage tissuewhich can now cover the joint surfaces and is almost as stable and resilient as the original Cartilage..
In the Abrasion chondroplasty the entire upper bone layer is removed with a knife-like device. That leads to a Hemorrhage in the joint, which ultimately creates one Healing process triggers, which ultimately results in the formation of a cartilage replacement tissue, just like with microfracture.
These two techniques are preferable to endoprosthesis when given a choice because they are one higher resilience of the knee and represent an endogenous repair process in which nothing is implanted and therefore there is no risk of rejection reactions or the need for a new operation if the prosthesis is worn out.
Of the Knee replacement (= Endoprosthesis) is therefore mainly carried out on older patients who on the one hand usually no longer put as much strain on their knees as younger people and also the limited shelf life of the artificial joint does not play such a major role. Even in very severe cases of knee osteoarthritis in younger sufferers, an endoprosthesis can be used after carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages.
Alternative therapy
In addition to surgical therapy methods, there is the option of treating knee osteoarthritis without surgery. Which therapy method promises the best therapeutic success in the individual case depends on a number of different factors. So have special individual factors the data subject how Age, occupation, physical activity, weight as well as that Extent of osteoarthritis as well as personal preferences the patient has an influence on the decision of the therapy method.
Osteoarthritis of the knee is common in most cases initially conservative treated. Only if conservative therapy is unsuccessful is surgical intervention the last option to treat knee osteoarthritis. It is important to know that osteoarthritis of the knee cannot be treated causally. Neither conservative nor surgical procedures can treat the wear and tear disease themselves and reverse damage to the articular cartilage. All available therapy options are aimed at one Symptom improvement as well as one Slowing down of progression the disease.
The most important measure of conservative therapy is ingestion pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs (please refer: Medication for knee osteoarthritis). Most are so-called NSAIDs taken, which promise not only to relieve symptoms but also to improve the local inflammatory reaction in the knee joint.
Local measures involve that Injections of anti-inflammatory drugs or from Hyaluronic acid in the joint. This measure can improve the symptoms of osteoarthritis for a certain period of time.
Alternative therapy options also exist in one targeted physiotherapy which can take up different treatment approaches. In addition to a professional physiotherapy, which is usually useful for osteoarthritis Heat treatment, acupuncture, or one Stimulation of the nerve endings on the knee (TENS) achieve an improvement in the typical symptoms.
Depending on the underlying cause of the osteoarthritis can also orthopedic measures help to minimize the progression of the disease and improve symptoms. Especially wearing orthopedic insoles is often recommended in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Ointments for knee osteoarthritis
There are different approaches to eliminating the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis and preventing the disease from progressing. Since knee osteoarthritis is a disease of the articular cartilage, only exist limited options, to get to the point of origin of the pain. Next orally Medicines taken or injected into the joint can also Anoint apply to the knee. As a rule, it is ointments, which pain relievers and anti-inflammatory substances how Diclofenac contain. However, it should be noted that the active ingredient contained in the ointments unable is to the inside of the joint to advance. Rather, as with oral intake, the active ingredient is distributed throughout the body and can reach the affected joint via the bloodstream.
A progression or Heal the knee osteoarthritis can be caused by the application of ointments cannot be achieved. If the symptoms are present, a A doctor should be consultedwho can assess the individual joint damage and make a therapy recommendation.
Prognosis for knee osteoarthritis
Is knee osteoarthritis curable?
Despite intensive research and development of new therapy options, it is so far not possibleto cure knee osteoarthritis. This is due to the fact that articular cartilage that has been destroyed cannot completely grow back and regenerate. Even with modern therapy methods, it is usually only possible to achieve one Symptom improvement as well as a Preventing progression to achieve the disease.
Though some alternative therapy methods promise a cure for osteoarthritis, they should critical can be seen, as a scientific proof of their effect has not yet been provided. In order not to risk any financial or health damage from these therapies, one is recommended detailed advice about possible therapy methods from a treating doctor.
Since the progression of the disease can be prevented, is one therapy osteoarthritis In any case makes sense. In most cases, symptom improvement can also be achieved using conventional medical methods.
If knee osteoarthritis is very advanced, it can Implant a new joint help that original mobility such as Freedom from pain to get.However, since the implantation of an artificial joint is not a measure that is understood as complete healing of the joint, osteoarthritis is still considered to be today not curable.
End-stage knee osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is one Wear and tear diseasewhich attacks the cartilage of the joint. In the course of the disease, this is so worn out that free bones are formed. If osteoarthritis is left untreated, disease progression is guaranteed. In particular, long-standing osteoarthritis diseases and untreated osteoarthritis develop into severe ones Cartilage loss.
It can total four stages osteoarthritis. The final stage of the disease represents that Stage 4 Here a complete loss of cartilage of the joint has occurred. Stage 3 also represents severe osteoarthritis and describes deep cartilage damage.
The Therapy options in stage 4 the osteoarthritis are opposite to the other stages limited. Often there is one operative care of the joint necessary to be able to remedy the symptoms of the wear and tear disease to some extent. Advice on individual therapy options can best be carried out by the attending physician.
Jogging with knee osteoarthritis

The knee osteoarthritis is one creeping disease of wear and tear of the knee joint. It is often not possible to definitively determine which cause is responsible for the individual development of the disease.
Especially when young people suffer from knee osteoarthritis, however, are one Overload of the joint Sports as well as a genetic predisposition suspected of being the trigger for wear and tear. However, sport alone can only rarely be blamed for osteoarthritis. So it is even discussed that regular exercise a protective factor before the development of osteoarthritis. In most cases, it is very unlikely that regular jogging will lead to the development of osteoarthritis of the knee.
When osteoarthritis of the knee is diagnosed, the question arises for many people whether this represents the end of sporting activity, especially jogging. In most cases it can targeted sporting activity, combined with a suitable therapy and implementation special exercises help alleviate the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee to mend
At the to jog however, care should be taken that the knee joint not a particularly heavy load is exposed. This can be done by using special shoes as well as the selection of the jogging route. Sprints and sudden stops should also be avoided. It is also true that training should be interrupted if pain occurs.
If the stress is only possible with painkillers, we advise against stress such as occurs when jogging. In these cases, a targeted physiotherapy help to strengthen the muscles of the legs and thus improve the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee.
If osteoarthritis is caused by a surgical intervention therapy is recommended first strict protection of the joint. In the course of healing, a Partial load as well as a full load on the knee joint as well as a Muscle building be possible and useful. The attending surgeon can best assess at which point in time resuming training does not pose a threat to the healing process, taking into account the surgical method and individual factors.
In general, a Resumption of exercise with simultaneous osteoarthritis of the knee not without a consultation should be carried out with the attending physician.