Vomiting and fever
General

Vomiting is a backward emptying of the stomach contents (or intestines), in which several body functions and organs are involved. This process is regulated and initiated via the vomiting center of the brain. Both the diaphragm, the abdominal muscles and the stomach itself are involved. Stomach contents leave the body via the esophagus and mouth. Vomiting can also be provoked externally by substances that induce nausea or mechanical irritation of the back of the throat or the uvula.
On the one hand, it is an important protective function of the body, as spoiled or toxic substances are excreted and not completely metabolized, on the other hand, it can be triggered by irritation of the vomiting center. This occurs, for example, with a concussion, meningitis or increased intracranial pressure.
Vomiting can also result from illness or severe irritation of the equilibrium organ.
Another protective or defense function of the body is fever. The core body temperature rises to over 38 ° C. The increased body temperature increases the mobility of the immune system's defense cells and microorganisms or particles recognized as foreign are eliminated more quickly.
If vomiting and fever occur at the same time, this can be an indication of certain inflammatory diseases in various organs. Depending on whether the person concerned is an adult, a child or a baby, different clinical pictures come into consideration.
Possible diseases that are more likely to affect an adult human
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is more likely to affect older adults, but people between the ages of 20 and 45 are more likely to be affected.
Due to different, not fully clarified processes, some people can develop sacs of the intestinal wall, so-called Diverticulum. These bulges can become inflamed when the much thinner intestinal wall here offers an entry point for microorganisms through the smallest of injuries. Abdominal pain, fever, vomiting and diarrhea / constipation tend to occur on the left side.
A low-fiber diet is likely to promote the formation of these bulges. The disease is treated through a diet with sufficient fluid intake, antibiotics or, in the case of more complicated courses, surgery.
Read more on this topic at: Diverticulitis
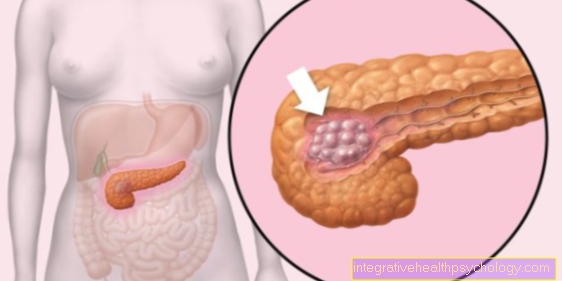
Acute pancreatitis
In an acute one Inflammation of the pancreas there is severe pain in the upper abdomen, which also spreads backwards in a belt-like manner. Symptoms can include fever and vomiting, Jaundice, Ascites (Ascites), a Intestinal obstruction stretching to shock.
Acute pancreatitis can be caused by a blockage of a biliary tract with a Gallstone, by Alcohol abuse or without recognizable or less common diseases to be triggered. She is treated as an inpatient, if necessary by means of surgery or antibiotics.
Crohn's disease
At Crohn's disease is it a chronic inflammation of the small intestine. This mostly affects young adults between the ages of 15 and 35, but the risk of the disease also increases from the age of 60.
Symptoms here in particular can be stomach pain and Diarrhea be, but also Loss of appetite, Vomit, fever, Weight loss or fatigue occur frequently. In the course of the disease, other organ systems such as the skin, joints, eyes, blood vessels or the kidneys can also develop differently.
Diseases without age restrictions
gastroenteritis
Here ignited the Mucous membrane of the stomach by bacteria / viruses, Allergens or Toxins. After a short incubation period of a few hours, vomiting and fever can result in severe abdominal pain and diarrhea. The symptoms often improve on their own after a few days. It is important to focus on one adequate fluid and electrolyte supply to be careful, otherwise the body may become dehydrated (Dehydration).
Known pathogens are here Noroviruses, Rotaviruses, Salmonella, Staphylococci and E.coli bacteria.
Both adults and children can be affected by this condition, as it is often transmitted through contaminated food.
sepsis
At a sepsis Increased bacteria get into the bloodstream and thus trigger a serious one Infection of the body out. These microorganisms find their way into the bloodstream, for example due to pneumonia, a wound infection or a reduced immune system.
It comes to Impaired consciousness, chills, accelerated breathing and heartbeat, diarrhea, alternately rising and falling fever and Vomit.
It is about a life threatening illness and must be treated as an inpatient. It can affect people of any age.
Conditions that are more likely to affect children or babies
appendicitis
The Inflammation of the appendix occurs very often between the ages of 10 and 30, but in some cases can also affect significantly older people.
Appendicitis occurs when an existing intestinal infection spreads to the appendix or when obstacles make it difficult to empty the appendix. It comes, among other things, in addition to vomiting and fever stomach pain, which after a while increases on the right lower abdomen focus. In addition, constipation can occur, which speaks against gastroenteritis in particular. In most cases, appendicitis is treated promptly by surgery.
meningitis
From one meningitis one speaks to one Inflammation of the meningeswhich is often caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. This disease tends to affect children and adolescents, but with certain pathogens it can be contagious and thus affect everyone.
Meningitis is noticeable through a pronounced feeling of illness, it can become Neck and headache, fever, Vomit, Clouding of consciousness, Convulsions or Photosensitivity come. Children under 2 years of age may experience more general symptoms such as pronounced drowsiness, poor drinking / eating, tenderness or weakness. Again there are Inpatient treatment and anti-vomiting medication necessary.
Read more on this topic: meningitis
teething
Many myths have revolved around teething for years. Today, however, it can be said that serious symptoms such as high fever, vomiting or diarrhea not caused by teething become. A slightly increased body temperature below 38.5 ° C, slight irritability, increased waking up and gum rubbing, on the other hand, often occur during teething and are completely harmless.
Usually the first milk teeth are between the 4th and 8th month of life visible. During this time, the so-called "nest protection" by the maternal antibodies in the child ends. Therefore, infectious diseases are more likely to suffer from infectious diseases during teething.
Vomiting and fever from medication
Many drugs can as an undesirable effect Induce vomiting, fever, or both. The symptoms can be caused by the direct action of the drug, a congenital hypersensitivity or an allergic reaction to it.
Commonly related drugs that can cause vomiting and fever are Antibiotics like penicillin, Chemotherapy drugs, antipsychotics, narcotic gases, or thyroid hormones. Some of these drugs induce vomiting or fever relatively often, while others very rarely.
If an undesirable side effect occurs, this should be discussed with the treating doctor. If, in addition to vomiting and fever, there are other signs of an allergy such as shortness of breath, circulatory problems, rash or swelling in the mouth, the emergency doctor must be called immediately, as the situation can be life-threatening.
Vomiting and fever after vaccination
Side effects are common after vaccinations very rarely. However, possible side effects include vomiting and fever. They are usually mild. Fever is much more common, mostly low and has already disappeared 2 days after the vaccination. Sometimes it also occurs as part of a so-called "Vaccine disease" on. In the case of live vaccines, a mild form of the respective illness with a slight fever (below 39.5 ° C) and general symptoms can occur 1-4 weeks after vaccination.
In very rare cases, severe side effects or one will occur allergic reaction on the vaccination, including vomiting and fever. In these cases a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.
therapy
The therapy for vomiting and fever depends on the underlying disease. If the person concerned is still doing relatively well and there are no further symptoms, vomiting and fever can be treated at home. There the fever does not usually have to be lowered: an increased temperature supports the body in fighting pathogens and should only be reduced if you are very unwell.
On the one hand, home remedies such as lukewarm calf compress or Medication such as paracetamol, ibuprofen or diclofenac can be used.
Subjectively, nausea and vomiting are highly stressful symptoms that can usually be treated well. In addition, they prevent fluid absorption, which is why treatment is particularly necessary in children. Liquid should be swallowed in small sips at short intervals. If this is not enough, you can Nausea medication, so-called "Antiemetics", As a tablet or suppository. Frequently used active ingredients are Metoclopramide and dimenhydrinate (Vomex).
If there is a simple gastrointestinal infection or a food intolerance, can Home remedies and abstaining from solid food for several hours already lead to the desired improvement. More serious illnesses such as meningitis make the rapid use of antibiotics in hospitals necessary. Appendicitis usually requires surgery.
homeopathy
In addition to conventional medicine, homeopathic medicines can also be used for vomiting and fever. they should but never alone with severe and severe symptoms can be used. While many individuals report effectiveness, studies have shown that the following drugs do not work better than a placebo.
Typical drugs that are used in the event of vomiting as part of gastrointestinal infections or after eating spoiled food are Arsenicum album, Podophyllum or Phosphorus. If you have a fever, Aconitum, Belladonna, Eupatorium perfoliatum or Ferrum phosphoricum can be used.
Vomiting and fever during pregnancy

Frequent vomiting is during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, due to hormonal changes completely normal. In rare cases, however, the nausea and vomiting do not stop after a short time, but occur again and again - sometimes even for several days. This is known as pathological vomiting. Symptoms such as severe thirst and fever ("Thirst fever“) And dehydration can also occur. If not enough fluids can be absorbed in this situation or if the fever rises sharply, a doctor should be called.
As the immune system weakens during pregnancy, infections are more common. These can also lead to vomiting and fever. Usually a harmless gastrointestinal infection triggers the symptoms. It is important to watch out for other symptoms, as some diseases can be dangerous for mother and child. If you develop a rash, severe diarrhea, circulatory problems or severe headache and back pain radiating downwards, you should see a doctor.
A high fever can be harmful to the child during pregnancy. It is therefore advisable not to let the fever rise above 39 ° C. For this purpose, calf wraps or paracetamol can be used.
Vomiting and fever in the baby
Babies have to choose between harmless Spit and the potentially dangerous vomiting can be distinguished. Spitting is used to remove air from the stomach, especially after a hasty meal, and can contain food residues. Vomit consists of a lot of food and has a very specific smell.
If the fever and vomiting last only a few hours, the all-clear can be given. On the other hand, persistent fever and repeated vomiting should be taken very seriously in newborns and infants. On the one hand, the risk of dehydration is very high in very young children, on the other hand, a serious illness that requires treatment can be behind the symptoms. In any case, it is important to offer the child frequent fluids to prevent dehydration.
Depending on which additional symptoms the baby is showing, a Gastrointestinal infection or a Urinary tract infection, in rare cases also one Meningitis, an obstruction of the stomach outlet, a twisted bowel (Volvulus) or blood poisoning is behind the symptoms. Also Vaccinations can cause fever and vomiting.
Read about this: Fever in baby after vaccination
Children under 3 months should already be at a body temperature of above 38 ° C be presented to a doctor, with older children temperatures above 39 ° C should ring the alarm bells.
Vomiting and fever in the child
Children vomit far more often than adults because their vomiting center in the brain and stomach are much more sensitive. Fever is also more common. Therefore, these symptoms often occur with minor illnesses such as one Gastrointestinal infection, with light Food intolerance or one Urinary tract infection on.
With any type of vomiting and fever, the child's fluid loss is very high adequate hydration must be observed. Solid foods should be avoided for the first 6-12 hours. If vomiting repeatedly occurs, a suppository against nausea can also facilitate fluid intake. If the child shows further symptoms such as extreme tiredness and fatigue, ear pain, it appears very weak and changed, if the abdomen is tense and very painful, if severe diarrhea occurs or if it shows persistently high fever above 39.5 ° C, this can be serious and potentially life-threatening illness behind the symptoms. Then a pediatrician should be seen.
Read more on this topic at: Vomiting in children and fever in young children
Vomiting and fever without diarrhea
Vomiting and fever are very common symptoms in adults, but also in children and toddlers, and can have many causes. Even without diarrhea, a harmless disease is usually like a Gastrointestinal infection responsible for. However, inflammation of the urinary tract, the bladder, the kidneys, appendicitis or - in rare cases - diseases of the brain or meninges can manifest themselves with fever and vomiting without diarrhea.
First of all, it is important to observe yourself or the (small) child. The following applies to children: if the symptoms persist for several hours and if they no longer consume food or fluids, there is a risk of dehydration. If it persists for a long time, it can even be life-threatening. It is therefore necessary to offer the child fluids frequently. Here, for example, tea with a little sugar, electrolyte mixtures or the child's favorite drink are ideal.
If the (small) child does not drink any fluids per se within half a day, the pediatrician should be consulted in the event of uncertainty in dealing with such a child.
In children and adults, a lack of fluid is often seen in dry lips, a dry tongue and sometimes standing folds of skin: when the skin is pressed together between 2 fingers, the resulting skin fold remains for a short time.
In order not to worsen vomiting, no solid food should be consumed or offered to the child for the first 6-12 hours. A suppository with an anti-nausea medicine can also make vomiting easier.
If vomiting has a dangerous cause with a fever, additional symptoms usually appear. At a Inflammation of the urinary tract or the kidneys can Painful urination or flank pain when you press or tap on the side of the trunk.
A Meningitis, also meningitis called, typically also shows a deterioration in the general condition. The children seem changed, tired and limp. These symptoms can occur relatively quickly, so it is important to monitor the symptoms.
A Appendicitis or other serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract need not cause diarrhea. They can also be manifested by abdominal pain or abdominal cramps and possibly tensing of the abdomen at the slightest touch.
If you have noticed any of these additional symptoms in your (small) child, you should consult a doctor immediately. If the symptoms started after an accident with a fall on the head, a doctor should also be consulted as soon as possible.