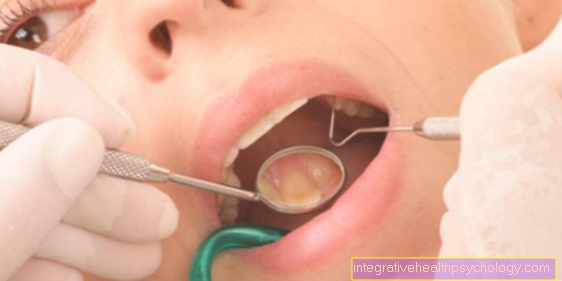
Fistula on the gums
synonym
Gum fistula
definition
A fistula on the gum is a non-naturally preexisting connection between an internal cavity (e.g. the Tooth root tip) and the gums. In the case of a gum fistula, a distinction must generally be made between the internal and external fistula. In the case of the gingival fistula, there is an external fistula.

General information on gingival fistula
A fistula on the gum is usually a tube-like connection between a small cavity in the area of the tooth root tip and the surface of the gum. The affected patients usually have chronic inflammatory processes in a tooth. In addition, suppuration in the area of the tooth root tip can lead to the formation of a fistula on the gums.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the gums pus
The Fistula on the gums consists of a Fistula base, one Fistulous duct and one Opening of the fistula. Under the term "Fistula base“One understands the Origin of the fistula at the tooth root. The formation of such a fistula is a reaction of the organism to inflammatory processes in the area of the tip of the tooth. By training this Fistula duct can he Removal of the purulent secretion guaranteed. A fistula on the gums can develop in both the upper and lower jaw. As a rule, the fistula duct emanating from the gums only leads to a single tooth root.
If there is a fistula on the gums typical symptoms to be watched. Most of the affected patients develop strong Swellingthat to pus-filled vesicles develop. In addition, those affected typically suffer shortly before these pus-filled blisters burst severe pain. Gum fistulas can especially common in children and young adults to be watched. The reason for this is the fact that these patients represent a risk group due to the not yet completed growth and development of the jaw and teeth. In principle, a fistula can develop on the gums even in adults. These cases are mostly chronic Infections within the oral cavity in front. In a direct comparison, however, adults are affected much less often.
Gum fistula in the child
Fistulas can also develop on the milk teeth in children. Usually small blisters are visible on the gums through which some pus can come out. The cause of this fistula formation is usually an inflammation in the area of the tooth root.
If a fistula is suspected in children, a dentist should be seen immediately. They can find out the cause of the fistula formation and treat it. The inflammation must be completely removed and disinfected, even in children. The course of treatment depends on the cause.
Is for example. If a caries has penetrated far into the tooth or has even reached the tooth nerve (pulp), this manifests itself in pain for the child. In this case, a deciduous root canal treatment can be performed if possible.
Furthermore, this can also be used when z. B. the tooth has died in an accident.
Depending on the severity and spread of the inflammation, the milk teeth are extracted to prevent the inflammation from spreading to the bones or other teeth.
Treatment of a gum fistula in the child
Since the enamel layer of the milk teeth as a substance is not as hard as that of the permanent teeth, they are potentially more susceptible to tooth decay. This allows tooth decay to spread more easily and quickly infect the pulp and the nerves and vessels in it. The inflammation can spread through the vessels beyond the tip of the root and often forms a fistula.
The inflammatory tissue is then therapeutically removed and the canal system rinsed and disinfected to kill the bacteria. The fistula is left in place and is not removed surgically. It forms itself back again when the bacteria are removed from the canal system and the inflammation subsides again.
The preservation of the milk tooth is important because it has a placeholder function in the dentition and is important for its development. For example, if the child is too young or unwilling to cooperate, tooth extraction may be the better therapy, as root canal treatment can be lengthy and exhausting. Then you can insert an orthodontic placeholder into the gap.
It is also important that the tooth germ of the permanent tooth is not damaged by the fistula.
However, it may also be necessary to surgically remove the entire fistula duct, provided that it does not recede by itself. The removal of the fistula is carried out by the oral surgeon or the oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Causes of a fistula on the gums
Fistulas in the gum or tooth area can be caused by various causes. In the majority of cases, inflammatory processes that are present directly at the tip of the tooth root cause the formation of a fistula. The discharge of the purulent secretion can only be guaranteed through the formation of this fistula.
The inflammatory processes responsible for the development of a fistula on the gums can arise from various causes. In many cases, advanced carious defects can be demonstrated in the affected patients. As soon as these carious defects reach deep into the tooth, bacteria can spread within the tooth pulp. The bacteria then arrive, starting from a so-called Pulpitis (Tooth pulp inflammation), through the root canal to the tip of the root. If appropriate treatment is neglected, inflammatory processes develop and a purulent secretion is released.
Furthermore, the bacterial pathogens can reach the root tip from a deep gingival pocket. Some of the affected patients had dental trauma before the fistula appeared on the gums. In addition, foreign bodies that penetrate deeply along the gumline can cause irritation. The permanent irritation can lead to the development of inflammatory processes and the formation of a fistula on the gums.
Read more on the topic: Gingival pocket
Since only a targeted therapy tailored to the cause can guarantee long-term treatment success, extensive diagnostics should be carried out.
Can a gum fistula occur after root canal treatment?
If a fistula occurs after a root canal treatment, the cause lies in the persistence of a deep-seated inflammation. Because bacteria may still be in the tissue, the inflammation cannot heal.
Furthermore, a fistula can form if the root is inadvertently perforated during the root canal treatment, i.e. is pierced. The difficulty is that each root canal can be curved or bent differently. If the dentist accidentally pierces the root, a hole is created towards the bone. In this case, bacterial colonization and accumulation of pus quickly develop and the fistula can find its way to the gums of the oral cavity.
Also read: Fistula on the tooth
Fistula after apicectomy
The apicectomy is usually the last step in saving a tooth after a root canal treatment has failed. However, the tip resection is also only an attempt to preserve it and there is no guarantee that the tooth will be symptom-free after the treatment. One possible complication is that a fistula forms.
The fistula is a sign that not all bacteria below the root tip have been removed and that secretion continues to form. Therapeutically, attempts can be made to save the tooth with a renewed root resection and removal of the fistula duct, but the probability that the tooth will be symptom-free is classified as low. If this is unsuccessful, the tooth must be extracted if it continues to radiate symptoms.
Symptoms of the fistula on the gums
The symptoms typical of a fistula on the gums depend mainly on the exact location, severity and stage of the fistula.
In the early stages, the gum fistula usually does not cause any symptoms. For this reason, the existing inflammatory processes are often not recognized as such and treated too late. Due to the natural immune reaction of the body, a purulent secretion forms and an increasing sensitivity to pressure occurs. After a while, the affected patients notice a significant swelling in the area of the inflamed tooth. In addition, there is a persistent state of tension and a slight throbbing pain. In the area of the fistula on the gums, which at this point usually appears as a small blister, there is an increasing accumulation of pus.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the gums pus
The pain typical of a fistula on the gums increases significantly due to the increasing pressure at the tip of the tooth. As soon as the pressure inside the fistula on the gums becomes too great, purulent secretion escapes through the fistula duct and reaches the oral cavity. As the patient progresses, the pain felt by the affected patient increases significantly in intensity.
Does a fistula on the gums cause pain?
A fistula usually manifests itself as a small white vesicle with a red halo around it in the immediate vicinity of the affected tooth. However, the fistula can also (almost invisible from the outside) lie on the gumline, i.e. between the tooth and the gumline.
Since the cause is usually an inflammation of the root, a fistula is associated with the typical signs of inflammation such as redness, swelling, pain and warming in the affected area. Patients describe the pain more as a feeling of pressure and as a light tapping pain, which is particularly annoying when eating or brushing teeth. In the case of fistulas, this usually subsides a lot after the pus has leaked.
This is why the fistulas are so dangerous. Those affected usually no longer feel any pain while the underlying inflammation continues to spread and possibly spread to the jawbone.
However, a fistula can also be completely painless, which is why it is not perceived in the majority of cases.
The constant leakage of pus from the outlet of the fistulous duct causes unpleasant bad breath and impaired taste.
Pain due to a fistula
A fistula can both cause pain and be completely painless, which is why it is not noticed in the majority of cases. If pain occurs, this is due to the inflammatory bacteria. The tissue around the fistula duct is swollen and red and feels warm. Light touches create an uncomfortable burning pain that is relieved by cold food and drinks. The constant leakage of pus from the outlet of the fistulous duct causes unpleasant bad breath and impaired taste.
Read more on the topic: That's how dangerous a fistula in the mouth is
Therapy of the gingival fistula
A fistula on the gum line can become very painful. Because of this, most affected patients require prompt treatment. At the beginning of the therapy of a fistula on the gums, an antibiotic is usually prescribed. By taking this antibiotic regularly, the causative bacterial pathogens can be rendered harmless. The attending dentist can then open the fistula on the gums and suck off the pus inside.
In some cases, however, the fistula duct opens spontaneously even before the dentist's visit. In these cases it should be checked whether the purulent secretion has already completely drained off. If pus can still be found inside the fistula, it should be removed with the suction device. Often these simple measures are sufficient to enable the patient to be free from pain.
However, further measures may be necessary in the case of a complicated fistula on the gums. In this context, the cause of the formation of the fistula on the gums plays a decisive role. Often the accumulations of pus can only be removed in the long term if the underlying disease is treated extensively. Root canal treatment usually has to be carried out in patients with a fistula on the gums caused by inflammation of the root tip. In this treatment method, the number is opened and the tissue located within the root canals is removed.
The tooth killed as a result can remain in the oral cavity, but often has to be provided with a tooth crown after some time. In the case of widespread inflammatory processes, however, it can happen that a root canal treatment remains unsuccessful. In these cases, the treating dentist can try to save the tooth by means of a so-called tip resection. With this treatment method, the gums are opened in the area of the inflamed tooth and the jawbone is exposed. The tip of the tooth root must then be exposed in the bone and separated. Even this procedure does not always offer 100 percent treatment success. Depending on the underlying disease and / or the extent of the disease, immediate removal of the affected tooth may therefore be unavoidable. As a result, the patient has to have the missing tooth replaced with an implant or some other type of denture. Otherwise, an unsightly gap will be left in the row of teeth.
Home remedies for gum fistula
In general, it is theoretically possible to make the fistula in the oral cavity smaller by using home remedies or to alleviate the symptoms. However, the cause of the actual formation of the fistula cannot be eliminated.
In the case of a fistula, an operation by the attending dentist is inevitable. The dentist opens the affected area and removes the inflammation from the tissue. In general, home remedies can also be used, for example, to relieve pain or support healing.
If there is a build-up of pus, rinsing with chamomile tea can help ease the discomfort a little. Furthermore, garlic or onions can be chopped up and applied to the affected areas several times a day.Clove oil is also often applied against pain in the jaw area using a cotton swab.
You might also be interested in: What helps against gum inflammation?
Homeopathy for fistulas on the gums
The symptoms caused by the fistulas can be alleviated with homeopathic remedies. However, they do not cure anything. The causal inflammation persists.
The treatment can take place, for example, with Silicea C4 or Hekla Lava C5. Here a homeopath can find the right remedy for the individual, depending on the severity.
In general, however, it is important to know that an operation is inevitable for a fistula. Homeopathy alone cannot cure this bacterial inflammation.
After an operative treatment, homeopathic remedies can be used supportively.
Is it possible to puncture a fistula on the gums?
A fistula is an unnatural connection between the root of the tooth and the oral cavity. This has formed due to an inflammation at the tooth root. The pus from the inflammation eventually drains into the oral cavity through a kind of tube acting as a drainage channel. From the moment it is emptied, the fistula in the mouth is usually no longer painful.
It is urgently advised not to prick the fistula yourself, as this usually allows more bacteria to enter the wound.
Another risk is that the pus and thus the bacteria will spill over a large area into the surrounding tissue when you pierce it. Therefore, it is recommended to see a dentist who will professionally remove the inflammation.
A small operation is usually unavoidable. The dentist removes the causative purulent inflammation (usually a root inflammation) and disinfects the wound. Depending on the spread of the inflammation, different treatment options are possible. If the inflammation has already spread massively, this can lead to the loss of the tooth.
Antibiotics are generally used to prevent re-inflammation and to speed up healing.
What risks can gum fistulas pose?
A fistula on the gums should be presented to a dentist as soon as possible. This can initiate appropriate treatment with regard to the clinical picture.
In general, the fistula does not pose a risk in itself. It is, however, a sign that there is chronic inflammation within the oral cavity. The main risk of such an inflammation is that the inflammatory processes can spread to the jawbone. In the long term, this will attack the jawbone and change its structure. The jawbone tends to get thinner and thinner and can no longer provide adequate anchorage for the teeth.
Patients who do not have a fistula on the gums treated promptly are at risk of losing their teeth. Due to the extensive bone decline, this can even affect perfectly healthy neighboring teeth. In addition, chronic inflammations, regardless of their location, have been shown to weaken the immune system. This in turn makes the affected patients more susceptible to other diseases.
Can a fistula lead to tooth loss?
A fistula does not necessarily have to result in tooth extraction, but it can occur as a complication if all other attempts at therapy have failed. The prognosis of a root canal treatment is positive, which is why the majority of fistula ducts recede simply by disinfecting the canal system and the root filling. If the fistula duct remains and pus emerges, a root tip resection is initiated as a therapeutic step in which the fistula duct is usually completely removed. If this attempt also fails, tooth extraction is an option. In some cases, the tooth can no longer be preserved.
Prophylaxis: what prevents fistulas?

Since there are a multitude of causes for the development of a fistula on the gums, the prompt treatment of any change within the oral cavity is in the foreground. Preventing a fistula on the gums, which can be accompanied by severe pain, primarily involves improving oral hygiene. In this context, participation in a dental care program should be considered. Individuals who have poor oral hygiene should start by consistently cleaning their teeth three times a day. However, it should be noted that it is not just the quantity, but above all the quality of oral hygiene that plays a decisive role in preventing a fistula on the gums.
In particular, the interdental spaces are often neglected by most of the affected patients. To ensure effective cleaning of these interdental spaces, so-called interdental brushes should be used at least once a day.Interdental brushes) and / or floss can be used. In addition, tooth decay should be promptly assessed by a dentist and treated immediately if necessary. In this way, the development of inflammatory processes within the oral cavity can be prevented. Regularly performing professional teeth cleaning (in short: PZR) is considered to be an effective method of preventing a fistula on the gums.
When should I go to the dentist?
The formation of a fistula can be a result of inflammation under a root tip, through which the inflammatory secretion can drain. As soon as the person concerned notices the fistula, he should see the doctor for appropriate therapy.
Often the patient cannot see the fistula, e.g. emerges on the palate side of the teeth and is only discovered as an incidental finding during the check-up.
If nothing is done about the fistula, pus will constantly leak out of the fistula, so the inflammation will persist and there is a risk of abscess formation.