Acyclovir
introduction
Aciclovir is an active ingredient from the group of so-called antivirals.
Antivirals use various enzymatic mechanisms to inhibit the virus that has entered the body from multiplying in the body's cells. Acyclovir is well tolerated and can be used without hesitation except for a few side effects and risks that need to be considered. As a rule, an application time of about one week is sufficient for successful virus treatment. In some long and persistent courses in which the virus breaks out again and again, it may sometimes be necessary to carry out low-dose long-term treatment with acyclovir.

Indications
This group of drugs is only used to fight certain types of viruses.
In today's medicine, acyclovir is mainly used in the treatment of the herpes simplex virus and its representatives. The clinical pictures include:
- Cold sore
- Genital herpes
- Shingles
- chickenpox
- Inflammation of the brain caused by herpes viruses
Acyclovir can be used in various dosage forms as mentioned in the treatment of herpes labiales, i.e. cold sores or genital herpes. It is also sometimes given to immunocompromised patients who have chickenpox.
The varicella zoster virus can also be successfully treated with acyclovir, which under certain circumstances triggers unpleasant shingles all over the body.
The herpes virus can also cause serious infections, such as herpes encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), which is a life-threatening condition and requires urgent treatment with acyclovir.
Acyclovir is given as an infusion over a longer period and the patient is treated in the intensive care unit.
In patients who have to endure an organ transplant, aciclovir is given purely prophylactically to prevent possible infections from developing in the first place.
During the irradiation of a cancer patient, acyclovir is often given as a pill over a longer period of time for prevention. The mode of action of acyclovir is always the same and usually very successful.
You might also be interested in these topics: Shingles medication such as Shingles of the eye
Indication for cold sores
There are several herpes viruses against which acyclovir can be used. Acyclovir is activated in cells suffering from herpes and leads to the destruction of the DNA of the herpes virus. The so-called herpes simplex virus, which often affects the face in the area of the lips, is very well known. Acyclovir can initially be used in the form of a cream to treat the herpes virus. If the effect of the cream is insufficient or if the disease occurs again and again, acyclovir can be taken as tablets and thus also serve to prevent new diseases.
Read more on this topic: Cold sore
Indication for genital herpes
Different herpes viruses can infect different parts of the body. The genital area can also be affected, the herpes simplex virus is the trigger for this. Acyclovir is an agent that helps very well against the virus responsible for genital herpes. Therapy with acyclovir should best be started within the first day after the appearance of symptoms such as redness, swelling and itching in the genital area. It can be applied to the affected area in the form of a cream. If the cream does not completely fight the disease, acyclovir can also be used in the form of tablets or via an infusion. A dosage of 200mg acyclovir five times a day or 400mg three times a day is used. This dose should be taken for approximately five to ten days and must be adjusted in children under two years of age and severe kidney disease.
For more information, see: Genital herpes
effect
Viruses that have penetrated the body attack individual body cells and bring numerous enzymes of their own into the cell, which are supposed to ensure that the virus can multiply unhindered in the infected cell. If there are enough viruses in the cell, the cell often bursts and the viruses swarm out to infect other cells and also multiply in them.
Acyclovir only penetrates the virus-infected cells. Interestingly, healthy cells are not attacked by acyclovir. This ensures that the body is largely unencumbered by acyclovir treatment. The virus needs an enzyme in order to multiply. This so-called thymidine kinase attaches phosphate to thymidine and helps the genome of the virus to multiply. Acyclovir works here and activates the thymidine before it has come into contact with the virus enzyme. This leads to a chain break in the reproduction and to the stop of the virus from spreading in the cell.
It is important to know, however, that the herpes virus group remains in the body for life, especially in the nerve cells with herpes simplex.Acyclovir only reaches the cells that are affected by stress or a weakened immune system during an outbreak of the virus, for example, but not the nerve cells themselves. For this reason, it can only contribute to symptom relief but not to complete healing.
Due to the special enzyme use of the herpes virus, acyclovir can only work with these viruses, more precisely only with the herpes viruses of the alpha group. Other viruses of the herpes family which belong to the beta or gamma group are not treated as successfully with acyclovir. These include the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes glandular fever, or the cytomegalovirus.
As a tablet, acyclovir works about one to two hours after ingestion. In order to reach high concentrations very quickly, the drug must be administered to the patient by infusion.
Acyclovir is excreted by the kidneys after its effects. Restricted kidney activity can therefore represent a contraindication to the use of acyclovir and should be observed.
Dosage forms of acyclovir
Acyclovir ointment
Acyclovir ointment is used very often and is also available from pharmacies without a prescription. The main area of application is cold sores, which can develop in the area of the upper or lower lip or at the corners of the mouth. In the case of a single occurrence and weaker symptoms, a treatment attempt with acyclovir ointment can be undertaken in any case and initially without taking acyclovir with tablets.
Acyclovir as an ointment should be applied regularly to the affected skin areas around the lips. It is important that it is applied at least 5 times a day and that an interval of approx. 4 hours is observed. As soon as the discomfort in the lip area has disappeared and the corresponding skin crusts are no longer visible, the ointment can be discontinued. Only after frequent and recurring cold sore infections can you consider taking acyclovir as a tablet in order to achieve a higher dose and a long-lasting effect.
Acyclovir ointment is usually very well tolerated. In individual cases, however, skin irritation or redness may occur after application to the skin area, it may cause burning or itching and the skin may become flaky. In this case, the ointment should be discontinued.
Sometimes shingles on the trunk can be treated with acyclovir ointment instead of tablets. However, the success rate is mixed and so if there is no improvement, you should switch to tablet form as soon as possible.
Read more on the subject at: Cold sores - this is how it is properly treated
Acyclovir as an eye ointment
Acyclovir as an eye ointment requires a prescription and must be prescribed. The preparation is sold in Germany under the name Zovirax® and is primarily approved for herpes infestation in the eye area.
Read more on the topic: Acyclovir eye ointment
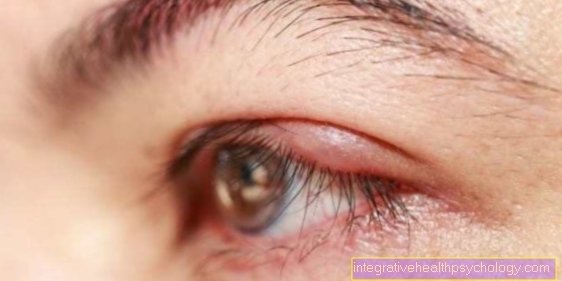
Herpes infection is a dangerous condition that must be treated by an ophthalmologist. The risk of impaired vision or loss of vision requires prompt and consistent treatment. The disease, also known as zoster ophthalmicus, is characterized by the formation of blisters around the eye.
The acyclovir eye ointment should be applied to the affected skin area regularly (at least 5 times a day with a four-hour time difference). Since it is an ointment, acyclovir eye ointment should also be applied to the conjunctival area. This can lead to blurred vision, but this will improve within half an hour of use. During this time, however, no car should be driven.
If, after a few days, either the blistering around the eye deteriorates or the vision deteriorates, an ophthalmologist should be consulted immediately. Possible side effects when using acyclovir eye ointment are conjunctival irritation in the area of the eye, as well as redness, burning and itching. It can also lead to excessive tearing. Whether a treatment should be discontinued and omitted should be discussed in detail with an ophthalmologist, as treatment of a herpes zoster on the eye is urgently necessary. You should refrain from stopping the aciclovir eye ointment on your own without consultation.
Read more on the subject at: Eye herpes - you need to know that! such as Zovirax® eye ointment
When is acyclovir given as an infusion?
Acyclovir is given directly into the vein through a port in various situations. In general, the drug can always be given as an infusion. However, taking it in tablet form is easier and more comfortable for most patients. When acyclovir is given as an infusion, the route through the stomach and the gastric mucosa is bypassed. For this reason, when taking acyclovir in tablet form, there may be losses in the absorption of the active ingredient. The absorption of the drug can be disturbed, especially in patients with a disease in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, acyclovir is given as an infusion. Acyclovir can also be given by infusion to patients who have trouble eating or swallowing.
Side effects
Acyclovir is generally well tolerated. Nevertheless, both short-term use and long-term use of the drug can become necessary Side effects come.
The more common side effects of using ointments on the skin area are the most common Reddening of the skin and irritation, Scaling, dry skin and itching or burning.
When using acyclovir as an infusion or as a tablet, it can also Itching, hives (rash), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, feeling unwell and tired come.
In some cases, they have been taking longer acyclovir treatment as well Changes in blood count were found, but they declined again after discontinuing the drug.
Above all, this included one Anemia (anemia), one reduced platelet count and decreased white blood cells.
Very rare became high while taking acyclovir fever and inflammatory reactions, Kidney pain, breathing difficulties, liver inflammation with accompanying jaundice (hepatitis) and neurological side effects such as speech or gait disorders, tremors, delusions and psychoses observed.
Some side effects made it necessary to stop taking it immediately.
At slight itching or small skin reactions If the treatment has already been carried out for a long time, it can be considered whether the acyclovir intake can still be brought to the end in order to achieve a final and lasting treatment success.
dosage
There are different dosages depending on the cause of the intake of acyclovir. The dose to be used also depends on the age, height, weight and previous illnesses of the patient. Acyclovir is available in tablet, infusion, and ointment form. The dosage varies between 200 mg and 800 mg.
In the case of herpes on the face or genital area, treatment can be started in the form of a cream with a dose of 200 mg acyclovir. If the application of the cream is no longer sufficient, you can switch to taking tablets. With each dose in the form of a tablet, enough water should be drunk throughout the day. For the treatment of a herpes disease in the face and genitals, tablets with a dosage of 200 mg acyclovir, which are taken every fourth hour, i.e. five times a day, are suitable for otherwise healthy adults. The individual intake can also be switched to, for example, a dose of 400mg, which is taken twice a day. This dosage can also be taken by patients who frequently develop severe herpes diseases to prevent the disease from returning.
Children from the age of two can receive the same dosage. Younger children are usually given half the dose. People who have a congenital or other medication-induced weakness of the immune system take a dose of 200mg every six hours as a preventative measure. If the immune system is severely restricted, for example after a liver transplant, the individual dosage can be doubled to 400mg.
In the event of an infection with the herpes zoster virus, which is responsible for shingles, a dosage of 800mg is used consistently five times a day at regular intervals over a period of one week. If shingles recurs, long-term treatment with acyclovir can be considered to prevent secondary diseases such as nerve damage. Here, acyclovir is used as a tablet in a dosage of 3x 500 mg over several months.
In old age and in the presence of a kidney disease, the dosage must be reduced in some cases. This should always be discussed with the attending physician. If acyclovir is used as an infusion, a dose of 5-10 mg per kilogram of the patient's body weight is given into the vein three times a day. The application of all dosages that are used to treat an acute illness should be carried out for approximately five days.
The application is similar to taking antibiotics. It is essential to ensure that acyclovir is taken to the end even after the symptoms have subsided (e.g. in the case of shingles).
Can acyclovir also be used for prophylaxis?
Acyclovir can also be used for prophylaxis. This is particularly useful for people who suffer from common and severe herpes diseases or shingles. For this purpose, a daily dose of approx. 1g is recommended, which should be divided into three to five ingestions per day. The dosage for the prevention of a herpes disease or shingles should not be used for longer than a year and always in consultation with a doctor. Aciclovir can also be used prophylactically in patients with a weak immune system. This also applies to patients who are taking medication intended to weaken the immune system as a result of an organ transplant. In this case, the dosage and the duration of the intake of the acyclovir must be discussed with the doctor and adjusted accordingly to the situation.
Does acyclovir require a prescription?
Acyclovir can be used in several forms. There are ointments for use directly on the affected area. These do not require a prescription and can be purchased from a pharmacy. In contrast, acyclovir in pill form requires a prescription. The tablets work throughout the body and therefore affect all other organs when taken. This is why there are more potential side effects with acyclovir in tablet form. It is therefore more effective in this form. If necessary, you can get a prescription from your family doctor.
What is the difference between acyclovir and penciclovir
The modes of action of acyclovir and penciclovir are very similar. However, the two substances show a small difference in their molecular structure. This is responsible for ensuring that penciclovir can only be used as a cream. Only one precursor of penciclovir, called famciclovir, can also be taken in tablet form and then converted into penciclovir in the body. Acyclovir can be used both as an ointment and in tablet form.
Furthermore, acyclovir is broken down faster in the body than penciclovir. Therefore, penciclovir has a longer duration of action than acyclovir. In addition, penciclovir also has a very good effect if it is used more than a day after the first symptoms or if you can already see blisters. In contrast, treatment with acyclovir should be started within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms, if possible.
Another alternative is the drug Zostex®, which is both faster and more effective. It is particularly suitable for treating shingles. In addition, only 1 tablet needs to be swallowed a day.
Read more about this under: Zostex®
Acyclovir in pregnancy
Herpes infections are not uncommon during pregnancy. Treatment should always be carried out for the child's safety.
Most often occurs in pregnancy Cold sore that can be successfully treated with acyclovir cream.
Sometimes it can lead to an outbreak of an outbreak as a result of great stress or also due to immune deficiency during pregnancy Shingles come in a specific part of the body. Here should also be treated with a consistent treatment with acyclovir in tablet form.
Despite few studies, there is no evidence that acyclovir can harm the fetus. First and foremost, it is important to ensure that the virus is harmless in the body.
Particular caution applies here with genital herpes, as an infection of the fetus at birth can also be triggered here. The dosage is the same as for non-pregnant women and should be taken 5 times a day at a dosage of 800 mg for shingles.
Some gynecologists recommend a dose of 400 mg over the same period.
Acyclovir can also be used after pregnancy to be applied if necessary. According to previous studies, breastfeeding with acyclovir treatment is also safe.
It is important that the viral infection does not spread to the unborn child and cause serious damage there.
Acyclovir in babies
Acyclovir can also be used in babies and children under two years of age. The use should always be discussed with the pediatrician, as he must decide beforehand whether it is really herpes or another type of rash. Usually, children under two years of age use half the usual dose of acyclovir. To make it easier for children to take the tablets, they may be crumbled or dissolved in water.