Amniotic fluid examination
introduction

The amniotic fluid test is used in medicine Amniocentesis called and is an examination of the fluid that the child is in uterus surrounds.
This investigation of the Amniotic fluid gives women the opportunity even before birth to find out, for example, whether your child is sick or whether there is one Blood group intolerance between mother and child.
The amniotic fluid test is from 35 years of age Covered by the health insurance company, as the risk of the child becoming ill increases from the age of 35.
The amniotic fluid test can take place from the 10th week of pregnancy, but it is only advisable under special circumstances to do the test as early as the 10th week. The risk of injuring the child during the examination is significantly lower from the 13th week and therefore most amniotic fluid examinations are carried out between the 13th and 18th week. Investigating blood group incompatibility is only possible from the 30th week.
Indications
Doctors usually advise pregnant patients to consider an amniotic fluid test if they have anything PregnancyUltrasonic discover, but it cannot be 100% determined on ultrasound or other examinations.
Even if the pregnant patient already has one or more children Malformations or Hereditary diseases this can be a reason to advise the patient to have an amniotic fluid test.
If the doctor finds a rhesus intolerance, an amniotic fluid test can help determine whether the child may have Anemia or Jaundice suffers.
Please also read our page on this topic High risk pregnancy.
execution
The amniotic fluid test is almost painless and only takes about 10-15 minutes.
However, it takes a few days to weeks before the results are there.
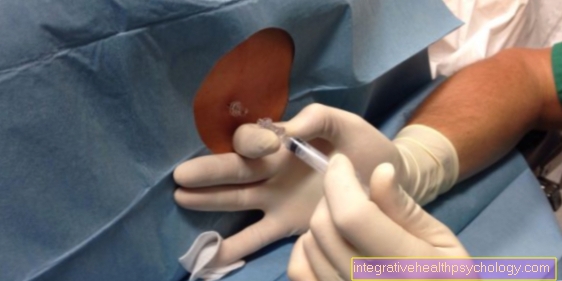
To that Risk of injury Keeping it as small as possible is done before the puncture sounded. In this way, the child's position can be determined and punctured as far away from the child as possible.
This is important because otherwise the child could be injured or, in the worst case, one Miscarriage can be triggered. It should be noted that in every week of pregnancy and regardless of the doctor, there is always a risk of losing or injuring the child.
While the child is being scanned, a suitable site for the puncture is found and a thin needle is inserted through the abdominal wall uterus introduced.
This puncture is often not felt to be particularly painful and is therefore not anesthetized beforehand. After the introduction, a few milliliters of amniotic fluid are removed. The amount is approx. 10 ml and max. 20 ml.
Then the needle is removed and the stab wound is treated.
Following the examination, the mother must observe an approximately one-day movement cessation period. This measure significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Since that Amniotic fluid If the child has a large number of cells that can be reproduced in the laboratory, the amniotic fluid test serves as a clear indication of the presence of various genetic defects.
Depending on the diagnostic procedure and the values to be examined, it can take 2 to 14 days for the first results to be available.
Diagnostic evaluation
By examining the amniotic fluid, some diseases can be diagnosed before birth.
An amniotic fluid test is usually done to examine chromosomal abnormalities, i.e. chromosome changes. One of the most famous chromosomal abnormalities is Down's syndrome, too Trisomy 21 called.
It can also:
- The Pätau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
- Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- Trisomy 8
- Trisomy 9
- Malformations such as cleft lip and palate
- Infections
In addition, the amount of alpha-fetoprotein can be determined, which can indicate an open back and then the acidity of the amniotic fluid can be examined, so statements can be made about the oxygen content.
Unfortunately, not all hereditary diseases and chromosomal changes can be discovered by examining the amniotic fluid. Many diseases are so-called mosaic anomalies, which means that not all cells are diseased and thus it may be that only healthy cells are in the examined amniotic fluid and the disease cannot be detected.
Read more on the subject at: Trisomy 13 in the unborn child and Trisomy 18 in the unborn child
Risks
This is one of the most feared risks Miscarriage.
Depending on the source, the complication rate in relation to miscarriages is 0,6% to 1,5%.
As a result, the risk of miscarriage due to the amniotic fluid test is very low.
The more common risks include;
- bruises at the puncture site
- Bleeding into the uterus
- Injuries to the uterus
- Injuries to the child
- Violations of Mother cake
- Infections
- Amniotic fluid loss
- Contractions of the uterus
For more information, please also read our page Pregnancy complications.
Alternative examination options
Apart from examining the amniotic fluid, there are other ways to examine various diseases.
This includes the following options:
Chorionic villus sampling, Umbilical cord puncture, Triplet test and then a new blood test, which has only been approved in Germany since 2012. Please consult your doctor for advice on which test is best for you. All tests involve risks and possible complications.
Further information can also be found under "Pregnancy check-up'.




.jpg)