Glucocorticoids
Formation of the glucocorticoids
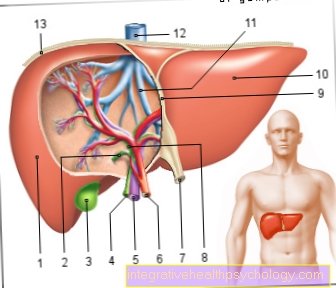
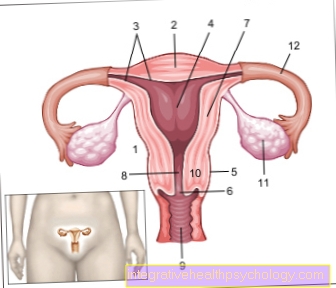
This Hormones include the adrenal cortex Glococorticoid, cortisol such as Cortisone. The hormones are formed cholesterol over Pregnenolone and progesterone as well as further intermediate stages. After being released into the blood, they are bound to the transport protein transcortin. The hormone receptors are located intracellularly in the cells of almost all organs.

Regulation of the glucocorticoids
The glucocorticoids are part of one Hypothalamus-Pituitary Control Circuit. Of the Hypothalamus forms CRH (C.orticotropin R.eleasing Hormone), the pituitary gland ACTH (A.drenocorticotropes Hormon), which in turn promotes cortisol formation and release. The secretion of CRH is subject to a day-night rhythm with a maximum in the morning. Also force it stress and hard physical labor its payout. The ACTH release is on the one hand by CRH, on the other hand by adrenaline stimulated and inhibited by cortisol in the sense of a negative feedback.
Effect of the glucocorticoids
The glucocorticoids are Steroids and take over in the body so-called catabolic tasks. This means that they mobilize the body's stored resources. You let yourself in natural, that is, hormones made by the body, and in synthetic Divide glucocorticoids that are administered in medication. Both types have the same effect on almost all cells in the body. However, they have a particular effect on cells of the muscles, adipose tissue, liver, kidneys and skin.
Most of the docking sites are in these organs, that is Receptors, for the glucocorticoids. They penetrate the cell wall and form a complex with their receptor. This complex has a direct influence on the DNA of the cell and can therefore the Influence the formation of substances. This mechanism takes some time, which means that the desired effects of the glucocorticoids can only set in after 20 minutes to days.
Above all, they promote the conversion of proteins and fats into sugar and continue to act as well Bone metabolism a. One of the most well-known tasks of the glucocorticoids is to Curb inflammatory reactions. They inhibit the release of inflammatory and immune messenger substances from the cells, which reduces the typical symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain and warming. Thus, glucocorticoids work antiallergenic and weaken the immune system (immunosuppressive).
Glucocorticoid side effects
The possible side effects that can result from long-term or high-dose intake of glucocorticoids are directly related to the main effects. Exists a Excess of glucocorticoids in the body, it can lead to the disease Cushing's disease come. In general, there is an individual dose for each patient, which must be ensured that it does not exceed the maximum threshold. This is called the so-called Cushing dose designated. Since glucocorticoids intervene in the bone metabolism, too high a dose or too long an intake can result osteoporosis to lead.
The increased sugar as a metabolic end product often leads to a Increase in blood sugar levels or to high blood pressure. Furthermore, water can accumulate in the cells (Edema) get to Muscle breakdown and therefore to Decrease in muscle strength. Due to the influence on the fatty tissue, there is a Redistribution of fat in the body. This manifests itself, for example, in the typical "full moon face" or in trunk obesity. In children it can be too Growth restrictions come. Due to its anti-inflammatory effect, it can also be strong at the same time Weakened immune system to lead.
Classes of synthetic glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids that are synthetically produced and thus administered in drugs can be used in four different classes subdivide. A distinction is made starting with class I drugs, the appear weak, up to class IV, where the effect very strong is. Important representatives of the glucorticoids are e.g. Cortisol with a relative effect of 1. This means, for example, to get a dose of 30 mg, these 30 mg of cortisol must also be administered here.
Another example is Prednisolonewhich has a relative impact of 4. Therefore, in this case, 7.5 mg would have to be administered in order to achieve the same effect as that of the 30 mg cortisol. The strongly acting glucocorticoids include, for example. Dexamethasone or Betamethasone with a relative glucocorticoid effect of 30 (e.g. class III). Here only 1mg must be administered to achieve the effect described above.
Glucocorticoids in ointments
Glucocorticoids that are added to ointments can usually be removed from the most effective Assign class. This has to be the case because the ointment has to work through the skin and a lot of its actual effect is lost in the process. Ointments with glucocorticoids are included eczema, progressive psoriasis (psoriasis), Skin allergies just like Skin inflammation scheduled. Corresponding tinctures with glucocorticoids are available for hairy skin.
Furthermore, indications itching or severe sunburn be. The ointments should not be applied over a large area or used for too long. The side effects are here mostly Intolerance reactions. Target of the topical (more local) Applying a glucocorticoid ointment is therefore to have an anti-inflammatory effect as quickly as possible without damaging the skin too much. However, it is very important not to apply the ointment too extensively or to an open wound. The undesirable side effects can increase in this case.
Glucocorticoids in doping
The glucocorticoids are standing officially on the list of doping agents and their use when administered systematically (orally, rectally, intravenously or intramuscularly) is therefore in any kind of sporting competition forbidden. The application on the skin with ointments or the intake by inhalation are permitted after registration. The reason glucocorticoids are considered doping agents is theirs anti-inflammatory effect.
Another important reason that athletes like to use glucocorticoids is that they are the Sensitivity to pain reduce in case of injuries. Often times, competitive athletes receive glucocorticoids as Therapy for injuries prescribed in the general course of treatment. Therefore, in such a case, it is easy to obtain them.
Glucocorticoids also have an effect slightly euphoric and suppress feelings of tiredness. In general, they increase blood sugar levels and break down fatty tissue. The body can use sugar and the breakdown products of fat metabolism Energy source be used.
Glucocorticoids for stress
Glucocorticoids are considered to be that Stress hormones of the body. Through them, the body can improve Injuries or Inflammationthat lead to stress react. Many different situations can cause the body to experience stressful reactions. These can be injuries, cold, pain, burns or lack of oxygen. However, it is also possible that psychological factors such as anger, fear or joy trigger a stress reaction in the body.
The body does not select what kind of stress it is. It will two different pathways set in motion in the body. On the one hand, the decisive role is played by Hypothalamus, part of the brain, and the other Adrenal gland. As a short-term response, among other things adrenaline which, for example, makes our heart beat faster in stressful situations. In a second reaction, signals are sent from the hypothalamus and at the end of a reaction chain, u. a. Glucocorticoids are released from the adrenal cortex. This happens with long-term stress. This can have serious health effects, leading to sleep disorders, headaches or a loss of concentration.
Glucocorticoids in asthma
Glucocorticoids are also used in long-term therapy bronchial asthma used. The aim is to contain the inflammation in the bronchi that has manifested itself in this disease. The hypersensitivity of the mucous membranes of the airways is to be reduced and the frequency of asthma attacks minimized. The ingestion takes place via inhalation. This means that the patient has to inhale the active ingredient, for example by means of a spray. It works directly on the mucous membrane of the bronchi and the lungs in the lower airways.
Glucocorticoids especially leave the Swelling of the mucous membranes and enable the patient to breathe better as the airways expand. You contribute to Relaxation of the bronchial muscles and inhibit the production of mucus in the airways. This also becomes less tough, which makes it easier for the patient to breathe.
However, when inhaling it can also be undesirable Side effects come. These include temporary ones Dry mouth, one rough voice or even small fungal infections. The reason for this are slight residues of the drug in the mouth and throat. With the correct dosage and use, however, these side effects can be minimized. However, the side effects are more pronounced when taking the drug Suppository or tablet form on. This form takes place in very strong forms of the bronchial asthma Application.