Brain metastases
introduction
A Cancer cell settlement into the brain tissue Brain metastasis called. A distinction is made between cancer cells that in the brain itself arise (Brain tumor) and cells produced by malignant tumors outside of the brain go out (brain metastases). Are tumors that frequently form brain metastases Lung cancer, Breast cancer, malignant melanoma and Renal cell carcinoma. More than half of all tumors in the skull are brain metastases. Brain metastases can be detected in around 10 to 30 percent of adults with malignant tumors.

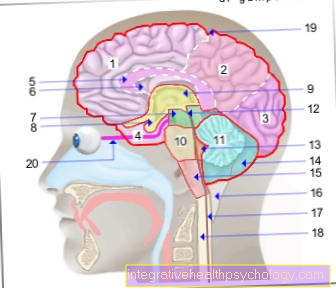
There is also a distinction between solitary brain metastasesin which there is only a single brain metastasis and no further colonization of cancer cells (metastases) in other places in the body. Different from that singular brain metastases (Individual brain metastases, further metastases in other parts of the body are present) and multiple brain metastases (several tumors in the head). Brain metastases are mostly in the area of the Cerebrum localized, in rare cases they can also be in Cerebellum and in Brain stem occur.
In the area of the brain, brain metastases are the most common malignant (malignant) tumors. You express yourself through a Variety of symptoms how a headache, Seizures, neurological failure symptoms (e.g. impaired vision) or Personality changes. About every tenth patient is diagnosed with cancer when brain metastases have formed, symptoms and complaints (e.g. a epileptic seizure) cause.
The treatment of brain metastases depends on many factors, in most cases the prognosis for brain metastases is rather unfavorable, since the presence of brain metastases always means an advanced stage of a tumor disease.
Emergence
Brain metastases are colonizations of cancer other organs. This means that the cancer was originally called a so-called Primary tumor started in body tissue outside the central nervous system. If individual cells of this primary tumor become detached, they can migrate through the body (e.g. via the Bloodstream) and settle (metastasize) elsewhere and multiply there. If this happens in the brain, one speaks of a brain metastasis. The exact mechanisms behind the development of a metastasis have not yet been fully explored. Also the fact why, for example Breast or lung tumors often metastasize and other tumors do not show this tendency has not yet been conclusively clarified.
So contain brain metastases no nerve cells, but are composed of a tissue similar to that of the primary tumor. However, since the cells are degenerate cancer cells, it is sometimes not possible to determine the location of the primary tumor in the body with the help of a microscope. So brain metastases are secondary brain tumors. "Real" brain tumors that originate directly from the brain tissue must be distinguished from this.
Symptoms
The symptoms that are caused by brain metastases are often very unspecific at first and are due to the increasing intracranial pressure (see also: Intracranial pressure sign) triggered. Only when sensitive brain regions are affected or when metastasis has progressed can the symptoms be assigned more specifically to a disease with brain metastases.
In around a third of cases, brain metastases cause symptoms before the primary tumor (e.g. lung cancer) is even discovered. Sometimes it is even impossible to determine the primary tumor despite an intensive search. In these cases one speaks of a so-called Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP). It also happens that brain metastases appear years later after the occurrence and treatment of the primary tumor. The symptoms that are caused by brain metastases are usually no different from the symptoms of a malignant brain tumor (e.g. glioblastoma). Often, brain metastases grow very quickly and cause swelling of the surrounding tissue (perifocal edema), which, if left untreated, leads to a life expectancy of a few weeks to a few months.
The most common symptom of brain metastases is headache. These are caused by the fact that the metastasis and the increasing swelling of the tissue exercise a space-occupying effect, whereby the pain-sensitive meninges are stretched and irritated.
Depending on the location of the brain metastases, a variety of other neurological symptoms can occur. Depending on where the brain metastasis has settled, symptoms such as:
- epileptic seizures
- Sensory disturbances
- Speech disorders
- Visual field defects
- Symptoms of paralysis (Paresis)
come. In some cases there are personality and mood changes (if the brain metastases are located in the frontal lobe), which is usually recognized by friends and relatives. Psychological changes in a person can also be a result of brain metastases, which is also called organic psychosyndrome or delirium and can express itself in paranoid or aggressive features. If the brain metastases are located in the cerebellum or in the brain stem, they are often noticeable through symptoms such as dizziness, ataxia (problems with coordination of movements) or brain stem syndromes.
You can find further information under our topic: Brain tumor signs.
Since in most cases the growth of brain metastases leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, symptoms such as apathy, tiredness and impaired consciousness can occur. In the late phase of a disease with brain metastases, insatiable vomiting or a coma can occur. These symptoms have a very poor prognosis.
Read more on the topic: Cerebral hemorrhage coma
diagnosis
If neurological symptoms occur, one must usually consider the possible presence of brain metastases, among other things. An orienting clinical examination gives the first indications of possible neurological deficits. For example, it is examined whether Intracranial pressure sign (e.g. a congestive papilla, swelling of the exit point of the optic nerve from the eyeball), central paralysis or Cranial nerve failure exist. When talking to the doctor, psychological changes occur, slowed response times or Disorders of experience on.
Since the clinical examination can only make assumptions about the cause of the symptoms, in most cases an imaging diagnosis follows. A MRI of the brain (Nuclear spin) is particularly well suited to Brain metastases to represent.
But also a computed tomographycomputed tomographic examination from the head (cCT) or the Investigation of the Nerve water (Cerebrospinal fluid) can be useful under certain circumstances.
In principle, when brain metastases are detected, the primary tumor that led to the metastases in the brain must be identified. Usually the entire body with the help of roentgen, UltrasoundUltrasonic and imaging procedures (e.g. CT, MRI).
forecast
The Prognosis for brain metastases is influenced by many factors, which is why it is often not possible to make a general statement on life expectancy. The age of the person affected, the time interval between the occurrence of the primary tumor and the brain metastasis, the number, location and size of the brain metastases and a few other factors influence the prognosis. Basically it is Overall prognosis for brain metastases rather poor. Under certain circumstances, the presence of a brain metastasis can lead to a rapid deterioration of the condition up to sudden death, as it can, for example, lead to a bleeding into a brain metastasis. Brain metastases that occur in the posterior fossa (in the area of the Cerebellum or des Brain stem) are localized, can lead to a so-called brain entrapment and thus to death, even with a small increase in size.
The prognosis for brain metastases can be determined by a optimal therapy be improved. The therapy focuses in particular on improving the quality of life by alleviating symptoms and complaints. An extension of survival is only around in isolated cases several months to a few years possible.
course
The course of the symptoms caused by the brain metastases is mostly independent of the development of the Primary tumor.
It can be the case that despite a good treatment of the primary tumor, the symptoms caused by the brain metastases progress.
However, the occurrence of brain metastases is always an indication of a fairly advanced stage of the primary tumor. Often the brain metastases are also the life-limiting factor of a disease.
In addition, the symptoms caused by the neurological failures are often much more stressful than the other side effects of cancer. Just symptoms like Seizures or Personality changes in an already emotionally stressful time are often very limiting.
The poor prognosis for brain metastases is also related to the fact that they can often only be treated very poorly or not at all. An operation is often not possible due to the location and number of metastases, or simply not feasible due to the patient's condition.
For an OP speaks e.g. the presence of only a single or fewer, very large brain metastasis and a high chance of being able to treat the underlying disease.
Even with very strong symptoms, surgery is more likely to be considered. If an operation is not possible, the symptoms can be alleviated and the life span can be extended as part of a palliative approach with the help of the radiotherapy success.
The tumor cells are bombarded with high-energy radiation.
This can partially destroy the tumor tissue or at least inhibit its growth. However, radiation therapy is felt by many to be very uncomfortable and stressful.
In addition, not all tumor tissues respond to radiation. Therefore you have to ask yourself to what extent this short more lifetime, this treatment is worth to you.
Some symptoms, such as Seizures can be at least somewhat alleviated with medication without radiation. The administration of cortisone preparations helps at least to alleviate the symptoms due to their decongestant effect. Partial meadow can also be a chemotherapy be promising. Especially with Testicular cancer This means that healing can still be achieved in some cases despite the presence of brain metastases.
Breast cancer as a primary tumor
Breast cancer represents the second most common of the typical primary tumors, which can lead to brain metases.
The brain metastases mainly occur in the so-called estrogen receptor negative forms of breast cancer.
As in general, the brain metastases are very unfavorable here too Forecast factor for further survival. An early diagnosis and small extent of the brain metastasis can, however, improve the prognosis slightly.
If neurological symptoms occur in a known or already untreated breast cancer, the occurrence of brain metastases should always be excluded.
Individual metastases are usually removed by neurosurgery and the brain is then irradiated as a whole or in the form of radiosurgery. Radiation mainly helps to contain the symptoms, but unfortunately has little effect on survival. In addition to being combined with an operating theater, some of the radiation therapy concepts can also be used individually.
Radiosurgery in particular is making great strides. In some cases, the administration of chemotherapeutic agents can also help slow down the growth of the metastases or improve the symptoms.
other topics
You might also be interested in the following topics:
- Brain tumor
- Anatomy brain
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- a headache
- stroke
- high blood pressure
- Speech disorder
- Increased intracranial pressure