Incubation period of Pfeiffer's glandular fever
introduction
The Epstein-Barr virus is a Human herpes viruswhich causes "infectious mononucleosis" and is also a virus that has been found to be carcinogenic works.
The acute form of the disease, Pfeiffer's glandular fever or, in other words, infectious mononucleosis, occurs in many different degrees of intensity. The incubation period also shows a wide range of different variants.
The incubation period describes the time from the time of infection to the onset and onset of the first symptoms - it literally means "Time of hatching“.
General information is available on the main page: Pfeiffer's glandular fever

That's how long the incubation period is
How long the incubation period lasts for Pfeiffer's glandular fever is individual for each patient. Basically, however, it can be said that the time from infection with the Epstein Barr virus to the onset of the disease can be around one to seven weeks.
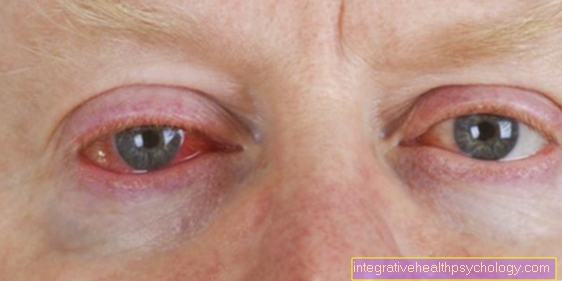
In some patients, the virus has multiplied so much in the human body within 7 days that the immune system can no longer adequately fight the intruder. The typical symptoms like Tonsillitis, Swelling of the lymph nodes and fever then signal that the disease has broken out.
In other cases it takes significantly longer and Pfeiffer's glandular fever only shows its symptoms after about 50 days. The incubation period ends with the onset of clinical symptoms.During the incubation period, the Epstein Barr Virus primarily attacks the B lymphocytes of the human immune system. In these he multiplies his DNA and is still inactive even after the disease has healed. In exceptional cases, the virus infection can reactivate or become chronic.
These symptoms already appear in the incubation period
The incubation period for Pfeiffer's glandular fever begins with the time of infection by the virus and ends with the onset of the disease. If the sick person shows the typical signs such as inflammation of the tonsils, fever, fatigue and swollen lymph nodes, he has passed from the incubation period into the phase of the disease.
Find out more here: You can recognize Pfeiffer's glandular fever by these symptoms
But even before the typical symptoms of infectious mononucleosis appear, many people show a general malaise during the incubation period. So it can too Body aches, one Feeling weak, Sore throat or fever come. This time is also known to many people as unspecific disease phase, before you know exactly which disease is breaking out.
The incubation period in adults differs from that of children / babies
Although the same virus causes Pfeiffer's glandular fever in adults and children, the incubation period can be different. Basically, the adult immune system is much more mature than that of a baby. In many diseases, the incubation period in children is therefore shorter than the duration in adults. The disease breaks out faster and is more likely to show clinical symptoms.
However, this is the case in which a toddler has a symptomatic course of Pfeiffer's glandular fever. Often, however, the course in babies is asymptomatic.
Read also: Glandular fever in the child
Are you already contagious during the incubation period?
Whether you are contagious during the incubation period depends on the pathogen causing the disease. During this time, the germ multiplies in the organism, so that there is theoretically the possibility that other people can become infected during the incubation period. In the case of Pfeiffer's glandular fever, there is even a proven chance of becoming infected during the incubation period, although there are no obvious symptoms of the disease.
This is particularly dangerous because the highly contagious virus is transmitted through saliva. If people share dishes or a drinking bottle in everyday life, for example, and are not careful due to the lack of symptoms, the virus can infect other people very quickly during the incubation period.
Studies have found that especially in the two weeks before the outbreak of Pfeiffer's glandular fever a great deal of virus is found in human saliva. At the beginning of the incubation period, the virus can already be detected, but the concentration just before the onset of clinical symptoms is drastically increased and is definitely sufficient for infection.
Am I in the incubation period or do I have an asymptomatic course?
Many courses of Pfeiffer's glandular fever are asymptomatic and, especially in young children, there are often no clinical symptoms. Almost all 40-year-olds in Germany have been infected with the Epstein Barr virus in the course of their life, but not all have gone through the typical symptoms of Pfeiffer's glandular fever. This means that in the majority of cases the disease was asymptomatic or was mistaken for a common cold. These unspecific symptoms of a cold or flu can also appear during the incubation period and signal that the virus is multiplying in the body. It is therefore very difficult to differentiate between the incubation period and an asymptomatic course. Even with targeted blood tests, it is difficult to make a definitive statement about whether the patient is now in the incubation period or the asymptomatic illness. In babies and young children, the course is often asymptomatic, and in young adults 25% of the courses are atypical or without clinical symptoms.
Read about it too: Diagnosis of Pfeiffer's glandular fever
Here you can find more information about Pfeiffer's glandular fever
- Glandular fever and exercise
- Glandular Fever - How Contagious is it Really?
- Rash in Pfeiffer's glandular fever
- Chronic glandular glandular fever
- You can recognize Pfeiffer's glandular fever by these symptoms