Broken bone
introduction
Humans have over 200 bones that are very stable in themselves. Therefore, a bone fracture only occurs with very high loads. However, the older the person, the more unstable the bones become and therefore the older generation in particular is more likely to break bones.

Bone building
The bone is made up of collagen fibers, calcium and many different fabrics. The main parts of the bone consist of one elastic, mineral and connective tissue portion. The bone is not completely stiff as one might think, but is elastic and easily stretchable. If the bones were only stiff, they would be much less able to endure everyday stress and would break more often.
The older you get, the less elastic and connective tissue there is. This makes the bones unstable and easier to break. In childhood, however, these proportions are still so high that when a bone breaks it often "Greenwood quarries" (please refer Childish fracture) is coming. This means that the bones splinter rather than break.
Illnesses can also lead to altered proportions of the substance and make bones break more easily. For women in the Menopause the changed hormonal balance often leads to one osteoporosis. The Density of bones decreases, making the bones weaker and easier to break.
If a bone breaks, the body can often repair it on its own. For this there are different cells in the bone, these cells are called osteoblasts, which produce bone material and thus allow the bone to grow together again. If the bone fracture is complicated or if it is an open fracture, an operation is often necessary, as otherwise the bone cannot grow together properly and this can lead to malposition of the bone.
Some bones break more often than others. This is because some bones have so-called predetermined breaking points. In these places the bones break more easily than in others.
Illustration structure of a bone
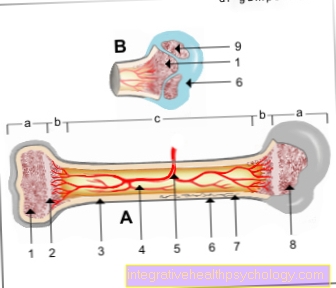
a - epiphysis
(Bone end)
b - metaphysis
(active growth zone)
c - diaphysis
(Bone shaft)
- Sponge-like built
Bone with red
Bone marrow -
Spongiosa substantia
+ Medulla ossium rubra - Epiphyseal line -
Epiphysial line - Dense (compact) bone -
Substantia compacta - Medullary cavity with yellow
Bone marrow -
Cavitas medullaris
+ Medulla ossium flava - Bony artery -
Nutrician artery - Periosteum -
Periosteum - Osteon (basic functional unit) -
Osteonum - Spaces filled with bone marrow
between the trabeculae -
Medulla ossium - Growth plate -
Lamina epiphysialis
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
causes
One of the most common causes is direct or indirect violence. Direct or indirect violence also includes, for example Car accidents or Falls.
Bones can break even without the use of force. Due to diseases such as:
- osteoporosis,
- Osteomalacia (please refer rickets) and
- Tumor diseases / metastases
"spontaneous" breaks can occur.
Symptoms of a broken bone
There are safe and unsafe characters for a broken bone.
To the unsafe heard:
- Redness
- swelling
- Pain
- Limited mobility and
- Warmth.
To the safe fracture sign (Fraction sign) belongs to:
- visible bones
- Misalignment of the bone, this can lead to a “gradation”
- Abnormal mobility and
- Crepitation (crepitation describes a bone rubbing that occurs when a broken bone is moved).
Diagnosis of a broken bone
The doctor usually uses to repair bone fractures X-rays fixed, there are always 2 pictures of two different levels made. Because not all breaks are visible in one plane. In addition, not all broken bones are visible on the X-ray.
For example, if there is a small splinter fracture in the foot, this can often only be done in the Computer tomograph be seen. Is it a break that also Muscles and annoy are often injured MRI be made there Soft tissue injuries are not visible in the X-ray and not clearly visible in the CT.
Broken bone foot
Broken bones in the foot can affect a wide variety of bones, for example the tarsal bones (Ossa tarsi), the metatarsals (Metatarsal bone) or the toe bones (Phalanges) break. The respectively occurring Symptoms are depending on the bone affected, the type of fracture and how the accident happened. Accordingly, the treatment takes place to different degrees. So can Fractures of the toe bones Go unnoticed or cause slight to severe pain, swelling and deformities. Most of the time, however such fractures heal by themselves without complications. Fractions of the Metatarsus (Ossa metatarsalia) kick common among athletes on or become from falling objects caused. They are usually associated with severe pain and functional restrictions when running. Treatment is based on the complexity of the fracture conservative by immobilization with help of a Plaster cast or by a operational procedure. Is one of the Tarsus (Ossa tarsi) broken, so usually kick Pain, Swelling and Exercise restrictions on. This type of fracture occurs frequently in traffic accidents or as a result of diseases such as osteoporosis. Here, too, the treatment can be surgical or conservative, depending on the type and severity.
Fracture wrist
There is a fracture of the wrist with 20% of all fractures the most common in humans occurring. The reason for this is that in the event of a fall we reflexively support ourselves with our hands to protect our head and torso. A fracture of the spoke (radius) above the wrist. The break becomes symptomatic immediate pain, which worsen with pressure and movement, as well as one Swelling and deformity.
The attending physician can usually make the diagnosis through the anamnesis (questioning) and the clinical examination. To confirm the diagnosis or if the clinical signs are uncertain, an X-ray image is made in two planes. Therapeutically, the Choice between conservative and surgical treatment. In the case of an uncomplicated break, the conservative Treatment chosen from the 6 weeks of wearing a plaster cast consists. As a result of the immobilization, the fractions regularly grow together again, but follow-up monitoring using x-rays is required at regular intervals. Is the Rupture postponed (dislocated), a Reduction (Return to normal position) be performed. Depending on the complexity of the fracture, this can be closed or open (as part of an operation). With adequate treatment of the broken wrist, no long-term effects are to be expected.
Broken bones in children
Children's bones are at greater risk of fractures than adult bones. The reason for this is that the Skeleton (skeleton) themselves with the child still in the development phase is located. So are the growth plates (Epiphyseal plates) not yet closed and also the inner and outer periosteum (Endost and Periosteum) are still under construction. The most common fracture in childhood is the wrist fracture (distal radius fracture), i.e. a broken spoke just above the wrist. Injuries to the elbow are also common, but this usually results in a dislocation (Dislocation) and less often a joint fracture on. In general, fortunately, children are more likely to fracture the bone shaft than the joints. Joint fractures are much more complex to treat and often associated with surgical interventions.
In addition, there are special types of fractures in children that are no longer found in adults because of the mature bone structure. These include the so-called greenwood fracture, the compression fracture and the epiphyseal injury. In children, fracture healing is usually faster than in adults and malpositions caused by the fracture can even be compensated for by increasing length. However, the potency of the possible correction depends on the age of the child, the affected bone and the type of deformity and the healing process should be medically monitored in each case. On the other hand, with fractures of the child's skeleton, there is a risk of growth disturbance, especially with fractures of the bone shaft or near the growth plate. The stimulation of the same can lead to an excessively increased length of the bone, so that 2/3 of the children with an injury to the growth plate show an additional length of 1 cm. If, on the other hand, the growth plate is partially closed as part of a fracture, this can lead to incorrect growth and shortening of the bones.
Therapy of a broken bone

Whether a broken bone operated on depends on various factors. The factors include, for example
- whether the bone is misaligned after the fracture and would grow together "incorrectly" without surgery,
- what kind of break it is (comminuted fractures, ..),
- where the break is
- how high the complication rate is
- and of course the age of the patient.
Apart from the operation, the bone can of course only immobilized become. This is usually done using a Plaster of paris, which one worn for several weeks must become. During this time, the broken bone should be stressed as little as possible. In addition, it must be ensured that a fresh break always results in swelling. Therefore, a fresh break is always provided with elastic material before it is plastered.
By being too tight plaster can it to Compartment syndrome come, but this complication is possible even without a cast. If the fracture is first put on with a bandage, a compartment syndrome can be detected much more easily than if a cast is put on.
Surgery is often only performed on displaced fractures, but not all displaced fractures have to be operated on, a broken bone can also be reduced manually, which means that the patient can often be spared surgery.However, surgery is essential if the fracture has shifted and cannot be repositioned without surgery. If the bone shows a tendency to shift again after manual reduction, it may also be necessary to operate the bone. Apart from that, a bone fracture must be operated on if the surrounding soft tissues, i.e. muscles and nerves, are also injured. If this is the case, it is often an open break.
cure
The type of healing of a broken bone (fracture healing) depends primarily on the Type of fracture. In addition, the initiated treatment of the bone fracture has a decisive influence on its healing. In general, the types of fracture healing are divided into two classes. In medical terminology, one speaks of the so-called primary and secondary bone fracture healing.
1. Primary healing for broken bones
A prerequisite for primary healing of a broken bone is one Treatment initiated early. In addition, primary healing is only possible if the ends of the broken bone are close to each other and cannot be moved against each other. As a rule, such an initial situation can only get through surgical measures (Osteosynthesis) be generated. The great advantage of primary fracture healing is the fact that if the fracture is successfully repositioned after healing, it usually occurs no inferior bone material (so-called callus) forms. In this type of fracture healing, the fracture ends connect through the ingrowth of trabeculae, or the Accumulation of newly formed bone tissue.
In primary healing in the presence of a broken bone, however, it must be ensured that the fresh bone substance for some time a lower load capacity than the surrounding mature bone. The newly formed bone material is replaced by bone-eating cells (Osteoclasts) and only then replaced by pressure and tensile strength bones. This process is called the so-called in medicine "Remodeling".
2. Secondary healing of broken bones
A bone fracture whose ends are less well adapted and / or not surgically corrected usually heals through secondary fracture healing. In this form of fracture healing, blood seeps from the ends of the fragments immediately after the onset of the force and is distributed in the surrounding tissue (Fracture gap). As a result, a bruise forms (Hematoma). In general, the secondary healing of a bone fracture is divided into five phases which, however, partially overlap.
Following the formation of the bruise, the release of various substances that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the area of the fracture ends is initiated. This second phase of the secondary phase of the fracture (inflammatory phase) lasts approximately 2 to 3 days. The blood in the area of the bone fracture begins to clot and over time is exchanged for so-called granulation tissue. In this way, as the bone fracture heals, a scar structure similar to connective tissue first forms around the ends of the fracture. The bone pieces are therefore initially only elastically connected to one another and in this way only limited in their mobility. In a further step in the secondary healing of the bone fracture, bone-eating cells (Osteoclasts) the destroyed bone substance. Then cartilaginous cells migrate (Chondroblasts) and start solid cartilage material (Fiber cartilage) to synthesize. After a while, the fibrous cartilage ossifies and the fracture finally heals. In medical terminology, one speaks of the so-called "Granulation phase".
After about 3 to 4 weeks, the broken ends are connected to one another partly by cartilage and partly by bone-like substance. The disadvantage of this type of fracture healing is the fact that, as the bone ends grow together, inferior bones (so-called "Callus") is coming. The stability of this bone substitute is considerably less than the load-bearing capacity of ordinary bone. In addition, callus tissue is characterized by an irregular surface. This can lead to long-term problems, especially in the area of the joints. For this reason, primary fracture healing should always be aimed for in bone sections near the joint. However, it is now assumed that even with the secondary healing of a broken bone, a kind of remodeling sets in after some time and the callus tissue is steadily replaced by stable bone.
Read more on the subject at: callus
Healing time

The healing time of a broken bone can be very different be. Various factors are decisive for the actual healing time. For one thing, it plays Type of bone fracture plays a crucial role in the rate of fracture healing. Simple fractures usually heal much faster than complicated fractures. On the other hand, the region in which the fracture occurred due to violence also has a decisive influence on the healing time.
Depending on Localization of the bone fracture For this reason, the healing time can span a period of two to six weeks. In addition, you can specific influencing factors of the organism shorten or lengthen the duration of fracture healing in individual patients. A broken nose, for example, is usually completely healed within two weeks. If the bone fracture is in the area of large tubular bones, for example the thigh, the healing time can possibly even cover a period of up to twelve weeks. In general, it can be seen that the Healing time of a broken bone is significantly longer with increasing age.
Surgery and complications
Fractures can occur in general anesthetic operated on. The duration depends on the type of bone fracture. The operation is carried out with various screws, wires and plates that hold the bones together.
One of the complications of an operation is always Bleeding, Infections, Injuries to surrounding structures, how annoy, Vessels and Muscles. Bone infections in particular can be dangerous as they heal slowly and poorly.
After the operation there is a some risk of thrombosisthat should be observed.
With or without surgery, there is also always the risk that a broken bone will not heal properly and develop Pseudoarthrosis forms. If this causes problems, you may have to operate again.
Overall these are But risks are very rare and shouldn't be too much of a problem if they occur.












-mit-ten-(titanic-elastic-nail)-oder-sten.jpg)


.jpg)