Cartilage transplant
Synonyms
- autologous chondrocyte transplant (ACT)
- autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI)
- autologous cartilage cell transplantation (AKZT)
introduction

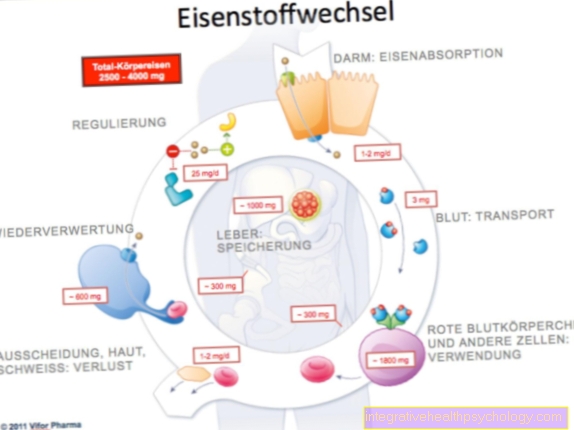
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is found in different places in the body, such as in Nasal bones or Auricles- but also occurs in joints. Depending on Cartilage type its consistency is somewhere between firm jelly and hard plastic, there is also fibrous cartilage.
In the joint comes the cartilage as Coating of the articular surfaces an important meaning too: he ensures that this low friction slide over each other and buffers to a small extent also from shocks.
In theory, it can damage cartilage in the joint (arthrosis called, if they go beyond the normal age range) through Accidents (Trauma) or inflammation within the joint cavity (arthritis) arise, but far more often they are a consequence years of wear and tear of the cartilage tissue in old age, or premature wear Bad posture, chronic overload or Cartilage weakness through innate Connective tissue defects.
This Cartilage damage can then, especially at Load on the corresponding joint, Cause discomfort, such as severe Pain or joint effusions, because the bone lying under the cartilage is now unprotected is exposed to the frictional forces of the joint and can even peel off.
This one increased cartilage damage there is already one in healthy people very limited healing ability of the cartilage, which can be further restricted in those affected by osteoarthritis. Several factors play a role:
- is cartilage tissue basically not supplied with blood, the local cells responsible for the repair (Chondrocytes) will only be very bad with potential building materials provided;
- is the Number of these cells quite limited (they only make up about 1% of the cartilage mass)
- is that in adults natural inclination of these cells to carry out repairs at all, very little.
The type of Cartilage transplant at least partially bypasses the first two points.
Treatment concept
Using the minimally invasive key-hole technique (Arthroscopy) becomes from a healthy, lightly stressed cartilage area a small amount of Cartilage cells (Chondroblasts) taken (around 250 milligrams) and in one Nutrient solution (this can either be patient blood or an artificial alternative) grown in the laboratory. After about two to six weeks the cells have multiplied so much that they introduced into the defective cartilage region can be. So they are common 2 surgical interventions necessary.
So that the cells (which are in a solution) stay in place, they are placed under a membrane sprayed that so fine sewn over the cartilage defect that the seam is waterproof. This membrane can either patient's own periosteum (also Periosteum called, e.g. from the shin), or from the Pig-derived connective tissue layer (Collagen) or one artificial membrane be replaced. Some providers attach the cartilage cells to collagen in the laboratory.
Now there are many well-nourished, endogenous cartilage cells in the area of the cartilage damage that can significantly promote cartilage healing.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
operation area
Especially with cartilage defects in the knee joint, the autologous cartilage transplant increasingly used, especially to prevent secondary osteoarthritis. Large cartilage defects or smaller defects that have already been unsuccessfully treated otherwise are an indication. In these cases, autologous cartilage transplantation is usually covered by health insurance in Germany.
Read also the topic: Cartilage flake
Alternatives
Alternatives to autologous cartilage transplantation are above all one extensive cartilage transplantationin which a larger amount of cartilage tissue comes from a part of the joint that is less stressed directly into the defect is introduced, as well as various techniques in the context of a joint endoscopy, which through the active placement of Micro injuries by small holes or by scraping one localized bleeding evoke and Push the healing process or the smooth the damaged joint surface (so-called Articulated toilet or Abrasion).
Other operative procedures like Joint replacement (Endoprosthesis), Joint stiffening (Arthrodesis) or Joint adjustment (Corrective Osteotomy) cannot be performed using arthroscopy, but require one open and thus major surgery with accordingly greater risks and longer recovery time, but may still be possible the better choice be.
Of course they are too Failure to intervene as well as one only symptomatic treatment (about Painkiller) Always alternatives that must be carefully considered, especially when through Comorbidities or that Age the risks always associated with an intervention significantly increased, or the Significantly worse chances of successt are.
Which decision to act (or not to act) is the best choice in the individual case - that is best ratio of risks and chances of recovery exhibits - depends on many factors such as Comorbidities, Age, Joint misalignments, anatomical Deviations from the norm etc from.
Regardless of the therapy decision, a Therapy success never guaranteed become; Success or failure of treatment always remains a matter of chance. Conversely, a failure or even the occurrence of serious complications does not automatically mean that the wrong therapeutic measure was chosen or that mistakes were made in implementing it.
Risks

Like any operation, this also harbors Autologous cartilage graft risks.
While through the surgical incisions scar and Pain can be expected as regularly as minor bleeding during and after the procedure, however, there are also more serious complicationswhich, if the measure is carried out properly, are very unlikely, but can never be completely ruled out.
Particularly noteworthy are stronger ones Bleeding during or after the operation, in the worst case also one Blood transfusion with all their risks like Immune reaction (which in turn leads to shock and at worst death can lead) or infectionmake necessary.
Also are Injuries to surrounding tissue like nerves and vessels or else des Joint even possible and can ultimately be a renewed operation or permanent damage mean.
Despite working under sterile conditions, a infection the operated region cannot always be prevented, in the worst conceivable scenario this can lead to life-threatening blood poisoning (sepsis) or develop a Stiffening of the joint require.
Likewise, allergic reactions to materials used during the operation or life-threatening anesthesia-related complications are very rare, but possible.
Furthermore, a Success of the therapeutic measure can never be 100% guaranteed.
Despite these risks, it is the one for the Autologous cartilage transplant necessary surgery for one Standard interventionthat has the more serious complications listed above very rare are.
Concerns are especially appropriate when Comorbidities as present or suspected that Blood clotting, Immune system, Wound healing or Cartilage metabolism and thereby increase the risks of the intervention. Also a decreased general condition or Cardiovascular failure In the course of previous illnesses or age, the general anesthetic and Operational risks increase.
A Weighing up the risks and the chances of recovery Comparing the therapy options is essential in each individual case and not always easy. In their personal decision-making process, patients should consider more than medical advice to catch up.
As with every pending operation, it is helpful here for a broader assessment of the personal health situation and its optimal treatment, one for each Technical specialists who can either carry out the measure under consideration himself (or have it carried out in his facility), or not.
forecast
About 85 percent of autologous cartilage transplants are classified as success. Since the method was only developed in the last few decades and varied over a number of years, and has gained in popularity and popularity, there are no results from large-scale scientific studies on the long-term success of autologous cartilage transplantation.
Nevertheless, experts judge the long-term development as promising based on individual experience. It is possible to achieve a relevant symptom reduction or complete freedom from symptoms even many years after the procedure with the autologous cartilage transplant.
Unfortunately, therapy success can never be guaranteed.