Abscess on the face
definition
An abscess on the face is a collection of pus in a tissue cavity that is surrounded by a tough capsule. The penetration of pathogens into small open wounds in the face area causes inflammatory processes that can lead to the accumulation of pus and the subsequent formation of an abscess.
In most cases, the pathogens are staphylococci, certain bacteria that are involved in normal human skin colonization.
In the context of small open areas or injuries on the face, they overcome the skin barrier and trigger inflammatory processes. On the face, an abscess shows up as a significant swelling that is accompanied by reddening and warming of the skin.
Read more on our main page on the topic: abscess

Cause of an abscess on the face
An abscess on the face is most often the result of a bacterial infection. Bacteria that are part of normal skin colonization in the facial area are often responsible.
In addition to the so-called streptococci, this also includes a certain subgroup of staphylococci, the so-called staphylococcus aureus.
Small injuries or abrasions of the skin on the face represent a possible entry point for the pathogens that cause the disease. These small skin irritations can develop very quickly, especially on the face.
Men in particular can quickly make small cuts during daily shaving, which serve as a possible entry point for the bacteria. If they penetrate the skin, the body's immune system is activated to fight the pathogens.
An inflammatory reaction of the tissues occurs and pus is formed.
Read more on the topic: Causes of an Abscess
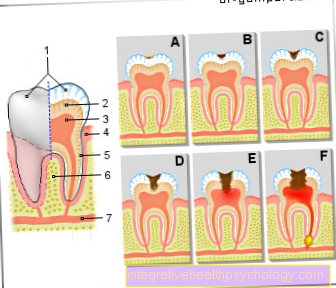
Of the pus consists bacteria, Immune cells and killed cells. The immune system reacts against the bacteria surrounding tissue destroyed and it imagines cavity where the pus can accumulate.
So that there is no further expansion into the depths, a capsule, which envelops the accumulation of pus and shields it from the adjacent tissue.
Visually you can see an abscess on a strong and above all tender swelling of the skinthat with a distinct Redness, warming, and tension the surface of the skin.
Many different factors can create a Abscess promote in the face. Above all, skin that has already been damaged, for example in patients with Neurodermatitis, stronger acne or psoriasis, represents a risk for possible entry points for pathogens in the facial area.
Even one that doesn't work properly or one that is weakened immune systemas with patients with Cancers or as part of a therapy that suppresses the immune system, for example in the form of Cortisone, poses an increased risk of abscesses developing on the face.
Often times, an abscess on the face also arises as part of an inflammation of the Sebum or sweat glands.
If the pores of the glands are clogged and there is no more discharge for the secretion, inflammation develops and pus develops, which can be accompanied by abscess formation.
Since there are many small ones in the face area hair grow, inflammation of the hair follicles can also lead to abscess formation. A Hair follicle inflammation can be recognized in most cases by the fact that it looks like it would grow a hair out of the pimple. If an abscess develops as part of a hair follicle inflammation that spreads to the surrounding tissue, this is known as a so-called abscess boil. If several inflamed hair cells are involved in the process, it is one carbuncle.
Another cause of the development of an abscess in the facial area is also posed Operations in the eyes, mouth or ENT area. If there is an accumulation of pathogenic germs in the wound after an operation, without a possible drainage for wound secretion, in the form of a drainage, has been closed, the pus that forms cannot drain away, builds up and favors the development of an abscess.
Accompanying symptoms of the abscess on the face
An abscess on the face presents as a circumscribed swelling that can fluctuate. This means that when you palpate the abscess, the pus moves back and forth inside. The corresponding area is reddened and overheated. Usually there is severe pain, which can also appear throbbing.
In addition, there may be fever, chills and a general feeling of illness. This is an absolute warning signal, which indicates the spread of the causative pathogens via the bloodstream (threatened blood poisoning).
Headache as an accompanying symptom of an abscess on the face is also a threatening sign and should definitely be a reason to see a doctor. Since the pathogens of an abscess on the face can spread via the bloodstream into the veins of the brain, here is a so-called Sinus vein thrombosis possible.
This leads to the formation of clots in the brain's own veins, which is associated with headaches and fever.
Furthermore, small injuries to the facial skin or diseases such as acne and neurodermatitis can give an indication of the cause of the abscess.
Pain from the abscess
An abscess on the face is most often associated with pain. This is due, on the one hand, to the tension in the tissue caused by the accumulation of pus and, on the other hand, to the inflammation of the skin tissue.
The pain can be throbbing and occur spontaneously or when touched.
The use of pain medication such as ibuprofen may become necessary. Often a surgical "cutting open" (excision, puncture, removal of abscesses) leads to a rapid pain reduction as the tension is relieved
Headache from the abscess
Headaches that occur as part of an abscess on the face are always to be seen as an absolute warning signal.
Especially when manipulating abscesses in the midface (through independent “expressing”) it can happen that the pathogens from the abscess get into the adjacent veins of the facial skin. These in turn flow into larger veins in the area of the brain, where the pathogens can form clots and thus become what are known as Sinus vein thrombosis to lead.
It is a serious clinical picture that is accompanied by headache and fever. Later on, epileptic seizures, impaired vision and paralysis can occur.
For this reason, on the one hand, the manipulation of abscesses in the facial area should be avoided and, on the other hand, a doctor should be consulted immediately if symptoms such as headache or fever occur.
Localization of the abscess on the face
Abscess on the chin
Bacteria such as staphylococci are usually responsible for an abscess on the chin. It is not uncommon for minor skin injuries to occur when shaving the chin, which enables the bacteria to penetrate under the surface of the skin.
Under unfavorable conditions, an encapsulated collection of pus, an abscess, can develop on the chin. This can lead to severe pain and a red, purulent swelling on the chin.
Pustules from acne can also lead to abscesses on the chin.
In addition, the roots of the facial hair in the chin area can become infected. If this inflammation spreads and the collection of pus is encapsulated, an abscess also develops.
Finally, abscesses in the chin area can also be caused by inflammatory changes in the teeth of the lower jaw. Therefore, when determining the cause, the mouth area, including the dental status, should always be inspected.
Read more about abscess on the chin- It's that dangerous!
Abscess on the nose
An abscess on the nose is caused by bacteria such as staphylococci. In healthy people, these inhabit the normal facial skin and can get under the surface of the skin through minor injuries such as abrasions. An abscess is formed as a result of an encapsulating accumulation of pus.
An abscess can also occur due to inflammation of the hair follicles on the nose. In addition, pus pimples can develop into an abscess as part of acne. Regardless of the cause, there is a circumscribed swelling on the nose that is often reddened. There is often a whitish point in the center of the bump that represents the collection of pus.
An abscess on the nose is usually associated with pain, the affected area is usually overheated and not infrequently throbbing.
Especially with abscesses on the nose, it is essential not to express or manipulate the abscess, as the bacteria can otherwise be carried into the brain via blood vessels. This can be life threatening Sinus vein thrombosis to lead.
At a Sinus vein thrombosis a blood clot can block a cerebral vein. As a result, the blood volume now increases as it can no longer flow out through the vein. The pressure in the brain increases and edema and infarcts (death of tissue in the brain) can occur.
Abscess on the lip
Abscesses often develop in the face area around the lips. Particularly at the transition from the red lips to the skin of the face, there are sebum glands that can become inflamed when clogged and thus lead to an accumulation of pus.
The hair follicles of the hair at the transition to the lip can also become inflamed. The result is a purulent, painful bump in the lip area.
Even small injuries during shaving can lead to the penetration of bacteria and thus to an accumulation of pus. Especially in the area of the upper lip there is a risk of the germs being carried over into blood vessels of the brain with the risk of a Sinus vein thrombosis. At a Sinus vein thrombosis cerebral veins occlude with severe symptoms. Edema develops and brain cells can die.
For this reason, please refrain from expressing the abscess!
Abscess on the forehead
An abscess in the forehead area can develop, for example, as part of acne.
Inflammation of the hair follicles in the fine hairs on the forehead can also lead to a boil.
As with the rest of the face, it is important to avoid expressing it. Otherwise there is a risk of the germs being carried over the bloodstream to the brain, with sometimes dramatic consequences.
Read more on the topic: Abscess on the forehead
Abscess on the cheek
Abscesses in the area of the cheek appear as painful, reddened and overheated boils.
It is not uncommon for them to develop as larger pus pimples as part of acne. The inflammation or the growing in of hair in the cheek area can lead to abscess formation.
In addition, inflammation in the area of the upper or lower jaw can trigger abscess formation in the cheek. For this reason, the oral cavity and the dental status should always be checked as well.
Since germs can spread from an abscess in the cheek area via the bloodstream to the brain, squeezing them should be avoided.
Read more on the topic: Abscess on the cheek
When should I see which doctor?
An external abscess on the face is easy to spot.
It is a very pressure-sensitive, tight, reddened and overheated area of skin. In most cases, there will be a hard and slightly raised area in the middle of the abscess.
Sometimes you can also feel the capsule that forms around the collection of pus. If the inflammation spreads to the draining lymphatics in the facial area, it can also lead to swelling of the lymph nodes along the lower jaw or neck.
If other symptoms such as fatigue, fever or chills occur, you should urgently consult a doctor, as this is a sign that the body's own immune system is not able to cope with the fight against the invading pathogens.
In this case there is a risk that the pathogen will spread further through the bloodstream and cause blood poisoning, a so-called sepsis being able to lead.
In the early stages of abscess formation on the face, it is often enough to see your doctor. He or she can prescribe ointments for topical application that can contain the inflammation or, if the spread is already advanced, administer an antibiotic.
Read more about: Abscess treatment
If the abscess is large and needs to be opened, a surgeon should be consulted who can provide wound care under sterile conditions.
Abscesses that develop after an ENT operation should urgently be presented to the competent ENT doctor.
If you notice an inflammation in the area of the oral cavity and the teeth, you should first consult your dentist, as the treating family doctor can usually do little in these cases. It hits e.g. towards an abscess in the upper jaw. Here, too, there is a risk of spreading, which can have life-threatening consequences.
Treatment of an abscess on the face
An abscess in the facial area is usually a visual diagnosis.
In contrast to a normal pimple, an abscess on the face is accompanied by a strong reddening.
If a laboratory diagnostic examination is carried out, in addition to an increase in the inflammation value (CRP), an increase in white blood cells (Leukocytes) on.
In the case of abscesses that lie deep inside and spread to the surrounding tissue, it often makes sense to carry out a further examination in the form of an ultrasound or a computed tomographic examination to determine the exact extent and the spread or infiltration of neighboring organs in the face to judge.
In the early stages of an abscess on the face, an ointment to be applied locally is usually used. This can also be purchased from a pharmacy without a prescription. A pulling ointment is usually used here, which is applied to the affected area of the skin on the face and prevents further spread of the pathogens and curbs the inflammatory reaction.
In addition, the pulling ointment leads to further maturation of the abscess. The ingredients of the ointment lead to a widening of the vessels in the skin of the face, which is well supplied with blood, whereby more defense cells are washed ashore to fight the invading bacteria.
The capsule of the abscess will loosen and melt, and the pus will be able to get to the surface.
Read about this: Abscess ointment.
When the abscess is mature enough, a surgeon can open and split it under sterile conditions.
It is important that you do not press or manipulate the abscess unnecessarily, as this can promote the possible spread of the pathogen.
Read more on this topic at: Abscess treatment.
Surgical therapy / OP

If the abscess on the face has developed further, surgical cleavage (operation) is the first choice for optimal treatment.
Under sterile conditions, the surgeon makes an incision in the skin with the help of a small scalpel. The capsule that has formed around the accumulation of pus is split open and the pus can flow outwards.
The opened wound cavity is then rinsed and cleared out several times with the help of a saline solution, so that all pathogens, pus and cell residues are removed.
The affected and inflamed surrounding tissue is also removed.
Read more on the topic: Operation of an abscess
So that there is no additional pain during the opening and since the skin is very thin and sensitive, especially in the facial area, the procedure is usually carried out under a small one local anesthesia performed.
The wound is initially not sewnso that the wound secretion that is still created can run off and any pathogens that may still be present are not enclosed in a capsule again and form an abscess again.
So that it doesn't become unnecessary Wound healing disorders should come periodically Wound cleaned and the association must be changed.
Especially in the facial area there are poorly healed wounds or big scars a clear cosmetic blemish that should be avoided as much as possible.
An abscess on the face goes mostly in the area Upper lip and the nose at high risk for one Procrastination the germs that have penetrated the brain.
Since these areas are particularly well supplied with blood and the vessels have a connection to the deeper vessels that pull into the head, this is the Risk of spreading germs very large.
That is why this must always be meticulous in these areas of the face Risk of abscess splitting against that Risk of initiating antibiotic therapy be weighed.
Treatment with antibiotics
The therapy that should be sought first is always surgical opening and irrigation of the abscess on the face.
As long as the pathogen has not spread to the surrounding tissue, antibiotic therapy is not absolutely necessary.
However, if the surrounding structures are also infected, there is a risk that the germs can spread through the bloodstream and lead to blood poisoning or spread to the brain.
Since an abscess is a disease that is triggered by bacterial pathogens, prescribing an antibiotic is suitable for combating the pathogens.
In antibiotic treatment, it is important to choose the correct form of administration and an adequate dosage. For light, small and rather superficial abscesses on the face, an antibiotic ointment that can be applied locally is sometimes sufficient.
So that a particularly efficient antibiotic treatment can be initiated, which is precisely tailored to the pathogen causing the disease, a smear should be taken by the surgeon during the opening of the abscess and examined microbiologically.
If the pathogen has not yet been precisely determined, an antibiotic with a particularly broad range of action should first be administered. In most cases, antibiotics from the subgroup of so-called Cephalosporins or Dicloxacillin used.
If the bacterium causing the disease has been precisely determined in the microbiological examination, a specific antibiotic can be selected that specifically eliminates the respective bacterium. Because abscesses on the face are in most cases based on the colonization with the skin germ Staphyloccus aureus and most staphylococci are resistant to penicillin, clindamycin, Flucloxacillin or so-called Macrolide antibiotics how erythromycin are used. Antibiotic therapy is carried out for about 7 days in most cases.
Read more on this topic at: Treatment of abscesses with antibiotics
Home remedies for an abscess
Home remedies can also be used to treat abscesses on the face. A certain natural medicine remedy, the so-called larch turpentine, is particularly successful in its use.
This is a balm that is obtained from the trunk of a larch and contains essential oils that have a germicidal effect. It promotes blood circulation and stimulates the body's immune system.
This increases the inflammatory response, but the abscess continues to mature so that it can empty outwards.
Another home remedy with an antibacterial effect is black tea. A boiled black tea bag can simply be applied to the affected area of the face and left in for a few minutes. In addition to killing germs, black tea also alleviates the inflammatory reaction and has a soothing effect on the affected areas of skin.
Normal chamomile tea can also be used in this context. This also has a calming effect on the skin and reduces inflammatory processes.
The application of tea tree oil has a particularly anti-inflammatory effect and helps to kill the pathogens. Boiled onion slices are also a tried and tested home remedy for treating abscesses.
These are put in a sachet or towel and can then be placed on the affected skin area. The onion pulls the inflammation out of the heavily stressed tissue and also relieves the stress on the surrounding skin and tissue.
Aloe vera leaves should have a good effect, especially in the initial stages of the formation of an abscess on the face.
They do not have a germicidal effect, but they do reduce the further growth and spread of the abscess.
Read more on this topic at: Abscess treatment with home remedies