Lymph node biopsy
What is a lymph node biopsy?
A lymph node biopsy involves the removal of one or more lymph nodes from a specific area in a small operation. In some cases, tissue can only be removed from a lymph node. The samples are then examined histologically under a microscope by a pathologist. Lymph node biopsies are performed if a lymph node is suspected to have degenerated or a tumor has spread to the lymph nodes.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph nodes

Indications
A lymph node biopsy is performed if so-called daughter tumors (Metastases) are suspected or should be excluded. A malignant tumor can spread along its lymphatic drainage pathways and affect the lymph nodes in the drainage area.
Read more on the subject at: Metastases
Another reason for a lymph node biopsy can be an abnormal lymph node. In the case of long-term, painless and very strong enlargement, it may be necessary to remove the lymph nodes to find out the cause of the enlargement. This cause could e.g. an infection or lymph node cancer (Lymphoma) be. However, the removal is only used for diagnosis and is not carried out as a therapeutic measure.
Read more on the subject at: Swelling of the lymph nodes
preparation
Before a lymph node biopsy is performed, a detailed medical history should be taken. If a lymph node enlargement has occurred, it should be asked how long it has existed, whether it has developed slowly or quickly and whether there are any other symptoms.
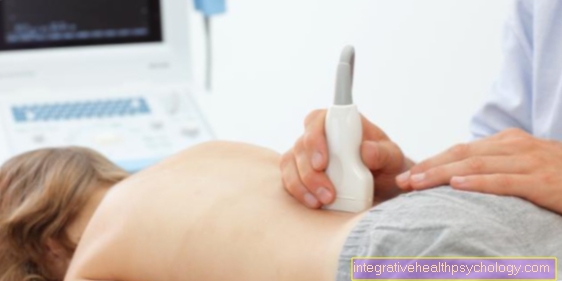
Imaging of the lymph node should then be performed. An ultrasound examination is usually sufficient. In rare cases, a CT or MRI examination can also be performed.
The patient should then be informed about the procedure and the risks of the biopsy and also be informed about the form and risks of the anesthesia by an anesthetist.
procedure
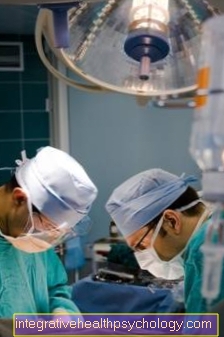
Depending on the location of the lymph node, the procedure can either be performed under local or general anesthesia. For superficial lymph nodes, local anesthesia while the patient is awake may be sufficient. Deeper lymph nodes are removed under general anesthesia.
First, an incision is made and the lymph node is exposed. During this step, care is taken to ensure that the surrounding vessels and nerves are spared. The lymph node is then removed. In the last step, the incoming and outgoing lymphatic pathways are desolated and the skin layers are sewn up in several steps. In the case of larger wounds, it may be necessary to insert a drain to drain the wound fluid from the wound. A bandage is placed over the surgical wound and the patient has survived the procedure.
The removed lymph nodes are placed in certain solutions for preservation and then sent to the pathology department for examination.
How painful is that?
The lymph node biopsy should not be painful during the procedure as the procedure is performed under either local or general anesthesia. After the operation, there may be slight pain in the wound area, as the tissue and also smaller skin nerves were injured. The pain can last until it is completely healed, but usually disappears after a few days. However, they can be managed with mild pain relievers like ibuprofen and paracetamol. Slightly cooling the affected area can also help relieve the pain.
Do you need an anesthetic for this?
Depending on the location of the lymph node, anesthesia may be necessary. In the case of very superficial lymph nodes, local anesthesia may be possible and the patient can remain awake during the procedure. However, if the lymph nodes are deeper or if several lymph nodes are to be removed at once, general anesthesia is necessary.
Is this possible on an outpatient basis?
In principle, an outpatient lymph node biopsy, in which the patient goes home a few hours after the operation, is possible. However, the decision must be made on an individual basis, depending on how large the procedure is and how the operation will proceed. The patient's general health and previous medical conditions should also be taken into account.
If a drain has to be inserted after the operation, it is also necessary that the patient remains in the hospital for a few days until the drain can be removed.
Results
After removal, the lymph nodes are placed in a solution for preservation and sent to the pathology department. Here they are first examined as a whole and then cut into thin layers and viewed under a microscope. Depending on the question, it can be clarified here whether a tumor has spread to the lymph nodes. It can be seen which cell type it is and thus conclusions can be drawn about the primary tumor.
In the case of a lymph node enlargement, it can be clarified whether the enlargement has an inflammatory cause or whether the lymph node is malignant. This information can also be used to make decisions about subsequent therapy.
Read more on the subject at: Causes of Lymph Node Swelling
Duration until the results
The first results of a lymph node biopsy can be available just a few hours after collection. However, it can take a few days for the material to be fully examined and for the final results to be available. The decisive factor for the duration is also whether the clinic in which the biopsy was performed also has a pathology or whether the samples have to be sent to an external clinic.
What can be the side effects / risks?
Like any surgery, the lymph node biopsy has some complications that can occur, although rarely.
After the operation, there may be an accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissue (Seromas) come. These seromas can, however, be emptied with the help of a drainage or they break down on their own over time. Damage to lymphatic vessels can also cause the lymphatic fluid to build up. Depending on where the lymph node was removed, this lymphatic congestion can occur in the area of the arm or leg. In most cases, lymph congestion will improve on its own over time. Lymphatic drainage can be tried as a support.
Read more on the subject at: Lymphedema
General complications can arise during the operation. Structures such as nerves or blood vessels in the surgical area can be injured. Furthermore, allergic reactions to the medication administered or the material used can occur.
Wound healing disorders can occur in the area of the wound and scarring can occur even though the incisions are kept as small as possible. However, the scar formation can be contained with good skin care and the scars also fade a little over time.
Read more on the subject at: Scar care
Duration
The duration of the procedure depends on various factors. The location of the lymph nodes, the number of removed lymph nodes and which method the surgeon chooses largely determine the duration. The length of the procedure can vary from a few minutes to several hours.
costs
No precise information can be given about the cost of a lymph node biopsy. They also vary depending on the duration of the procedure, the type of anesthesia and the selected surgical procedure.
Who pays the costs?
If the lymph node biopsy is sensible and necessary from a medical point of view, the costs for the operation, the subsequent histological examination and follow-up treatments are covered by the patient's statutory or private health insurance.
What are the alternatives?
Imaging should always be done before a lymph node biopsy is performed. In many cases, this can already provide information about the cause of an enlarged lymph node.
However, if there is a suspicion that a tumor has spread to the lymph nodes, a biopsy is the only method to confirm this suspicion. Since the biopsy and its result also have consequences for further therapy, this should also be carried out.
According to location
Sentinel lymph node biopsy
Sentinel lymph nodes, also known as sentinel lymph nodes, are the first lymph nodes in the drainage area of a tumor.They are usually the first to show daughter tumors (Metastases) on.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy is performed primarily for breast cancer, but also for other cancers. First of all, the sentinel lymph node is shown with the help of contrast agent and then exposed and removed. This lymph node is then sent to the pathology department using the so-called rapid incision method. After about 20-30 minutes, the surgeon receives the result of the examination. If the lymph node is affected, further lymph nodes are removed from the drainage area. However, if the sentinel lymph node is free of tumor cells, this means that the lymph nodes in the further drainage area are also tumor-free.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph node involvement in breast cancer
On neck
There are countless lymph nodes in the neck area. These can be quickly, e.g. swell as part of an infection of the upper respiratory tract. However, if a lymph node is suspicious, the lymph node biopsy can usually be performed under local anesthesia. This is because the lymph nodes on the neck are relatively close to the surface. They can be easily visualized with the help of an ultrasound device and the subsequent biopsy usually only takes a few minutes.
Tumors that form daughter tumors in the lymph nodes of the neck are mainly cancer of the tongue and the larynx.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph node swelling in the neck - how dangerous is it?
In the bar
In the groin, too, the lymph nodes are relatively close to the surface and can usually be removed under local anesthesia. Lymph node swelling in the groin area can also have harmless causes, such as infection. However, behind the swelling, a malignant lymph node cancer (Lymphoma) lie. If a malignant swelling is suspected, a lymph node biopsy should be performed in the groin to confirm or refute the suspicion.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph node swelling in the groin
In the armpit
Swelling of the lymph nodes in the armpits can also have harmless causes, such as an infection in the hands or arms. However, breast cancer can also be a cause. Here the lymph nodes are usually enlarged painlessly. A lymph node biopsy in the armpit can be used to find out whether there really is cancer.
Read more on the subject at: Signs of breast cancer
If breast cancer has already been diagnosed, a sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be used to find out whether the cancer has already spread to the armpit lymph nodes.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph node swelling in the armpit


.jpg)